Chapter V. Ensuring the security and protection of information. Security internal and external
Has a significant impact on the state of affairs in the company internal security In the organisation.
The long-known aphorism “personnel decides everything” has not lost its meaning today, not only because you cannot survive in market conditions without great specialists, but also because the reliability of employees is not always ideal. According to statistics, a company suffers more than 3/4 of its losses due to the direct participation of its own employees in certain criminal acts.
Employees and clients occupy a special place among the sources of information about the company as active elements that can act not only as sources of information, but also as objects of malicious actions. Experience shows that the safety of enterprise secrets depends 80% on correct selection, placement, training and education of personnel.
Overall to internal threats to the security of non-state economic entities include:
Illegal and other negative actions of personnel employees of the facilities;
Violations of the established security regime for information constituting a trade secret;
Violations of the terms of use technical means;
Other violations of the order and rules of compliance with the security regime at the facility, creating the preconditions for criminal elements to realize their goals and the occurrence of emergency incidents.
Illegal and other negative actions of personnel employees discussed in this manual assume the absence of a direct connection with the structures organized crime and industrial espionage. Reasons similar manifestations there may be all sorts of conflicts and other negative life situations, as a rule, of a material or psychological nature, the means of exit from which is chosen to commit illegal acts.
It is known that a person’s choice of criminal or lawful behavior depends on the system of value orientations, views and social attitudes that he professes. Studies by criminologists highlight distortions in the structure of needs that determine specific interests and value orientations, which in turn shape the direction of actions of company employees.
Experts identify several reliability criteria personnel, and ideally an employee of a commercial enterprise should meet each of them. These include: professional, psychological and moral reliability.
An analysis of specific cases of threats to the security of a company from its employees shows that they most often arise “thanks to” the following reasons: low qualifications; moral dissatisfaction with work; bad habits and etc.
There are still no universal recipes to completely protect a company from the negative actions of its own employees, just as there are no means of ensuring 100% security, but it is possible to minimize this danger, keep it under control and avoid it undesirable consequences. This is a conscious, organized, consistent and targeted personnel policy. It constitutes an equally necessary condition normal operation companies, as well as well-thought-out business plans. This policy is based on three main principles:
- reasonable selection of personnel using modern methods
- a well-thought-out and well-structured system of remuneration and career growth;
- an organizational culture that maintains a microclimate in the company that is favorable for staff collaboration.
When hiring new employees, a thorough background check should be carried out. During the preliminary interview, you should check the candidate’s professional qualities and the presence of favorable characteristics from the previous place of work. Thorough testing should be performed when deciding whether to use a given candidate. This will provide an opportunity to study it more thoroughly individual characteristics in order to identify a tendency to mental disorders, alcoholism, drug addiction, increased level conflict.
Great importance has the prevention of penetration into the company's personnel by representatives of economic intelligence of competitors, representatives of organized criminal groups and individuals with the goal of causing damage to the facility. This is achieved by using complex methods studying and checking a prospective candidate for work at the company.
One of the components of the internal security system is a mechanism for identifying sources of information from organized crime structures and industrial espionage among company employees. Along with this, work is carried out to detect sources of internal security threats, periodic preventive checks of personnel are carried out, internal investigation facts of forgery, theft and other damage.
Already developed enough effective methods social psychology, allowing conflict situations in a team and healing the “atmosphere” of relationships. Experts consider gaming and psychotechnical forms of teamwork to be the most effective.
Organizational events employee relations include:
interviews when applying for a job. In this case, 1, an agreement is concluded on fulfilling the requirements for the protection of trade secrets;
familiarization with work rules and procedures with confidential information. In confirmation of the requirements for maintaining a trade secret, the employee entering the Work gives a signature (undertaking) to maintain the trade secret;
training employees on work rules and procedures with "confidential information in accordance with their job responsibilities;
systematic control for compliance with the requirements for protecting trade secrets;
conversations with those leaving, whose main goal is to
Prevent information leakage or misuse. It is possible to obtain a subscription on non-disclosure of confidential information known to the employee """ after his dismissal.
The main danger that threatens an organization from within is unhealthy socio-psychological environment a team. These may be conflict situations in relations with the administration, aggravation of relations on ethnic grounds, threats of strikes, group violations public order, etc. Work to identify and eliminate the causes and conditions of negative processes is carried out using special and socio-psychological methods, using various forms studying public opinion and exerting a favorable influence on it through persuasion and coordination of the interests of conflicting parties, as well as the use of administrative disciplinary methods.
Not everyone knows that any organization built on the principle of selecting personnel from relatives and friends has a certain “critical mass”. Having reached the level of this "mass", the organization generates " chain reactions"intrigues, misunderstandings, suspicions, etc., which have an extremely negative impact on the work of the company, and are also causes of leakage important information or outright betrayal.
The psychological and sociological security system provides for the appropriate preparation of the management and personnel of the facility for negotiating with partners, acting in extreme situations, developing in them the moral and psychological qualities necessary for the performance of official duties, and instilling a sense of devotion to the company. It also provides for the study of the moral and psychological climate among employees using sociological methods, maintaining it at the proper level in order to successfully counter external and internal security threats, assessing the psychophysiological state of employees, and preventing negative processes in the team that can contribute to crime.
It should be borne in mind that any person in his actions is guided by certain motives, the understanding of which makes it possible to select the keys to him and ultimately obtain the necessary data.
A generalized socio-psychological portrait of people who, on their own initiative, commit actions to the detriment of the safety of objects, suggests that among them the spiritually and morally defective, careerists, vain, arrogant, unprincipled, unadapted to life’s troubles, who consider themselves disadvantaged in some way predominate. . Many of them usually suffer from serious mental illnesses.
Basic reasons for criminal behavior a company's employee, as a rule, are based precisely on known human weaknesses. American experts have even come up with a special abbreviation that describes the formula for recruiting agents and finding out secrets - SMISE: Sex (sex), Moneu (money), Leo10gy (ideology), Compromise (compromising materials), Ego (personality characteristics).
Employees who infringe on the legitimate rights and interests of the company are subject to appropriate measures of influence, determined by the nature of their actions. When implementing internal security tasks, appropriate coordination and interaction is carried out with internal affairs bodies and the prosecutor's office, especially when identifying signs of a crime.
Work to ensure internal security should not, on the one hand, suffer from excessive trust in personnel, and on the other, create an atmosphere of total surveillance and suspicion in the company.
A problematic issue is the obligation to report crimes committed at enterprises by employees of these enterprises. As a rule, this is done in rare cases. Typically, applications are made against employees whom they don’t like and want to get rid of.
According to a study by the German Institute of Forensics, working in the field of criminology. M. Planck, approximately 16.8% of crimes, i.e. every sixth illegal act becomes known at the enterprise. But in small enterprises, due to their disabilities carry out investigations of crimes, the willingness of employees to report crimes committed is higher than in large enterprises.
Violations committed are usually punished by “factory justice”. Therefore, we can say that the main task of enterprise security services is to create conditions for the activities of factory ships. Factory courts and factory justice use fines and warnings as sanctions. They often try to resolve the conflict peacefully with violators.
Violations of the established regime for the security of information constituting a trade secret create conditions for the effective operation of structures specializing in industrial espionage and the illegal extraction of important documents or products.
Typical situations creating favorable conditions for criminals are:
Absence of personal responsibility of officials for the safety of information constituting a commercial secret;
Access to information constituting a trade secret,
excessively wide range persons; " " violation of the rules of special office work;
Lack of conditions to maintain the protection regime at the required level;
Failure to comply with the established procedure for holding particularly important meetings and confidential negotiations; violation of access control and facility security;
Insecurity of technical channels for information leakage; irregular conduct preventive measures
at the office.
It should be noted that internal threats to the security of market entities are constant categories, independent of the role, location, significance of the object in economic activity and the direction of sources of external security threats.
(Document)
n1.doc
Chapter 3. System structure national securityInternal and external security. Types of national security
When studying problems and organizing national security important acquires its structural classification. Of course, any classification is quite conditional, and each of them is built with specific goals and objectives.
Currently, for the first time in accordance with the Law Russian Federation 1992 “On Security” national security is divided depending on the location of the source of danger into two types - internal and external security (Diagram 3). This division is based on the territorial boundaries between states. Now, in the context of globalization and internationalization of all aspects of public life, the line between internal and external security is very blurred, and many threats - international terrorism, drug trafficking, environmental and natural disasters - are sometimes difficult to link to any single source. Nevertheless, such a division seems to be very useful from a practical point of view, since, first of all, it allows one to clearly classify certain conceptual approaches to solving problems of ensuring national security. In addition, the division into internal and external security is also necessary to understand that ensuring internal security requires completely different methods, forms and methods than ensuring external security.
Scheme 3. Types of national security depending on the location of the source of danger
The main directions of ensuring Russia’s internal security now are the solution of the following tasks: acceptance of all possible measures to get Russia out of the crisis, which is crucial for its revival as a world power;
Successful implementation of market reforms; reducing the severity of social contradictions; ensuring the protection of Russian spiritual, intellectual and cultural values; strengthening defense capabilities; formation of a democratic legal federal state; preventing the aggravation of social and political confrontation, which creates the danger of political crises that could escalate into military conflicts; achievement public consent, healthy socio-psychological and moral climate in society; reliable protection life, health, property, human rights and freedoms, creating decent conditions for his existence, as well as conditions for the existence and development of the family as a unit of civil society and its governmental support; increasing the efficiency and level of education in Russia.
The Russian state is distinguished by its vast territory. Hence, an important direction of internal security policy, ensuring sustainable democratic development of Russia, is a balanced regional policy, an optimal balance of interests of the center and regions, republics and regions located in different natural, climatic, socio-economic and ethnopolitical conditions.
From this point of view, a particular threat to stability in the country is the large gap in the standard of living of individual regions of the country; many regions practically exist only due to subsidies from the federal government.
The number of autonomies within Russia has increased - from 22 to 31, and their relative area has also increased - from 28% (relative to the current territory of Russia) to 53%. At the same time, more than 50% of administrative boundaries within Russia do not have a solid legal basis. This is also a factor of potential destabilization of the situation in the country.
And yet, the real threat not only to Russia’s vital interests in certain regions and spheres of economics and politics, but also to its very existence is posed by regional rather than national-territorial separatism.
The adoption by subjects of the Federation of normative legal acts and decisions that contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal legislation is one of the most hazardous factors eroding the country’s unified legal space.
Violation of the principle of the supremacy of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal laws in the constitutional, statutory law-making of the subjects of the Federation is expressed in the unilateral assignment of the right to suspend the validity of federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, if they to some extent do not comply with the Constitution of Russia, the charter, laws of the subjects of the Federation or the legal interests of the subjects of the Federation. From the standpoint of ensuring national security, one cannot ignore attempts to adopt regulations in areas related to exclusive competence Russian Federation, in particular in the field of establishing the state border, ensuring the integrity of the territory of Russia, etc.
A characteristic violation is the desire of individual republics to secure for themselves such rights as declaring martial law; making decisions on issues of war and peace; consent to the deployment of military formations on its territory; regulation of issues foreign policy and international treaties.
In a number of subjects of the Federation, laws on security were adopted, which contain provisions that contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation and Russian legislation; even ministries for security issues were created, which is a direct violation of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On Bodies Federal service security of the Russian Federation”, which do not allow their double subordination. In regulatory legal acts subjects of the federation contain provisions on the appointment and dismissal of heads of territorial security agencies, which also violates the principles and legal norms regulating personnel issues in the system of bodies of the Federal Security Service, General Prosecutor's Office etc.
To create and improve federalism and strengthen the country's national security, it is necessary to ensure the preservation of state sovereignty as a single and indivisible throughout Russia, suppression of the process of confederalization, transition from the current spontaneous desovereignization of the Russian state to a thoughtful, consistent, balanced decentralization of powers and functions of bodies state power within the framework of the constitutional and legal space.
All these circumstances explain special meaning internal component in ensuring Russia's national security at the present time.
Russia's approach to external security problems is characterized by the understanding that in the conditions of the modern nuclear era it is unacceptable and impossible to ensure its own security by reducing the level of security of other countries.
Any security concept is developed in accordance with specific historical conditions. Previously, each state cost mainly on our own to prevent and reduce the severity of emerging threats. Currently, many external security problems cannot be solved alone, which is why it is objectively necessary to unite the efforts of all states of the world. The world of endeavor is so integrated that it is impossible to reduce external security to national borders. Therefore, the only reasonable way to ensure external security is to achieve a certain balance of one’s interests and the interests of other countries, a certain compromise within the framework of international security.
