State bodies of control over labor protection. State supervision and control of labor safety
State management of labor protection is carried out by the Government of the Russian Federation directly or on its behalf by the federal executive body for labor, etc. federal authorities executive power.
The federal executive authorities, which have been granted the right to exercise certain functions of normative legal regulation, special permitting, supervisory and control functions in the field of labor protection, are obliged to coordinate their decisions in the field of labor protection, as well as coordinate their activities with the federal executive body for labor.
In accordance with the Federal Law "On the Fundamentals of Labor Protection in the Russian Federation", labor protection is managed by the executive and legislative authorities and the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
The local administration, in accordance with the Federal Law "On Local Self-Government in the Russian Federation", ensures compliance with sanitary standards and hygiene standards in the territory of their districts, incl. and at production facilities.
The most important body for managing labor safety is the labor protection service of the enterprise, which monitors compliance with safety requirements determined by legislative and regulatory legal acts, and organizes work to improve conditions and labor protection at the enterprise.
In organizations, at the initiative of the employer and (or) employees, committees (commissions) on labor protection are created, which include representatives of the employer, trade unions or other representative body authorized by employees, and which organizes joint actions of the employer and employees to ensure labor protection requirements, prevent production injury and occupational diseases, conducting inspections of conditions and labor protection at workplaces and informing the employee about the results of these inspections, collecting proposals for labor protection.
Supervision and control over compliance with legislative and regulatory legal acts is carried out through state supervision and departmental