International security- this is the security of the system international relations from the threat of their destabilization, confrontation, armed conflicts and wars.
Unfortunately, our legislation in the field of national security, which affects almost all spheres of public relations, almost completely ignores the problems associated with the federal structure of the Russian state. Regional and local aspects of ensuring internal security, not to mention external, are not even identified and are not reflected in the main legal acts and regulations.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” of 1992 only states that the legislative framework for ensuring security also includes constitutions, laws, other regulatory acts of the republics within the Russian Federation and regulatory acts of state authorities and administrations of territories, regions, autonomous regions and autonomous okrugs, adopted within their competence in this area (Article 6). But the limits of this competence are not indicated. And in the Concept of National Security of the Russian Federation (as amended in 2000), which presents a system of views on ensuring the security of the individual, society and state in the Russian Federation from internal and external threats in all spheres of life, regional aspects are bypassed.
Russian society has historically developed on a heterogeneous basis. The vast territory of the country, the multitude of peoples inhabiting it, cultural traditions, various religious denominations, unequal psychological make-up, peculiarities of labor, everyday life, cultural, etc. factors largely determine the interests of regional communities.
Accordingly, different content and specific features regional interests throughout the country also affect the nature of activities to ensure the security of the region. As a result, the stability of the situation and the security of the regions determine the level of national security as a whole.
In this regard, it is advisable to divide internal security into two types: internal federal and internal regional security (Diagram 4).
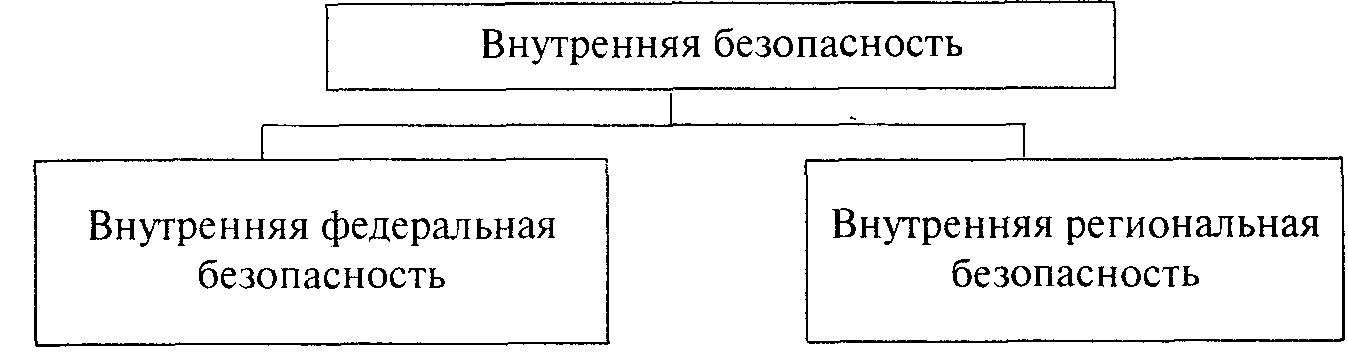
Diagram 4. Structure of internal security in territorial terms
Homeland Security is the protection of federal interests from internal threats, and internal regional security is the protection of regional interests from internal and external threats. The structure of federal and regional interests has much in common. First of all, this is the unity of security objects (individual, community, society, state), as well as the functional qualities of the interests of these objects.
Nevertheless, there are many fundamental differences in the structure of federal and regional interests, which serves as the initial basis for their separation. Among federal interests, the interests of the state and society as a whole dominate, and regional interests - the interests of the individual and community.
When studying the problems of regional security, the most important methodological importance is to resolve the question of what is meant by the category “region”. It should be noted that our country has not yet developed a single generally accepted clear and unambiguous definition of this concept.
Regional security means the protection of the interests of a constituent entity of the Federation from internal and external threats. External threats are those whose sources are located outside the boundaries of a given subject of the Federation.
This circumstance further emphasizes that internal regional security must be ensured by the forces and means of the subject of the Federation in close cooperation and with the support of appropriate forces and means federal center and other subjects of the Federation where sources of threats are located.
International security is divided into global, or universal, regional and collective (Diagram 5).

Scheme 5. Classification of types of international security
Global Security- this is the protection of the system of relationships of the entire world community from the threat of destabilization of the situation, crises, armed conflicts and wars.
Regional security- this is the protection of the system of relations between states of a particular region of the world from threats of destabilization of the situation, crises, armed conflicts and wars of a regional scale.
Collective Security- this is the protection of the interests of a group (union) of states from external threats, guaranteed by mutual assistance, cooperation in the military sphere and collective actions to prevent and repel aggression.
International security is based on compliance by all states with generally recognized principles and norms international law, excluding the solution controversial issues and disagreements between them by force or threat of force.
The most important principles international security are the principle of equality and equal security, as well as the principle of not harming anyone’s security in relations between states.
In addition to distinguishing the two types indicated above in the structure of national security - internal and external security - its classification by type of security is important, which contributes to the development of more specific policies and strategies for ensuring national security.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” provides for the division of national security into the following types: state, economic, public, defense, information, environmental and others (Article 13). However, the legislator did not provide a strict interpretation of the principles of classification by type of security, nor a definition of these concepts, which in practice led to real chaos in a completely unjustified fragmentation of the generic concept. In literature and in the media you can find federal, constitutional, genetic, planetary, etc.
Any classification should be based on some of the most essential common features. Among them, first of all, it is necessary to highlight security objects, the nature of threats, and areas of life.
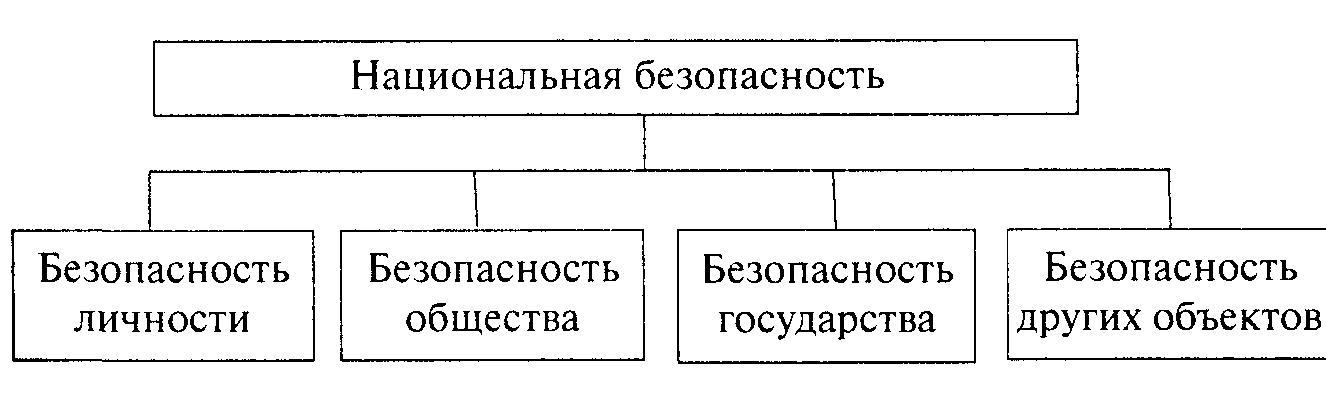
Scheme 6. Classification of types of national security by object
Depending on the object, the vital interests of which are protected from internal and external threats, types of security are distinguished, such as the security of the individual, society, state, Russian-speaking population, civil servants, etc. (Diagram 6).
At the same time, the security of a particular object means the protection of the vital interests of this object from internal and external threats.
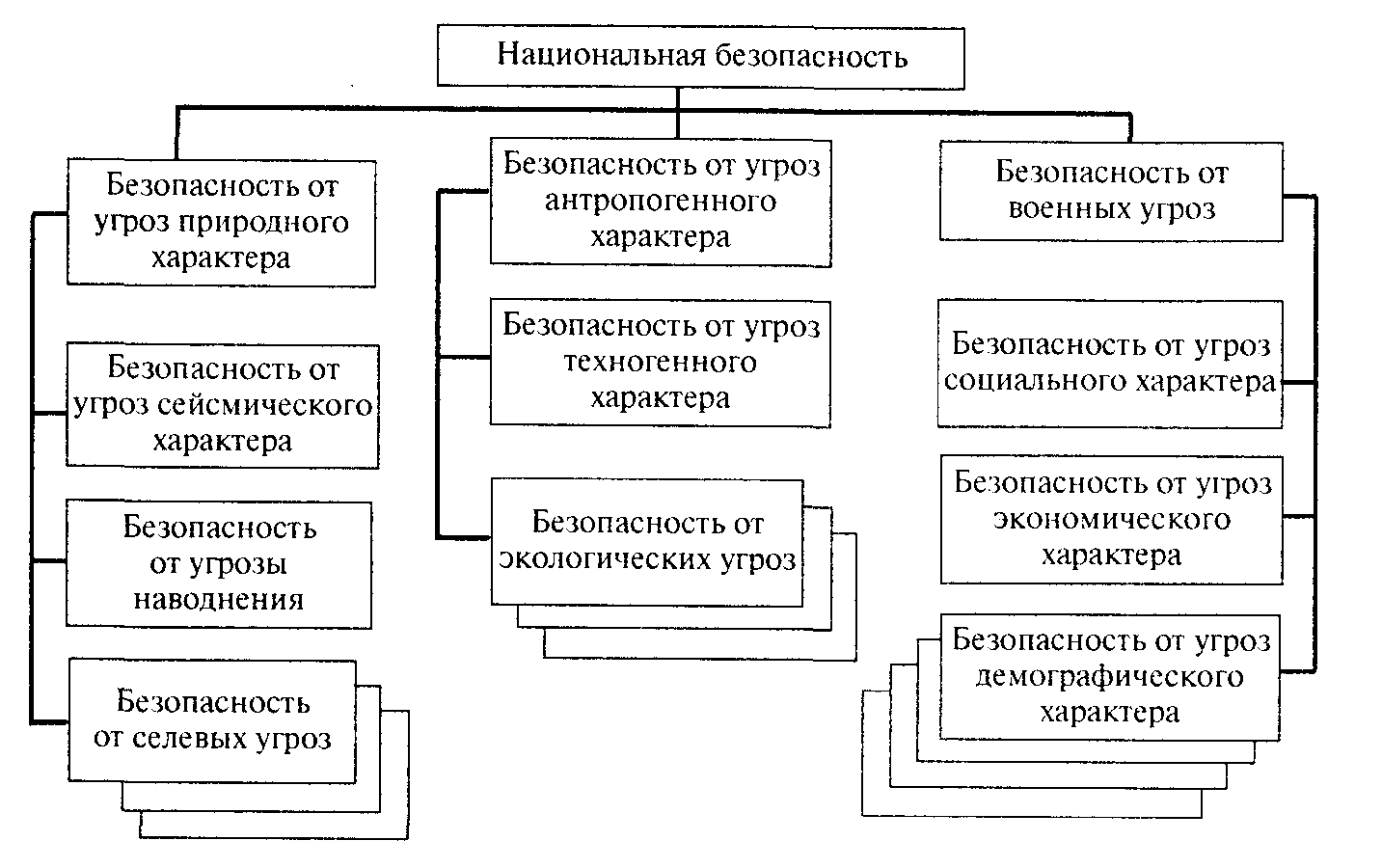
Scheme 7. Classification of types of national security by spheres of life
Depending on the nature of the threats, their source, and specifics, we can distinguish such types of security as security from natural threats, security from anthropogenic threats, security from social threats, which in turn can be divided into more small species security from specific threats (Figure 7).
At the same time, security from one or another type of threat is understood as the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and state from threats of this type.
In human society, the vital interests of all security objects are exposed to a wide variety of threats, therefore special practical significance has a division of types of security by spheres or areas of life in which these threats manifest themselves. It is by this principle that vital interests, threats and directions for ensuring national security are classified in the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation. Most generally, such a classification can be limited to identifying six types of security, which can be divided into smaller types of security for specific areas of life (Diagram 8).
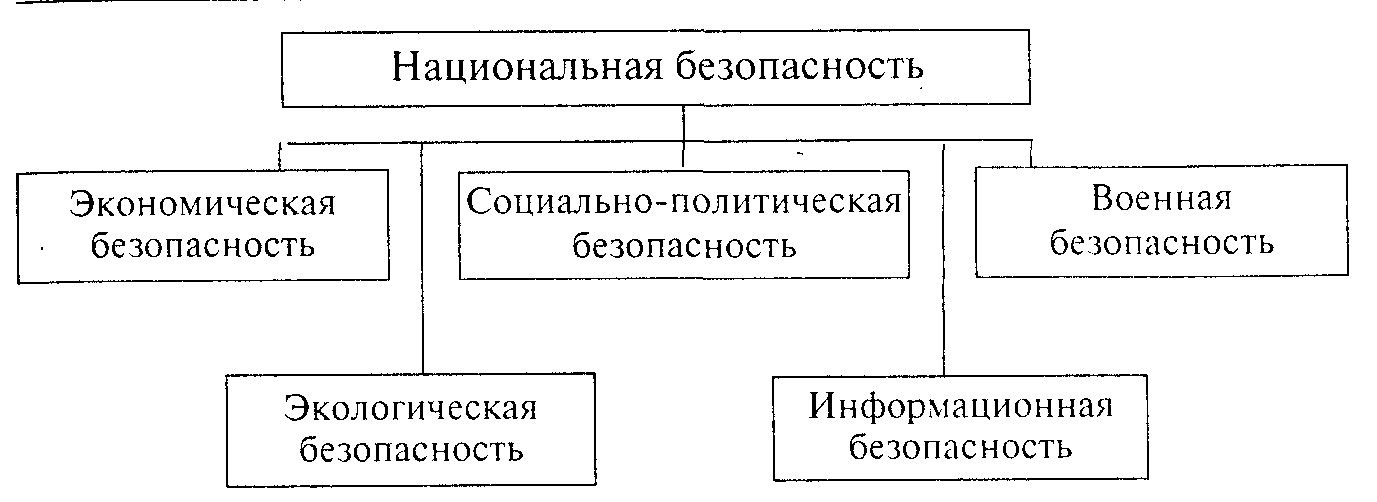
Scheme 8. Classification of types of national security by spheres of life
In this case, one or another type of security is understood as the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the specified sphere of life from internal and external threats.
So, military security- this is the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the defense sector from internal and external threats.
Respectively economic security- this is the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the economic sphere from internal and external threats.
Other concepts are defined in a similar way. It should be borne in mind that in this classification there are special type“state security” seems illegitimate, since the state is organically present in all spheres of life and it is impossible to limit state activity to one area.
This classification when considering problems of internal security, it is of a country-wide nature and represents the structure of internal federal security.
The structure of regional security, depending on the specifics of a particular region, may have a different classification according to spheres of life.
Such an approach streamlines the classification of types of security, makes it possible to avoid the current confusion of classification principles and allows us to consider national security as a unified system of types of security, each of which is an independent subsystem with its own characteristic features. Practice shows that all these subsystems are closely interconnected and are in dialectical interaction. In practical activities to ensure national security, not a single type of national security should be consigned to oblivion, as happened, unfortunately, in the recent past, when Soviet Union collapsed at the peak of its military power, achieved at the expense of economic and social security. Of course, at each stage of historical development, the priorities of certain types of security objectively change, and therefore the most important task of ensuring national security is to achieve in each time period a certain rational parity between various types security.
Questions for self-control
1. What are the grounds for dividing national security into two types - internal and external?
2. What is international security?
3. What is the classification of national security by sphere of life?
4. Why is it necessary to classify internal security at a territorial level?
Literature
2. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation. M., 2000.
3. Problems of internal security of Russia in the 21st century. M., 2001.
© Prokhozhev A.A.
Chapter 4. Modern concepts national security and the dynamics of their changes
The origin and formation of the concept of national security abroad.
Modern features of foreign concepts of national security
Modern concepts of national security of individual foreign states began to be created and function after the Second World War. This process took on the widest scope in the United States of America, which was the result of the foreign policy experience accumulated by the country's leadership during the war, as well as the features that determine American approaches to ensuring the country's security in specific historical conditions. Other foreign states did not undertake such a radical restructuring of the foreign policy mechanism, but took the path of gradual, evolutionary alteration. This happened either due to conservative thinking or due to lack of opportunities. But almost all Western countries took American views on the security problem as a basis.
During " cold war“The tough confrontation in the military and ideological fields determined the priority of the foreign policy and military-political approach to national security problems in the United States. Therefore, the US national security strategy in those years concerned only external security, with virtually no impact on internal spheres.
During the presidency of B. Clinton, a special section on economic issues appeared in the US national security strategy, which, in particular, stated: “On the one hand, we must revive the economy if we want to maintain a high level of combat readiness of the armed forces while implementing our foreign policy initiatives and expanding US influence in the world, and on the other, we need to be active abroad if we want to open up foreign markets and create new jobs for Americans.”
The Bush administration decided on its strategy in the field of national security, but in 2002 its first steps in this area and practical actions after the terrorist attacks in September 2001 indicate that general course in the field of national security, developed in previous years, has not changed, but only acquired more imperial and unceremonious features in an American way.
The US National Security Act of 1947 does not define the concept of “national security”. American political scientists have come up with a lot of different definitions of this concept. The US Department of Defense Dictionary of Military Terms defines US national security as the area of joint military and foreign policy efforts and as the desired condition (state) provided primarily by American military and defense superiority over any foreign power or groups of powers, a favorable position in international relations, as well as defensive capability and invulnerability, allowing one to successfully resist hostile or destructive, overt or covert actions of other countries, including their use of military force 12 .
In fact, this definition expresses the idea of an ideal situation of absolute military superiority of the United States over the armed forces of the whole world, which once again indicates the closest connection in the United States, activities in the field of national security with foreign and military policy based on military force.
The US national security concept is theoretical basis American military and foreign policy. Now that Russia’s approach to national security problems has been completely de-ideologized, the United States is strengthening the ideological side of its concept of national security on the principles of the “new world order” theory.
The United States directly points out that foreign policy cannot but be ideologized, since ideology is a form of manifestation of national interests. This is also evident in the US National Security Strategy, presented by US President George W. Bush in September 2002 to Congress as a document defining the goals, objectives and directions of the American administration’s activities in the field of foreign and military policy for the coming year. In it, along with the distinct geopolitical foundations of “national security,” there is also a clearly expressed ideological side:
“The War on Terror is not a clash of civilizations... It is a battle of ideas, and that is the battle that America must win.” This strategy is based on the idea that ensuring US national security is directly related to the establishment and functioning of freedom and democracy in other countries through the establishment of a new world order with the leading role of the United States. According to the American political scientist Nolan, we're talking about neither more nor less about improving the whole world.
The US national security strategy, first of all, formulates national goals, which the national strategy of the US administration is aimed at achieving. During the Clinton administration, the national strategy in this document covered three areas: political, military and economic, and the priority goals were: strengthening security, ensuring the prosperity of the nation, and developing democracy.
The actual content of the national goals remained unchanged, but in the National Security Strategy of the Bush administration this triad of goals was formulated somewhat differently: political and economic freedom, peaceful understandings with other states and respect for human dignity.
To achieve these goals, it is believed that the United States must:
Support the desire of states to ensure respect for human dignity;
Strengthen the alliances of states to combat international terrorism and prevent a possible attack on the United States and its allies;
Cooperate with other countries in resolving regional conflicts;
Prevent threats to use weapons of mass destruction against the United States and its allies;
Strive for the creation of free markets and promotion of free trade;
Stimulate the development of open societies and democratic institutions in new states;
Determine the main directions of joint actions with other world powers;
Reform the structures that ensure US national security and give them the ability to adequately respond to threats of the 21st century.
This Strategy states: “Defending the country from its enemies is the first and primary responsibility of the federal government.” But it is emphasized that this task has now changed dramatically. The geographic isolation of the United States no longer ensures the country's security. Current and future adversaries will seek to strike the country and its armed forces with new and in unexpected ways. The United States faces a new urgency: it must achieve victory in the modern war on terrorism while preparing for future wars that are fundamentally different from the wars of the last century and the conflicts of today. If in the past, to threaten America, you needed strong army and huge industrial potential, today a small group of terrorists may pose a threat. Terrorism, as carefully planned, politically motivated violence against innocent people, has been declared the main long-term enemy of the United States. At the same time, it is stated directly and frankly that the war against international terrorism means a fight for American values and way of life. It is also argued that to protect the United States and American interests both at home and abroad, threats will be identified and eliminated before their impact reaches American borders. At the same time, while making efforts to enlist the support of the international community, the United States explicitly states that without such support, it will not hesitate to use the right of self-defense and will launch preemptive strikes against terrorists wherever they are.
It is believed that the traditional concept of deterrence and response does not apply to terrorists. Instead, the concept of an imminent threat is put forward, taking into account the capabilities and goals of current US adversaries, according to which the US must be prepared to take preemptive action, even if there is no complete information about hostile actions against the US.
It is especially emphasized that the time has come to reaffirm the critical role played by military power in ensuring US security. The military's highest priority is the defense of the United States. In order to effective solution To achieve this mission, the US military must:
Guarantee the security of our allies and friendly countries;
Convince potential opponents of the futility of developing military competition with the United States;
Contain threats to the national interests of the United States, its allies and friends;
Inflict a decisive defeat on any enemy if containment measures prove ineffective.
The declared goal of the American armed forces is to protect and promote US national interests and, if the deterrent factor is not effective enough, to defeat threats to these interests. The United States has global interests, responsibilities and obligations. At the same time, the United States is subject to trends, events and influences that have origins beyond its borders. When U.S. interests are protected, the United States and its friends prosper. When U.S. interests are challenged, they must have the power necessary to defend them. At the same time, four risk areas needing to be addressed have been identified.
The risks associated with the maintenance of the armed forces are due to the problems of recruiting, maintaining military service, training and equipping a sufficient number of highly trained personnel and maintaining the armed forces in combat readiness.
Operational risks arise from the factors that determine the ability to achieve military objectives in future conflicts.
Risks associated with future challenges arise from issues that impact the ability to act, manage, and control so that resources can be used effectively and contribute to the successful operations of the Department of Defense.
The unprecedented strength of the US military and its forward presence have ensured peace in some of the most strategically important regions of the planet. However, as the nature of the threats to our interests and the potential adversaries we must confront have changed, changes must also be made in the military. The structure of the US military, focused on containing the huge armies of the Cold War, must be reformed based on a model that puts first priority the question of how an adversary could fight fighting, and not where and when a war might start.
Intelligence and how its results are used is the first line of defense against terrorists and threats posed by hostile states. The intelligence community, which was created to extract enormous amounts of information about a fairly large static entity - a bloc led by the Soviet Union - must now cope with the task of tracking multiple targets that are much more complex and less visible.
It is necessary, the Strategy states, to reform existing intelligence structures and provide them with new capabilities in order to bring the intelligence community into line with the nature of existing and potential threats. Intelligence must work closely with the Department of Defense and law enforcement agencies and coordinate efforts with similar structures of American allies and friends.
Intelligence initiatives include:
Expanding the powers of the head of central intelligence to manage the development and activities of national forces and assets foreign intelligence;
Commissioning new scheme intelligence warning, which should provide unobstructed and comprehensive warning across the full range of threats facing the United States and its allies;
Continue to develop new methods of obtaining and collecting information to maintain advantages in the field of exploration;
Investing in the development of advanced intelligence capabilities while simultaneously strengthening measures to protect related information;
Organizing the collection of intelligence information on terrorist threats, involving all necessary government agencies and analyzing information from all possible sources.
At the same time, the Strategy understands respect for human dignity as promoting American ideals and principles of freedom and democracy to other countries and encouraging those states that follow this path. This area aims to focus on consolidating new democracies, expanding their commitment to democracy, expanding markets, and preserving the US position in regions of greatest security concern and where it can achieve best results. It is also argued that this is not a crusade to establish democracy, but a pragmatic policy to maintain freedom where it will best serve American interests.
In the economic sphere, attention is focused on the need to strengthen measures to combat industrial espionage, which undermines the foundations of free competition. At the same time, it is argued that US protections ensure that the benefits of free trade do not come at the expense of the well-being of American workers.
In the US national security strategy in the 21st century. For the first time, national and international security are so openly and unambiguously identified. This can be explained not only by the global nature of American interests and presence, but also by a global approach to protecting them from threats.
The leading position of the United States in the world provides for the inevitability and irreversibility of the rapid integration of the entire world community. The main condition for the construction and preservation of " global civilization“It is considered to ensure stability at any cost, in all regions of the world without exception, using all means available to the United States and its Western allies.
Stability is understood in the United States in a narrow and broad sense. In a broad sense, this is a certain state of international relations, and in a narrow sense, it is a concept that defines approaches to assessing the balance of forces of opposing states (their coalitions). Within the framework of the issue under consideration, stability in a broad sense is of interest, since it is one of the basic elements ideology of the “new world order”.
In accordance with this ideology, international stability came to be understood as a state of the world in which “all leading powers would belong to a democratic community with the gradual accession of other market and democratic states to it.” In other words, we are talking about a global movement to establish American-style democracy throughout the world and maintain a state of stability with the leading role of the United States. And this becomes not only an ideology, but also a practice of the foreign policy of the United States.
To stimulate the development in other states of the principles of an open society and democratic institutions, naturally following the American model, the strategy puts forward to the United States and others developed countries the specific goal of helping the world's poorest countries double their gross domestic product in ten years.
In the US national security strategy, when defining comprehensive regional approaches, the American administration gives priority to ensuring its national interests in Europe and Eurasia. The United States also intends to ensure the preservation of stability in this vast super-region at any cost. It is obvious that the ideological premises contained in NATO documents largely copy the ideology of the US national security strategy.
In particular, an analysis of NATO documents with an assessment of the ideological side of the Partnership for Peace program suggests that ensuring stability in Europe is directly related to the establishment and functioning of freedom and democracy according to the American standard, and new NATO partners in Eastern Europe and the Baltic is assigned the role of a kind of buffer between Western Europe and Russia.
Talking about main goal modern American national security strategy, it should be noted that it is in the sphere of ideology and is aimed at promoting the spread of a market economy and democracy in the world. In the past, this goal took the form of well-known concepts of messianism, the struggle for human rights, the struggle against totalitarian regimes, etc. At the current stage, taking into account the changes in recent years, the concept of a “new world order” aims to maintain Western values and the system as a whole in modern stage evolution of humanity.
The American national security strategy, as noted above, continues to focus on force and, above all, military force. Many American scientists themselves note that the spread of democracy in the world through the use of military force can become a source of destabilization of the international situation.
Apparently, the experience of Vietnam, Yugoslavia and Iraq did not teach that in modern conditions It is impossible to resolve any contradictions and disputes by armed struggle.
Throughout the entire period after the Second World War, ensuring international security was based on compliance by all states with generally recognized principles and norms of international law, excluding the resolution of controversial issues and disagreements between them by force or the threat of force. But since March 1999, as a result of the aggressive attack by the United States and NATO on Yugoslavia, this world order ceased to exist. This aggression clearly demonstrated the readiness of the United States and NATO from now on, at their own discretion, without paying attention to the UN and international law, to impose by force of arms on sovereign states their own version of resolving any crisis situation, including artificially created ones. At the same time, it is specifically stipulated that any US efforts in the field of ensuring international security and protecting American interests should not be weakened by the actions of the International Criminal Court, whose jurisdiction does not extend to American citizens and whose decisions the United States does not recognize. Instead, the United States will fully enforce its American Employee Protection Act, which is designed to provide and enhance the protection of American personnel and officials. The aggression in Kosovo and the military operations of the United States and Great Britain in Afghanistan have clearly shown all states that do not want to act on orders from the United States that from now on they will be able to defend their interests by relying only on their own forces and having the appropriate deterrence potential.
This awareness of the costs of a multipolar world has already caused a new wave of arms growth in many countries and will undoubtedly increase the number of states seeking to develop their own nuclear weapons or other weapons of mass destruction.
Until humanity abandons the use of armed struggle as a method of resolving contradictions, it is impossible to ensure true national security, relying, of course, on the entire aggregate power of the state. Of course, this is not so simple, since it took the UN more than two decades to define the concept of “aggression”. But, obviously, it will be possible to ensure national security not by uniformity of forms of democracy and economy according to the American or other model, but only by achieving unity in approaches to the problems of ensuring national security.
It should be borne in mind that as the concepts of human development, globalism and sustainable development are formed and improved, Western ideologists accordingly modify their views on the problem of security and persistently promote them through international organizations to other countries of the world. The West openly proclaims that “the time has come to make a transition from a narrow concept of national security to a comprehensive concept of human security” 13 . This transition is supposed to be carried out in two directions: to replace the security of countries and territories with the security of people, and also to replace the provision of security through weapons with progressive human development.
These principles of the new security concept look very attractive, but extremely utopian. In addition, they clearly demonstrate a clear desire to accustom the world community and leaders of developing countries to the idea that it is in their own interests not to pay attention to issues of ensuring their national security, protecting their territory, and their identity. Instead, they should think of human security as the absence of threats from hunger, disease, repression and abuse Everyday life in the family, workplace or community.
It is characteristic that all Western countries are in no hurry to abandon their own national security.
In the United States, by analogy with the theory of sustainable development, a theory of sustainable national security is being formed: “Each generation must create the opportunity for the next generation to ensure security. Currently, the safety of the next generations is in our hands...” This position seems completely justified, since in full accordance with the objective state of the world community at the present time, the importance of ensuring the national security of any country in the world will not decrease in the slightest, both in the short and long term.
In the era of globalism, the state of national security of any country is determined by the level of its competitiveness in various fields life activity within the framework of world space. Developing countries, in the stable conditions of the currently promoted model of globalism, are completely uncompetitive in comparison with developed countries. Consequently, their level of security is equally low, and the West, naturally, is not going to protect the national interests of these countries. In the current situation, these countries will be able to increase the level of national security, that is, the level of protection of their national interests from both internal and external threats, only through destructive influences on the system of globalism created by the West. Preventing such a development of events, ensuring the stability of the existing world order by any means is the strategic task of the world politics of the countries of the “golden billion”. In this policy, an important place is occupied by the marked course of the West to replace the problems of ensuring the national security of developing countries with the tasks of their internal development in the socio-economic sphere. Confusion of the concepts of “development” and “security” in in this case is far from accidental and has a purposeful nature, arguing that “ human development is a broader concept." Thus, “security” is included in the concept of “development” as its component. However, these concepts are fundamentally different, but quite equal in their significance in people’s lives.
An important feature of foreign approaches to national security problems in last years is a sharp turn to internal problems, whereas previously, for the most part, they were only designated as imperatives. Extremely little attention was paid to environmental problems and issues of preventing and eliminating the consequences of man-made and natural disasters were completely excluded from the national security strategy, although their influence is global in nature.
After the tragic events in September 2001 in the United States, fundamental changes began in internal security policy. Already on October 8, 2001, the President of the United States, in addition to the post of Assistant to the President for National Security, established new position Assistant to the President for Homeland Security with a significant apparatus in the form of the Office of Homeland Security. The tasks of this department are to develop and implement an internal security strategy and coordinate the activities of the intelligence services that provide it.
In November 2002, the Department of Homeland Security was created as most important organ US executive branch to solve the following main tasks:
Preventing terrorist attacks in the United States;
Reducing the United States' vulnerability to the threat of terrorism;
Minimizing damage from terrorist attacks in the United States and eliminating their consequences.
The number of the ministry is determined at 170 thousand people, and its structure, powers and functional responsibilities officials are developed based on an assessment of actual and potential threats to US internal security.
Currently, the ministry’s activities are carried out in the following main areas:
Collection, synthesis and analysis of intelligence information in order to identify possible threats to US internal security;
Protection of critical economic and infrastructure facilities;
Ensuring the protection of the state border and the safety of transport;
Protection of the population and national territory from possible application chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear weapons, including conducting R&D to counter this threat;
Preparing the population to act in emergency situations, including natural and man-made disasters;
Ensuring the safety of representatives of the country's top leadership.
The system of preparedness for emergency situations and liquidation of their consequences has undergone a radical restructuring. The ministry includes about 80 government organizations that previously operated independently or as part of various federal departments. Among them Federal agency for emergency operations (FEMA) - an analogue of our Ministry of Emergency Situations, the Office of Domestic Preparedness from the FBI, the Office of Emergency Preparedness from the Ministry of Health and social security, Disaster Medicine, Coast Guard, Immigration Service, etc. This is an unprecedented case of such strict centralization of executive power in the United States, uniting the efforts of federal agencies, state agencies, municipalities, the private sector and the entire society in the fight against terrorism. This experience deserves serious attention on our part.
Questions for self-control
1. What is meant by the term “national security” in the United States?
2. What are the features of the American approach to the problem of national security?
3. What is the structure American system ensuring internal security?
Literature
1. Zhinkina I.Yu. Russia's security strategy: problems of forming a conceptual apparatus. M., 1995.
2. Zhinkina I.Yu. National Security Strategy of US President B. Clinton. M., 1997.
3. Chernigova N.K. Fundamental changes in US national security policy: Collection of scientific articles. M., 2004.
© Prokhozhev A.A.
Chapter 5. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation: structure, content, problems
The formation of Russia as a federal, democratic, rule-of-law state entails radical transformations of the state structure, the formation of new socio-economic and socio-political relations. And this requires a reassessment of the interests of the individual, society and the state, taking into account new opportunities in representative democracy and a market economy, and Russia’s participation in the global civilizational process.
Today our country finds itself in the zone of influence wide range threats that created real danger the existence of the state itself, its citizens, their being and consciousness. There was a need to develop a conceptual document that would reflect long-term strategic objectives and priorities in the implementation of national security policy and identify the main directions of activity of all structures to ensure national interests in the 21st century.
Over the years, efforts have been made to overcome negative phenomena and threats generated by both modern reality and the Russian history. The adoption in January 2000 by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of a new edition of the Concept of National Security of the Russian Federation was the result of eliminating many of the shortcomings of the previous edition of the 1997 Concept and became an important legal framework in defining public policy in the field of national security. But it is obvious that the formation of a mechanism for ensuring national security cannot be considered complete. The main thing is to further consolidate and develop the content of the provisions of the Concept in laws and regulations in specific areas of security.
It was assumed that the activities of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation would be based on the principle that lawmaking should be carried out in accordance with the program for the systematic strengthening of the foundations of the state set out in the Concept. Undoubtedly, this process should be carried out against the backdrop of harmonizing the activities of all branches of government and strengthening federalism as the main condition for the development of the Russian Federation.
The new edition of the Concept especially emphasizes that the national security of the Russian Federation is understood as national security, the security of the entire multinational people as the bearer of sovereignty and single source authorities in the Russian Federation. As for the concept of the Concept itself, the preamble states that this is a system of views on ensuring the security of the individual, society and state in the Russian Federation from external and internal threats in all spheres of life.
The first section characterizes Russia in the world community and determines its place after the end of the era of bipolar confrontation. Mutually exclusive trends in the world are identified, when, first of all, the economic and political positions of a significant number of states and their integration associations are strengthened, and the mechanisms of multilateral management of international processes are improved. Will Russia contribute to this? Undoubtedly, Russia will play its role in shaping the ideology of the formation of a multipolar world on this basis.
And the second trend, in relation to which it is also necessary to develop your position. It manifests itself through attempts to create a structure of international relations based on the dominance of developed Western countries in the international community under the leadership of the United States and designed for unilateral, mainly military-force solutions to problems of world politics, bypassing the fundamental norms of international law.

Diagram 9. Scope and subjects of ensuring national security of the Russian Federation
In the future, Russia objectively maintains a commonality of interests with other states on many international security issues - in countering the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, preventing and resolving regional conflicts, combating international terrorism and drug trafficking, solving environmental problems of a global nature, ensuring nuclear and radiation safety .
The second section defines the national interests of Russia as a set of balanced interests of the individual, society and the state, which are long-term in nature and determine the main goals, strategic and current tasks of the state’s domestic and foreign policy.
Revealing the content of the interests of the individual, society, and state, the Concept defines eight priority areas for ensuring the protection of these interests: economic, domestic political, social, international, information, military, border, environmental. Ensuring the protection of national interests is carried out by government institutions in cooperation with public organizations. And one cannot but agree with this. Ensuring national security is a set of measures of a political, legal, economic, military, informational, social, environmental and other nature, and this is the business of both the state and the people themselves. It is achieved by pursuing a unified state policy to ensure national security, as well as specific measures supported by society and adequate to the threats.
The third section presents the threats and their spheres of influence, starting with the social one, where they create a deep stratification of society into a narrow circle of rich people and the predominant mass of low-income citizens, an increase in the proportion of the population living below the poverty line, and an increase in unemployment. It is noted that the deepening of the crisis in the internal political, social and spiritual spheres may lead to the loss of democratic gains.
As for such an important sphere as the international one, threats to national security are manifested in the attempts of other states to counteract the strengthening of Russia as one of the centers of influence in a multipolar world, to prevent the realization of national interests and to weaken its position in Europe, the Middle East, the Transcaucasus, Central Asia and the Asia-Pacific region. These obvious trends have led to an increased threat to Russia’s national security in the information sphere and an increase in the level and scale of threats in the military sphere.
The Concept especially emphasizes the threat of deterioration of the environmental situation in the country and its depletion natural resources. It is due to the predominant development of fuel and energy industries, the underdevelopment legislative framework resource-saving technologies, low environmental culture. Weakening state supervision, the insufficient effectiveness of legal and economic mechanisms for preventing and eliminating threats in Russia are characteristic not only of the environmental sphere, but also of others.
The fourth section of the Concept defines the main tasks in the field of ensuring national security, for example, timely forecasting and identification of external and internal threats; improving the system of government; federal relations; local government and legislation of the Russian Federation; formation of harmonious interethnic relations, strengthening law and order and maintaining socio-political stability of society; ensuring equal and mutually beneficial cooperation between Russia, first of all, with the leading states of the world, etc. And yet, the tasks of protecting national interests in the economic sphere are priority areas of state policy.
In addition to the objectives, the fourth section indicates the main directions of the state’s activities to protect national interests in all areas of human life. For example, in the field of protecting and promoting the health of citizens, it is necessary to increase the attention of society and government authorities to the development of state insurance (federal and municipal) and private medical care, implementation of state protectionism in the domestic pharmaceutical industry, implementation of federal programs in the field of sanitation and epidemiology, child health, provision of ambulance and emergency medical care.
The system of ensuring national security as a whole is considered. It is based on bodies, forces and means of ensuring national security, implementing measures of a political, legal, organizational, economic, military and other nature aimed at ensuring the security of the individual, society and the state.
Participating in the formation and implementation of national security policy are: the President of the Russian Federation, Federal Assembly Russian Federation, Security Council of the Russian Federation. Federal executive authorities ensure the implementation of the legislation of the Russian Federation, decisions of the President of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Russian Federation in the field of national security, within the limits of their competence, develop normative legal acts in this area and submit them to the President and the Government.
This is the structure of the four sections of the Concept and their summary. This important conceptual document reflects the need to highlight national security as the main problem in the development of Russian statehood and society. The main objects of national security are defined here - the individual, society and the state, where the individual and his interests are put in first place. For the first time, a legal document stipulates that Russia’s national interests “are a set of balanced interests of the individual, society and the state” (Diagram 10).
The National Security Concept of the Russian Federation recognizes “a system of views on ensuring in the Russian Federation the security of the individual, society and state from external and internal threats in all spheres of life.” However, in this interpretation, the Concept acts as a certain system of unknown views, ensuring security as if only in the Russian Federation, which conflicts with the Law of the Russian Federation of March 5, 1992 “On Security”, according to which security objects also include And Russian citizens located outside of it. The state guarantees them protection and patronage.
Taking into account the above, the definition of the Concept should be stated in the following wording: “This is an officially adopted system of views in the Russian Federation on ensuring the security of the individual, society and the state in all spheres of life.”
The new edition of the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation contains provisions that fuel the practice of mixing the functions of development and security. As tasks for ensuring national security, the Concept puts forward a number of tasks that affect security, but are not directly related to it and are tasks for the development of the country. Of course, the more developed a country is, the easier it is to ensure its security. But the functions of realizing interests must not be confused with the functions of protecting them. These are close, but fundamentally different tasks. Thus, if we include the tasks of economic recovery, improving the system of state power of the Russian Federation, ensuring equal and mutually beneficial cooperation between Russia and other states, forming a single economic space with the CIS states and others to the tasks in the field of ensuring the national security of the Russian Federation, as specified in the Concept 14, then in accordance with the same document they are obliged to be solved by the bodies, forces and means of ensuring national security, i.e., security forces 15

Diagram 10. Concept of national security of the Russian Federation
Such a substitution is not only illiterate, but also essentially harmful, since it reflects the desire of a number of departments to solve their problems by forceful methods or to shift responsibility from themselves to law enforcement agencies, as has already happened many times in practice.
At the same time, the text of the Concept contains reasonable, correct wording dividing the above tasks and identifying from them, in addition to the tasks of ensuring national security, those that should contribute to ensuring national security 16. Consistent orientation towards such an approach will avoid discord and contradictions and strengthen terminological discipline
The second section of the Concept contains a very serious clause, according to which “the implementation of Russia’s national interests is possible only on the basis of sustainable economic development.” With this formulation, the viability of the Concept as a whole seems to be called into question.
In addition, among the areas of ensuring national interests there is no such important area as demographics. Justifying the inclusion of this type of threat would not be difficult given such an obvious phenomenon in Russia - depopulation of the population, especially since the Government of the Russian Federation has developed a draft Concept demographic policy for the period until 2015. Since 1992, the country has experienced an absolute decline in population - at the beginning of 2002, the permanent population was 144.0 million people compared to 148.3 million people in 1992. In 2001, the number births decreased to 1.2 million people per year compared to 1.6 million people in 1992. Thus, the relevance of the rapid development and approval of the doctrine of demographic security of the Russian Federation and the entire range of accompanying documents and corresponding business programs to ensure it is constantly growing . In the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation, demographic interests are not included in the system of national interests and are not protected in section three, which classifies threats to national security.
However, being a holistic integrated system adequate to a certain historical period of time, the Concept predetermines the essence and interconnects a number of state security concepts (doctrines) of a lower rank: “Military Doctrine of the Russian Federation” (2000), “Concept of Foreign Security Policy of the Russian Federation” "(2000), "Doctrine of Information Security of the Russian Federation" (2000), etc. However, a complete system of conceptual legal regulation has not yet been created in Russia. This affects the clarity, predictability and effectiveness of the course pursued by the state authorities, at least in the most important areas of activity.
The fundamental legal basis of the National Security Concept of the country is represented by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the laws of the Russian Federation “On Security”, “On Defense”, federal constitutional and federal laws, as well as international treaties and agreements concluded or recognized by Russia, regulating the sphere of national, collective, regional and global security.
Serious problems caused by the complex federal structure of the Russian state, increased uncertainty, and in some cases unpredictability of development give rise to new challenges and threats to Russia's security in almost all spheres of life. They can be resolved only over a long period of time and thanks to the focused efforts of all government bodies and public organizations. The direction of this activity should be regulated by a coherent regulatory and legal system, which consists of: laws adopted by the legislative branch, decrees and orders issued by the President of the Russian Federation, orders and resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation in the field of national security.
Unfortunately, the creation of the legislative basis is still far from complete. Although many of the defining pieces of legislation in this area are already in force, others are in the process of being finalized. The legislative process continues.
For this process, both at the federal level and in the constituent entities of the Federation, it is important to have a conceptual official document, the formation of which would be based on an analysis of security problems for the period under review. Of course, this is the most complex and painstaking analytical work of all information and analytical centers of state and non-state subsystems for ensuring national security. It assumes:
1. Analysis of the role and place of Russia in modern world (historical roots Russian statehood, prospects for international development, justification of the geopolitical status of the country).
2. Determination of the entire range of vital interests of the individual, society, and state in all areas.
3. Comprehensive analysis and assessment of the nature of real and potential threats to national interests in various fields of activity.
4. Identification and assessment of resources and capabilities to neutralize or counter actual and potential threats.
5. Development of options for measures (means and methods to counter threats) to ensure the national security of the state.
6. Creation of an adequate government process and mechanism for implementing the National Security Concept.
And then there is hope that a political document, set out in the form of a decree and issued to guide it, will be the basis for the formation and implementation of national security policy (Diagram 10).
In the proposed scheme an attempt is made to put national problems into the plane direct action and, if possible, tie not only to space and time, but also to all branches of government and society, guided by the fact that, firstly, the policy of ensuring national security is the main directions of activity to achieve the national goals of the Russian Federation over a certain period and, secondly, the strategy for ensuring national security is specific actions of the state and society, expressed in the use of resources, bodies, forces, means, methods and forms to neutralize real threats to the vital interests of the individual, society and the state.
Of course, security guarantees in the modern world are still largely ensured by force or the threat of force. It is no coincidence that in the current National Security Concept of the Russian Federation, most of the text of the fourth section is devoted to military security. And yet everything higher value in the world, scientific, technical, economic, political, moral, ethical and other non-force factors of ensuring national security are acquired.
Peaceful existence, and not war, now increasingly determines both the relations between individual states and the system interstate relations at the regional and global levels.
True peace in the future may be based not on a balance of forces, but on ensuring a balance of interests of states and communities on the basis of contractual legal principles. Further improvement of the legal and regulatory framework for national security is a condition for the democratic development of the processes of self-organization of society and the state guarantee of the stability of the Russian Federation in the modern world.
Questions for self-control
1. What does the concept of “national security concept” include?
2. Name the main directions of protecting the constitutional system of Russia.
3. What problems of the life of society and the state are not reflected in the structure and content of the Concept of National Security of Russia?
Literature
1. Constitution of the Russian Federation. M., 1993.
2. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation. M., 2000.
3. Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” // Gazette of the Congress of People’s Deputies and Supreme Council Russian Federation. 1992. No. 15. Art. 769.
4. Vozzhenikov L.V., Passerby A.A. Public administration and national security of Russia. M., 1999.
5. Ryzhak N.I. Legal regulation of the activities of special services in the system of ensuring national security of the Russian Federation. M., 2000.
© Krivelskaya N.V.
Chapter 6. Law of the Russian Federation “On Security”
The formation of the Russian Federation as an independent state brought the problems of ensuring national security to the forefront. This could not but affect the content of regulatory legal acts and, in particular, the current Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” of March 5, 1992.
If we consider the structure of this law, it consists of a preamble that sets out the provisions on the purpose of this legislative act and its basic structural elements;
General Section I, which defines the concept of security, objects and subjects of security, types of threats, principles and legislative framework for security. Section II reveals the security system of the Russian Federation, its main elements and functions, delineates the powers of government bodies, forces and means of ensuring security. Section III establishes the legal status of the Security Council, its composition and procedure for its formation, the main tasks and procedure for decision-making by the Security Council, as well as the procedure for the formation of interdepartmental commissions. Section IV defines the financing of security activities and emphasizes that it is carried out depending on the content and scale of the programs, the nature emergency situations and their consequences. Section V establishes the organization and procedure for control and supervision of the activities of security agencies.
For the first time in legislative practice, concepts such as “security”, “vital interests”, “security threats”, “security entities” are being legally enshrined.
Security is defined by law as “the state of protecting the vital interests of the individual, society and the state from internal and external threats,” and the threat to security itself is “a set of conditions and factors that create a danger to the vital interests of the individual, society and the state.” To create and maintain the required level of protection of security facilities, the law provides for the development of systems of legal norms regulating relations in the field of security, determines the main directions of activity of public authorities and management, the formation or transformation of security bodies and a mechanism for control and supervision of their activities.
These provisions of the law are still relevant today. Despite the dynamic nature of the security situation, varying degrees and the level of security, their dependence on time, the severity of internal and external threats and the ability to respond to them control system, the principles of provision remain unchanged. Moreover, today they are the methodological and legal basis for theoretical and practical activities in the field of national security. “This law, according to the ideas contained in it, is now one of the most progressive in the world, since it provides for the need systematic approach to consider all national security issues. This consistency lies not only in the triad of “individual, society and state”, but also in the combination of external and internal security, as well as a number of individual species security" 17.
The triad “personality, society, state” was widely used in the theoretical works of Russian scientists back in the 19th century. Thus, based on the characteristics of the threats, it was noted: “The dangers, the prevention of which creates security in the country, are represented by three categories: some of them can threaten both an individual and the whole society and state, others - directly to the government, others - mainly to an individual citizen. Some dangers threaten the entire state, but they manifest themselves directly and directly in relation to the government” 18.
Currently, for the first time, in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation “On Security,” national security is divided depending on the location of the source of the threat into two types - internal and external. In the context of globalization and internationalization of all aspects of public life, the line between internal and external security is very blurred, and many threats (international terrorism, drug trafficking, environmental and natural disasters) are sometimes difficult to link to any single source. Nevertheless, such a division seems to be very useful, since it allows one to clearly classify certain conceptual approaches to solving problems of ensuring national security.
Consistent orientation towards such an approach will avoid disagreement in the presentation of definitions, contradictions in the approach to security, and will strengthen the terminological discipline in the field of security.
As for the main elements of the security system, in accordance with Art. 8 of the Law it is formed by the legislative, executive and judiciary, state, public and other organizations and associations, citizens participating in ensuring security in accordance with the Law, as well as legislation regulating relations in the field of security.
The main functions of this system are defined by this Law:
Identification and forecasting of internal and external threats to the vital interests of security facilities, implementation of a set of operational and long-term measures to prevent and neutralize them;
Creation and maintenance of security forces and means;
Management of security forces and means in everyday conditions and in emergency situations;
Implementation of a system of measures to restore the normal functioning of security facilities in regions affected by the emergency;
Participation in security activities outside the Russian Federation in accordance with international treaties and agreements concluded or recognized by the Russian Federation.
Of course, in practice the range of functions of this system is much wider. This may include planning the activities of agencies and security forces in various modes functioning of the system; organizing interaction between various government, commercial and public organizations; coordination of the actions of bodies and forces to carry out activities in the field of ensuring national security; ensuring unity of action to strengthen security at the federal, local and regional levels, etc.
Structural and functional components provide an opportunity to define the concept of both the security system of the Russian Federation as a whole and the forces and means of ensuring it. By ensuring the security of the Russian Federation, based on the content of the Law, we mean the purposeful activities of state and public institutions, as well as citizens, to identify and prevent threats to the security of individuals, society and the state. And as a mandatory and indispensable condition for protecting national interests, countering these threats is necessary.
The main goal of ensuring the security of the Russian Federation, based on general provisions The law is to create and maintain the required level of security for all security facilities. The economic, political, international and military-strategic position of the country should eliminate the danger of weakening the role and significance of Russia as a subject of international law, and create favorable conditions for the development of the individual, society and state.
The main subject of security is the state, which exercises functions in this area through the legislative, executive and judicial authorities. In accordance with current legislation the state ensures the security of every citizen on the territory of the Russian Federation. Citizens of the Russian Federation located outside its borders are guaranteed protection and patronage by the state. To directly perform functions to ensure the security of the individual, society and the state in the system of executive power in accordance with Art. 12 of the Law defines forces and means.
Security forces include: Armed forces, federal security agencies, internal affairs bodies, foreign intelligence agencies, security services for legislative, executive, judicial authorities and their senior officials, tax service; emergency response services, civil defense formations; border troops, internal troops; bodies ensuring safe work in industry, energy, transport and agriculture;
Communications and information security services, customs, environmental authorities, public health authorities and other government security authorities operating on the basis of legislation. As for means, security is ensured by all means at the country's disposal - political, economic, legal, military, organizational and resource. Security forces and means are created and developed in accordance with decisions of the President and Government of the Russian Federation, short-term and long-term federal security programs.
Basic support resources, in addition to objective advantages geographical location Russia and the presence of strategic nuclear weapons are associated with its intellectual wealth, fairly high scientific and technical potential, the capabilities of its nature and subsoil, prospects in the field of demography and a number of other factors.
The creation of security bodies not established by federal laws is not allowed, says Art. 8 of the Law, and regarding forces and means - in Art. 12 states that the heads of security agencies, in accordance with the law, are responsible for violating the established procedure for their activities.
It remains to be noted that the foreign policy body, which is the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, is not named among the main bodies of the support system. This ministry carries out public administration in the field of relations of the Russian Federation with foreign states and international organizations. Currently, when ensuring national security, the emphasis is on the priority of political, diplomatic, international legal, economic and other non-military means. This approach demonstrates that ensuring national security is the duty of all government bodies, and not just individual departments, even the law enforcement agencies. The task is to ensure that public authorities and government controlled all levels realized their mandatory involvement in solving problems of ensuring national security and did not try to shift this function only to the army, police or counterintelligence.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” does not completely solve this problem today, just like ten years ago, despite its progressive concept. It turned out to be frame legal document, which outlined the contours of the national security system.
Due to the complexity of the socio-political situation in society and, in particular, in view of the threat to the constitutional security of the Russian Federation, it seems necessary to develop a qualitatively new the federal law on national security, which should:
Determine the system of national security bodies and the scope of their activities;
Regulate the coordination of their activities and interactions;
Determine the content and modifications of the operational activities of the special services and establish the procedure for using its results in for preventive purposes and so on.
When developing a new version of the Security Law, it would be necessary to recognize the need to adopt not a Federal, but a Federal Constitutional Law on National Security.
It should also be recognized that the Federation has the unconditional right to apply the entire range of measures to protect national interests. National interests lie in maintaining the integrity of the state, asserting the unified sovereignty of the Federation, maintaining a common economic space, and maintaining homogeneity legal status person and citizen throughout the country.
Instruments for protecting the interests of the Federation and sanctions against subjects of federal legal relations must be clearly stated in the law. Modern Russian law does not contain the necessary mechanisms to guarantee the state and legal unity of the country.
There is still no consensus in defining both the very concept of legal liability and the classification of its types. If such types of legal liability as criminal and civil are known and sufficiently developed. administrative, disciplinary, material, then issues of state legal responsibility are just beginning to be developed and stated by Russian legal scholars.
As a recommendation for inclusion in the concept of the future National Security Law, elements such as subjects of federal responsibility can be proposed; a list of government bodies vested with various powers to initiate and carry out the process of applying measures of federal responsibility; main features and types of federal responsibility.
Such a radical proposal in the field of ensuring national security is defended by the fact that legal measures differ from political ones. Measures of political responsibility are on everyone's lips: the dissolution of parliament, the resignation of the government, etc. They are applied in accordance with legal procedures, but not due to a violation of the law, but for reasons of political expediency. Federal responsibility arises only and exclusively in case of violation of the norms of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal legislation.
The list of federal intervention mechanisms is quite wide:
Declaration of a state of emergency;
Introduction of direct presidential rule; redistribution of powers between federal authorities and authorities of the constituent entities of the Federation;
Use of impeachment proceedings;
Dissolution of legislative (representative) authorities;
Financial measures;
Transfer of police units under the direct subordination of the federal government;
Cancellation of illegal decisions of legislative (representative) and executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Federation;
Liquidation of a subject of the Federation as an independent entity.
Perhaps these measures are not exhaustive for the preservation and safe functioning of the state and society. Therefore, the draft Law must spell out the rationale for the state’s right to take extraordinary measures. Like the National Security Law, the forms of specific legal mechanisms and procedures for federal responsibility are promising and are subject to development in domestic law.
Leaving a situation of legal irresponsibility of the subjects of federal relations, as well as the absence of a new edition of the Law on National Security, is fraught not only with disintegration processes and the destruction of the country, but also threatens the preservation and development of national values in Russia.
And in conclusion, it is fair to turn to G. Hegel, who noted that “the strength of a country lies not in the number of its inhabitants and soldiers, not in the fertility of the land and not in the amount of territory, but in how, through the reasonable connection of parts into a single state power, all this is used to realize the great goal of common defense” 19. This goal remains unrealized at the present stage. The Russian state, unfortunately, does not provide complete security to every citizen of our country, full protection of his interests.
Questions for self-control
1. What is the structure and content of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Security”?
2. What are the contradictions between the Law and other regulations in the field of ensuring national security?
3. What should the concept of the draft National Security Law include, in your opinion?
Literature
1. Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” // Gazette of the Congress of People's Deputies and the Supreme Council of the Russian Federation. 1992. No. 15. Art. 769.
© Krivelskaya N.V.
Security internal and external
Russia is a country in which the army and law enforcement agencies work effectively and enjoy high prestige in society for the worthy fulfillment of their mission: defending the country from external threats and maintaining law and order within the country.
Russia's nuclear missile potential remains a reliable guarantee against aggression from any state. This potential decreased after the conclusion of agreements with other nuclear powers - first bilateral with the United States, and then with England, France and China. Nevertheless, Russia (as well as the United States) maintains a “nuclear shield” that is significantly superior to the arsenals of all other countries.
The Armed Forces are formed exclusively on a voluntary basis. The military budget is analyzed in detail by parliament: defense committees State Duma and the Federation Council have the necessary financial and political instruments to determine the military policy of the state. They have all the information to analyze and direct the development of the Russian Armed Forces. This ensures genuine civilian control over the military sphere.
The Russian army has become professional not only in the method of formation, but also in the equipment and level of competence of its personnel. Its weapons meet the requirements of the ongoing revolution in military affairs throughout the world. Wide use information technologies provides comprehensive information about the enemy’s actions and allows you to strike with high-precision weapons, located hundreds and thousands of kilometers from the conflict zone. Robotic means of warfare are being intensively developed.
The Armed Forces, built in accordance with the latest scientific and technical achievements, require high level education and combat training of all military personnel. There was no longer a need for a mass mobilization army. The peacetime size of the Armed Forces was reduced to 500-600 thousand military personnel. The number of trained reserves also decreased to 700 thousand, but its high-quality composition and constant retraining (reservists receive a small salary) allow the army to be deployed to meet the requirements of any potential conflict.
Control for large areas and extended borders are ensured not by the size of the Armed Forces, but by their ability to quickly deploy. To ensure such deployment, all formations of the Armed Forces are permanently ready, and heavy weapons depots have been created in threatened areas.
Military service has become prestigious - including in terms of the quality of education and level of pay and material goods. It is recognized as a good “career ladder”, especially for men (although women Russian army also quite a few) from families with low social status, people from rural areas and small towns.
The officer corps is formed from citizens who have received, along with a military specialty, a fundamental humanitarian and natural science education. The system of career advancement and the procedure for appointment to higher positions have become competitive and transparent; there is a system of continuous education for officers when prerequisite Receiving the next military rank is not only length of service, but also advanced training and success in training your unit or unit.
The most important element of the new Armed Forces is the corps of professional sergeants. The junior commander has a complex military specialty, and it is he who brings into the barracks the professional morality of not mercenaries, but career military personnel, whose job is to defend the Fatherland. To train this category of military personnel, there are special educational establishments.
The income level of an officer with a certain length of service significantly exceeds the average salary in Russia, a sergeant is slightly above the average level. In addition, military personnel enjoy free additional medical insurance and have significant benefits for mortgage lending. Retired privates and sergeants receive benefits when enrolling in government-funded places at universities, and distance learning is also common among them. higher education. At the same time, special benefits (for example, a scholarship for higher education) are available to those retired military personnel who agreed to become reservists.
The use of increasingly complex weapons and equipment requires more and more long terms training: this is what led to the refusal of conscription.
The leadership of the Armed Forces is carried out by orders that follow from the Minister of Defense through the General Staff directly to the operational-strategic commands of the Armed Forces. With such an organization, the General Staff does not have direct operational control functions. Its tasks are limited to the management of the Strategic Nuclear Forces, the Space Forces, coordination of actions between the operational-strategic commands, organizing the use of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief's reserve, as well as strategic planning and providing recommendations to the Minister of Defense and the political leadership of the country. The General Staff participates in assessing military threats, and most importantly, in developing proposals to counter them and prevent war. At the same time, the assessment of the military-political situation, plans and capabilities of a potential enemy is carried out on the basis of information received by the Main Intelligence Directorate, subordinate directly to the Minister of Defense, in interaction with the apparatus of the Security Council.
The army maintains the traditions of Russian military glory, great attention is paid to the preservation of memorials of the Great Patriotic War and other monuments military history.
The reform of the law enforcement system has become one of the main modernization projects, which radically predetermined the approach to organizing internal security in the state - from police-repressive to the protection of citizens and legitimate manifestations of freedom.
The country's main police agency, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, has been liquidated. Various functions law enforcement are clearly separated by levels of public authority, i.e. The “police vertical”, which combined the fight against crime with maintaining public order, disappeared.
Law enforcement functions are adequately decentralized and carried out by several departments and services. The lower level - the municipal police - is controlled by local governments.
The successor to the Ministry of Internal Affairs was the Federal Criminal Police Service (FSKP). Its main tasks are to combat serious violent and mercenary crimes, i.e. “qualified” (“classical”) crime, incl. organized. Structural divisions of the FSKP exist in all regions, but the territory under their jurisdiction does not coincide with the borders of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Regional police services are subordinate only to the authorities of a given subject of the Russian Federation. Their functions include:
Prevention, detection, suppression and investigation of less serious violent and mercenary crimes;
Patrolling of non-urban highways and the functions of municipal police in inter-settlement areas;
Maintaining order during public events;
Performing the functions of environmental police;
Providing physical (force) protection for both the police of a given subject of the Russian Federation, primarily criminal, and regulatory authorities;
Security private security; ensuring a permitting system (weapon licensing, etc.).
Disputes about the “jurisdiction” of the regional and federal police are resolved according to the principle of “seniority”, i.e. if a representative of the FSKP claims that the case falls within the jurisdiction of this service, it is transferred to the FSKP.
At the level of urban and rural settlements, there is a municipal police, subordinate only to the local community. It is financed from local budgets - this is the only way to guarantee that law enforcement agencies will guard the rights of citizens and be under civilian control. Municipalities with insufficient levels of their own income receive subsidies from the regional budget before legislative established level financing.
The main task of the municipal police is to protect public order - a patrol service with powers of inquiry, an institute of district police officers, police children's rooms, etc. In cities, this police is also entrusted with security. traffic.
The functions of the long-liquidated traffic police are divided between regional police (on roads outside settlements), municipal police and civil traffic service, responsible for monitoring the technical condition of cars, issuing licenses and methodological support traffic organization.
Internal troops The Ministry of Internal Affairs has been transformed into the National Guard: they report directly to the President of the Russian Federation. The tasks of this structure are: ensuring an emergency situation; suppression (prevention) of large-scale terrorist acts; suppression (suppression) of the activities of large illegal armed groups; protection of strategic facilities (if they are not within the jurisdiction of the Armed Forces).
Military ranks are retained only in the National Guard and power protection units (such as OMON or SOBR), which exist in all law enforcement services. In other structures, there are special titles - the hierarchy of titles has become shorter and does not dominate the meritocratically built management structure.
The Federal Financial Police Service (FSFP) is engaged in the fight against economic crimes with its divisions throughout the country; it works closely with the Federal Criminal Police Service. The main tasks of the FSFP are to combat economic crimes and corruption, incl. in police and militia services.
The Federal Migration Service is completely an independent body, subordinate to the Government of the Russian Federation.
The Federal Drug Control Service is retained along with its area of responsibility.
The prosecutor's office oversees the legality of the activities of all police agencies and intelligence services, as well as in the penal system. The prosecutor's office retained the right to initiate criminal cases with subsequent transfer for investigation according to their affiliation, and the function of drawing up indictments and maintaining charges on behalf of the state in court. Prosecutors long ago abandoned uniforms, but retained the system of special ranks.
The recreated Federal Border Service (FBS), to its traditional tasks of protecting the State Border, added the task of ensuring (mainly security) activities of the Federal Customs Service at border checkpoints. Employees of the federal counterintelligence service are assigned to the FPS agencies.
The Federal Customs Service has ceased to be a law enforcement agency. Their employees only draw up reports of offenses and submit them to the financial police.
The Military Police operates under the Ministry of Defense. The purpose of its activities is the prevention, detection, suppression and investigation of offenses (administrative and criminal) committed by military personnel. IN Military Police There is a system of military ranks and there are force protection units.
The Federal Security Service has been abolished. The Federal Counterintelligence Service (FSK) has been recreated with competence corresponding to this name. In addition to identifying and suppressing the actual intelligence activities of foreign intelligence services (in the military, scientific, economic fields), the FSK ensures information security, including the preservation of state secrets. FSK is not a police agency, but a special service, since the dominant type of its activity is not procedural, but operational investigative, incl. agent The FSK does not have military ranks, but has its own gradation of special ranks. As soon as the functions of the FSK were limited, the need for territorial formations down to each region of the country disappeared. FSK provides counterintelligence cover for specific objects from which certain secret information may “leak.”
The Federal Service for the Protection of the Constitution (FSOC) was created. It is responsible for preventing and suppressing terrorist acts; preventing and responding to threats of separatism; identifying and combating illegal armed groups.
However, the main subject of countering large-scale terrorist acts (including the release of hostages) is National Guard(or her special units). Military ranks remained only in the FSOC special forces. The remaining employees have special titles.
The Security Service of the President of the Russian Federation (SBP) was removed from the Federal Security Service (FSO). Its current functions and powers are maintained. In the Federal Security Service itself, the function of protecting witnesses and victims, as well as judges and officials of regulatory authorities, appears. Accordingly, the staff of the FSO is expanding. An order for the protection of specific persons (terms, conditions of protection, etc.) is given by the relevant prosecutor.
For civilian control over the activities of the police and special services, an independent government agency- The Civil Investigation Committee, which, at the request of citizens, investigates the actions of law enforcement agencies if there is suspicion of their illegality.
When studying problems and organizing national security, its structural classification becomes important. Of course, any classification is quite conditional, and each of them is built with specific goals and objectives.
Currently, for the first time, in accordance with the 1992 Law of the Russian Federation “On Security,” national security is divided depending on the location of the source of danger into two types - internal and external security (Diagram 3). This division is based on the territorial boundaries between states. Now, in the context of globalization and internationalization of all aspects of public life, the line between internal and external security is very blurred, and many threats - international terrorism, drug trafficking, environmental and natural disasters - are sometimes difficult to link to any single source. Nevertheless, such a division seems to be very useful from a practical point of view, since, first of all, it allows one to clearly classify certain conceptual approaches to solving problems of ensuring national security. In addition, the division into internal and external security is also necessary to understand that ensuring internal security requires completely different methods, forms and methods than ensuring external security.
Scheme 3. Types of national security depending on the location of the source of danger
The main directions of ensuring Russia's internal security now are solving the following tasks: taking all possible measures to get Russia out of the crisis, which is crucial for its revival as a world power;
successful implementation of market reforms; reducing the severity of social contradictions; ensuring the protection of Russian spiritual, intellectual and cultural values; strengthening defense capabilities; formation of a democratic legal federal state; preventing the aggravation of social and political confrontation, which creates the danger of political crises that could escalate into military conflicts; achieving public harmony, a healthy socio-psychological and moral climate in society; reliable protection of life, health, property, human rights and freedoms, creation of decent conditions for his existence, as well as conditions for the existence and development of the family as a unit of civil society and its state support; increasing the efficiency and level of education in Russia.
The Russian state is distinguished by its vast territory. Hence, an important direction of internal security policy, ensuring sustainable democratic development of Russia, is a balanced regional policy, an optimal balance of interests of the center and regions, republics and regions located in different natural, climatic, socio-economic and ethnopolitical conditions.
From this point of view, a particular threat to stability in the country is the large gap in the standard of living of individual regions of the country; many regions practically exist only due to subsidies from the federal government.
The number of autonomies within Russia has increased - from 22 to 31, and their relative area has also increased - from 28% (relative to the current territory of Russia) to 53%. At the same time, more than 50% of administrative boundaries within Russia do not have a solid legal basis. This is also a factor of potential destabilization of the situation in the country.
And yet, the real threat not only to Russia’s vital interests in certain regions and spheres of economics and politics, but also to its very existence is posed by regional rather than national-territorial separatism.
The adoption by the subjects of the Federation of normative legal acts and decisions that contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal legislation is one of the most dangerous factors eroding the country’s unified legal space.
Violation of the principle of the supremacy of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal laws in the constitutional, statutory law-making of the subjects of the Federation is expressed in the unilateral assignment of the right to suspend the validity of federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, if they to some extent do not comply with the Constitution of Russia, the charter, laws of the subjects of the Federation or the legal interests of the subjects of the Federation. From the standpoint of ensuring national security, one cannot ignore attempts to adopt regulations in areas within the exclusive competence of the Russian Federation, in particular in the area of establishing the state border, ensuring the integrity of Russian territory, etc.
A characteristic violation is the desire of individual republics to secure for themselves such rights as declaring martial law; making decisions on issues of war and peace; consent to the deployment of military formations on its territory; regulation of foreign policy issues and international treaties.
In a number of subjects of the Federation, laws on security were adopted, which contain provisions that contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the legislation of Russia, even ministries for security issues were created, which is a direct violation of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On Bodies of the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation”, not allowing their double subordination. The regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the federation contain provisions on the appointment and dismissal of heads of territorial security agencies, which also violates the principles and legal norms governing personnel issues in the system of bodies of the Federal Security Service, the Prosecutor General's Office, etc.
To create and improve federalism and strengthen the country's national security, it is necessary to ensure the preservation of state sovereignty as a single and indivisible throughout Russia, suppression of the process of confederalization, transition from the current spontaneous desovereignization of the Russian state to a thoughtful, consistent, balanced decentralization of the powers and functions of government bodies within the framework of constitutional and legal space.
All these circumstances explain the special importance of the internal component in ensuring Russia’s national security at the present time.
Russia's approach to external security problems is characterized by the understanding that in the conditions of the modern nuclear era it is unacceptable and impossible to ensure its own security by reducing the level of security of other countries.
Any security concept is developed in accordance with specific historical conditions. Previously, each state relied mainly on its own to prevent and reduce the severity of emerging threats. Currently, many external security problems cannot be solved alone, which is why it is objectively necessary to unite the efforts of all states of the world. The world of endeavor is so integrated that it is impossible to reduce external security to national borders. Therefore, the only reasonable way to ensure external security is to achieve a certain balance of one’s interests and the interests of other countries, a certain compromise within the framework of international security.
International security- this is the security of the system of international relations from the threat of destabilization, confrontation, armed conflicts and wars.
Unfortunately, our legislation in the field of national security, which affects almost all spheres of public relations, almost completely ignores the problems associated with the federal structure of the Russian state. Regional and local aspects of ensuring internal security, not to mention external, are not even identified and are not reflected in the main legal acts and regulations.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” of 1992 only states that the legislative framework for ensuring security also includes constitutions, laws, other regulatory acts of the republics within the Russian Federation and regulatory acts of state authorities and administration of territories, regions, autonomous regions and autonomous districts , adopted within their competence in this area (Article 6). But the limits of this competence are not indicated. And in the Concept of National Security of the Russian Federation (as amended in 2000), which presents a system of views on ensuring the security of the individual, society and state in the Russian Federation from internal and external threats in all spheres of life, regional aspects are bypassed.
Russian society has historically developed on a heterogeneous basis. The vast territory of the country, the multitude of peoples inhabiting it, cultural traditions, various religious denominations, unequal psychological make-up, peculiarities of labor, everyday life, cultural, etc. factors largely determine the interests of regional communities.
Accordingly, the different content and specific features of regional interests across the country’s territory also affect the nature of activities to ensure the security of the region. As a result, the stability of the situation and the security of the regions determine the level of national security as a whole.
In this regard, it is advisable to divide internal security into two types: internal federal and internal regional security (Diagram 4).
![]()
Diagram 4. Structure of internal security in territorial terms
Homeland Security is the protection of federal interests from internal threats, and internal regional security is the protection of regional interests from internal and external threats. The structure of federal and regional interests has much in common. First of all, this is the unity of security objects (individual, community, society, state), as well as the functional qualities of the interests of these objects.
Nevertheless, there are many fundamental differences in the structure of federal and regional interests, which serves as the initial basis for their separation. Among federal interests, the interests of the state and society as a whole dominate, and regional interests - the interests of the individual and community.
When studying the problems of regional security, the most important methodological importance is to resolve the question of what is meant by the category “region”. It should be noted that our country has not yet developed a single generally accepted clear and unambiguous definition of this concept.
Regional security means the protection of the interests of a constituent entity of the Federation from internal and external threats. External threats are those whose sources are located outside the boundaries of a given subject of the Federation.
This circumstance further emphasizes that internal regional security must be ensured by the forces and means of the subject of the Federation in close cooperation and with the support of the corresponding forces and means of the federal center and other subjects of the Federation where the sources of threats are located.
International security is divided into global, or universal, regional and collective (Diagram 5).
 |
Scheme 5. Classification of types of international security
Global Security- this is the protection of the system of relationships of the entire world community from the threat of destabilization of the situation, crises, armed conflicts and wars.
Regional security- this is the protection of the system of relations between states of a particular region of the world from threats of destabilization of the situation, crises, armed conflicts and wars of a regional scale.
Collective Security- this is the protection of the interests of a group (union) of states from external threats, guaranteed by mutual assistance, cooperation in the military sphere and collective actions to prevent and repel aggression.
International security is based on compliance by all states with generally recognized principles and norms of international law, which exclude the resolution of controversial issues and disagreements between them by force or the threat of force.
The most important principles of international security are the principle of equality and equal security, as well as the principle of not harming anyone's security in relations between states.
In addition to distinguishing the two types indicated above in the structure of national security - internal and external security - its classification by type of security is important, which contributes to the development of more specific policies and strategies for ensuring national security.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” provides for the division of national security into the following types: state, economic, public, defense, information, environmental and others (Article 13). However, the legislator did not provide a strict interpretation of the principles of classification by type of security, nor a definition of these concepts, which in practice led to real chaos in a completely unjustified fragmentation of the generic concept. In literature and in the media you can find federal, constitutional, genetic, planetary, etc.
Any classification should be based on some of the most essential common features. Among them, first of all, it is necessary to highlight security objects, the nature of threats, and areas of life.
Scheme 7. Classification of types of national security by spheres of life
Depending on the nature of the threats, their source, and specifics, we can distinguish such types of security as security from natural threats, security from anthropogenic threats, security from social threats, which in turn can be divided into smaller types of security from specific threats ( diagram 7).
At the same time, security from one or another type of threat is understood as the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and state from threats of this type.
In human society, the vital interests of all security objects are exposed to a wide variety of threats, therefore, the division of types of security into spheres or areas of life in which these threats manifest themselves is of particular practical importance. It is by this principle that vital interests, threats and directions for ensuring national security are classified in the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation. Most generally, such a classification can be limited to identifying six types of security, which can be divided into smaller types of security for specific areas of life (Diagram 8).

Scheme 8. Classification of types of national security by spheres of life
In this case, one or another type of security is understood as the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the specified sphere of life from internal and external threats.
So, military security- this is the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the defense sector from internal and external threats.
Respectively economic security- this is the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state in the economic sphere from internal and external threats.
Other concepts are defined in a similar way. It should be borne in mind that in this classification it seems unlawful to single out a special type of “state security”, since the state is organically present in all spheres of life and it is impossible to limit state activity to one area.
This classification, when considering problems of internal security, is of a country-wide nature and represents the structure of internal federal security.
The structure of regional security, depending on the specifics of a particular region, may have a different classification according to spheres of life.
Such an approach streamlines the classification of types of security, makes it possible to avoid the current confusion of classification principles and allows us to consider national security as a unified system of types of security, each of which is an independent subsystem with its own characteristic features. Practice shows that all these subsystems are closely interconnected and are in dialectical interaction. In practical activities to ensure national security, not a single type of national security should be consigned to oblivion, as happened, unfortunately, in the recent past, when the Soviet Union collapsed at the peak of its military power, achieved at the expense of economic and social security. Of course, at each stage of historical development, the priorities of certain types of security objectively change, and therefore the most important task of ensuring national security is to achieve a certain rational parity between different types of security in each time period.
Questions for self-control
1. What are the grounds for dividing national security into two types - internal and external?
2. What is international security?
3. What is the classification of national security by sphere of life?
4. Why is it necessary to classify internal security at a territorial level?
Literature
1. Law of the Russian Federation “On Security” // Gazette of the Congress of People's Deputies and the Supreme Council of the Russian Federation. 1992. No. 15. Art. 769.
2. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation. M., 2000.
3. Problems of internal security of Russia in the 21st century. M., 2001.
interferes with the achievement of certain humanly desirable goals.
The solution to the problem of life safety is to ensure comfortable conditions for human habitation, to protect people from exposure to harmful factors environment exceeding normatively permissible levels.
Maintenance optimal conditions human activity and recreation creates the prerequisites for high performance and productivity!
Ensuring safety at work and rest helps preserve the life and health of people by reducing injuries and morbidity. Therefore, the object of studying human life safety is a complex of negatively impacting phenomena and processes in the “Man – Environment” system.
The fundamental formula for human life safety is warning of any potential danger.
On December 28, 2010, Federal Law of the Russian Federation N 390-FZ “On Security” was adopted. It determines the basic principles and content of the activities of citizens of our country to ensure the security of the state, public safety, environmental safety, personal safety, other types of security provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the powers and functions of all government bodies in the field of security, as well as the status of the Security Council of the Russian Federation.
1.2.2. Types, directions, methods, ways and means of ensuring the safety of human life
The following types of security exist: National security; environmental Safety; Industrial Safety; Fire safety;

officially accepted views on the goals and state strategy in the field of ensuring the security of individuals, society and the state from external and internal threats of a political, economic, social, military, man-made, environmental, informational and other nature, taking into account available resources and capabilities.
Ensuring national security is a set of political, military, economic, social, health and legal measures aimed at ensuring normal existence and eliminating possible threats to the individual, society and the state.
Ensuring national security includes: protection of the state system; protection of the social order;
ensuring the territorial integrity and sovereignty of the state;
ensuring the political and economic independence of the nation; ensuring the health of the nation; public order protection; crime control;
ensuring safety in emergency situations.
To ensure national security, special bodies are created in the state.
Bodies ensuring national security:
1. armed forces;
2. intelligence and counterintelligence services;
3. law enforcement agencies;
4. sanitary-epidemiological service.
Environmental safety is prevention existing threat significant deterioration of biosphere factors, species composition of flora and fauna, as well as the danger of depletion of non-renewable natural resources as a result of human activity.
This is also the process of ensuring the protection of the vital interests of the individual, society, state and all humanity from real or potential threats created by anthropogenic or technogenic human impact on the environment.
Industrial safety is the state of protection of the vital interests of the individual and society
And states from emergency situations at hazardous production facilities and their consequences.
This is achieved through labor protection, improving working conditions, mechanization and robotization of production, and increasing the professionalism of workers.
The main goal of labor protection– is to preserve the life and health of workers.
Emergency situations are quite possible that do not cause harm to the life and health of workers, and, conversely, harm to the life and health of workers can be caused without emergency situations. This can happen, for example, if sanitary and hygienic requirements for the production process are violated.
Fire safety - this is the state of the object,
characterized by the ability to prevent the occurrence
And the development of a fire, as well as the impact on people and property of dangerous fire factors.
The fire safety of the facility must be ensured by fire prevention and fire protection systems, including organizational and technical measures.
Information Security - This is the state of security of the information environment.
Information protection is an activity to prevent leakage of protected information, unauthorized and unintentional impacts on protected information. The purpose of implementing information
security of any object is the construction of a system for ensuring the information security of this object.
Economic security is the state of any
of an economic entity, characterized by the presence stable income, which allow us to maintain an acceptable standard of living at the moment and in the foreseeable future.
It includes:
maintaining solvency; the ability to plan future cash income;
job security.
Economic security of the state is a state of production in a country in which the process of sustainable economic development and socio-economic the stability of society is ensured almost regardless of the presence and effect of external factors.
Military security is the protection of individuals, society and the state from military threats.
This is also a state when the possibility of war is reduced to a minimum, due to the lack of motives for the use of military force, as well as the implementation of measures to prevent military danger.
Military security has external and internal aspects:
External aspects- reflect the ability to restrain military force from the outside;
Internal aspects- cover a system of measures to create and maintain the readiness of individuals, society and the state to prevent military threats by creating military organization to carry out mobilization preparation of the economy and population of the country.
Internal security is security within the country.
In Russia there is corruption, bribery, banditry, hooliganism in different forms, drug addiction, prostitution, theft, great amount various offenses with
side of the population. Something appeared that did not exist before - mass unrest, unauthorized demonstrations and rallies. All this significantly destabilizes the situation in the country and increases the degree of dissatisfaction of the population with this state of affairs.
External security- this is the absence of dangers emanating from threats outside the state, aimed at its destabilization, loss of sovereignty and even its destruction.
It comes from political, economic, social situations in other countries.
The main external danger today is international terrorism.
Many terrorist groups have appeared in the world, of different types, names, purposes, directions and religions. There are terrorist groups in Russia too. A big concern for Russia is the deployment of NATO missiles and bases near the borders with Russia. An important issue for Russia is weak defense state borders, especially in the Far East. Russia is a huge, rich country, and many dream of breaking up Russia and getting its wealth. Russia's external security also depends on other factors occurring in the world, such as wars, natural disasters, possibly cosmic factors and threats. Russia must be ready at any time to defend itself against an external threat and, if possible, to help other countries defend themselves when they ask for help.
Areas of activity to ensure human life safety are elementary components of this process
Directions for human life safety allow you to find optimal solutions protection against hazards based on comparative analysis competing options. They reflect the variety of ways and methods of ensuring safety in the “human environment” system, including both purely organizational measures, specific technical solutions, and ensuring adequate management that guarantees the stability of the system, as well as
some methodological provisions indicating the direction of searching for solutions.
Directions for human life safety can be applied in various areas in:
technology; medicine; labor organization; rest.
By area of implementation, i.e. Depending on where they are applied, life safety areas can be divided into:
engineering and technical; methodological; medical and biological.
Based on implementation, i.e. Based on how they are implemented, areas of human life safety are divided into the following groups:
orienting, i.e. giving a general direction for the search for solutions in the field of security. The guiding directions include -
directions of the systematic approach, professional selection, rationing negative impacts and so on.;
managerial, these include - areas of control, stimulation of activities aimed at improving safety, areas of responsibility, feedback and etc.;
organizational,These include- time protection,
when the time during which exposure to a person is allowed is regulated negative factors, direction rational organization labor, rational regimes works, organization of sanitary protection zones, etc.;
technical, this group of areas involves the use of specific technical solutions to improve safety.
Security areas must be considered in interrelation, i.e., as elements that complement each other.
Security methods.
A method is a way to achieve a goal, based on knowledge of the most general laws.
Security methods:
preventing an attack (distance gap,
deviations, camouflage, conclusion of a non-aggression pact);
increasing resistance to destructive influences (development and strengthening of immunity);
creation of a protection system; creation of a consequences mitigation system
destructive influences; destruction (or isolation) of threat sources.
Ways to ensure safety.
Any animal reacts to a threat to its life with protective actions. Man's actions, thanks to his mind, differ from the instinctive actions of animals.
A man is looking for ways to protect himself from dangers: anticipation of developments; assessing the consequences of your actions; analysis of the causes of hazards;
choosing the most effective option actions. A person not only intelligently defends himself in an already established
situations, but also, anticipating dangers, tries to avoid them. Having established the causes of dangers, through its activities it transforms the environment in order to eliminate these causes.
It is transformative activity that allows a person to fully use the mind to increase his security.
Security features are special devices, the use of which prevents or reduces the impact of hazardous and harmful environmental factors on workers.
Human safety equipment: collective; individual.
If we take the technosphere, the role of automatic safety equipment is currently increasing, for example, for preventing fires, monitoring water quality, then these are collective means of ensuring safety. The use of durable cabins, goggles, masks, helmets, etc. is an individual means of ensuring safety.
1.3.Legal basis ensuring human life safety
1.3.1. Legal basis for ensuring the safety of human life in the Russian Federation
The legal basis for ensuring the safety of human life consists of the relevant laws and regulations adopted by authorities at all levels of the Russian Federation (until 1992, RSFSR) and its member republics, as well as by-laws:
Constitution of the Russian Federation; federal laws; presidential decrees;
resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation
local government regulations; decisions of specially authorized bodies.
Among the latter, we should highlight first of all: Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation; State Committee Russian Federation for environmental protection; Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation;
Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation; Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense Affairs,
emergency situations and consequences management
natural disasters (MES) and their territorial
documents in the field of human life safety are state, industry and enterprise standards, rules and regulations, which contain various requirements for labor safety, environmental safety, etc.
Legal issues of environmental management are regulated as Constitution of the Russian Federation (Articles 9, 36, 42, 58, 72), and near the federation
ral laws, among them: Civil, Land and Water Codes of the Russian Federation, laws: “On fauna”, “On environmental protection” etc., relevant regulations of the President and Government of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local governments.
The legal basis for environmental protection in the country and ensuring necessary conditions labor is
Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population” dated March 30, 1999 No. 52 (with
subsequent editions). This Federal Law is aimed at ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population as one of the main conditions for the implementation of the constitutional rights of citizens to health protection and a favorable environment.
December 30, 2001 introduced in our country The federal law " Labor Code Russian Federation" N 197-FZ.On establishes guarantees for the implementation of workers' rights to labor protection and ensures a unified procedure for regulating relations in the field of labor protection between employers and employees at enterprises, institutions and organizations of all forms of ownership. This document is aimed at creating working conditions that meet the requirements of preserving the life and health of workers in the process labor activity and in connection
with her.
IN Currently, the Russian Federation has also adopted federal laws:
“On the protection of the population and territories from emergency situations”
situations of natural and man-made nature", "About fire safety", "On radiation safety of the population", "On the use of atomic energy". The procedure for dealing with emergency situations is also reflected in in Art. 56 and
88 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
A number of federal target programs have been developed,
aimed at preventing and preparing for liquidation of the consequences of emergency situations. The fundamental feature of the created protection of the population is to concentrate efforts on preventing their occurrence and development, reducing the amount of damage and losses, and eliminating the consequences.
In addition to those listed above, legislative documents in the field of human life safety are
state, industry and enterprise standards, rules and regulations, which contain various requirements for labor safety, environmental safety, etc.
State standards cover broad issues of human activity and are fundamental regulatory documents in the indicated areas.
Based state standards are being developed
industry and enterprise standards,
taking into account industry and local conditions, as well as specific production conditions and technologies.
Uniform rules that contain requirements for ensuring labor safety during the design, construction and operation of industrial facilities,
are “Building Norms and Rules” (SNiP) , as well as various sanitary norms and rules (SN, SanPiN).
Another group of normative and technical documentation consists of various Rules, Regulations and Instructions.
These documents are developed and approved by ministries, departments, and State Supervision bodies.
For violation of all types of legislation on human life safety, the following liability is provided::
Disciplinary, which is imposed on the violator by a higher administrative person (remark,





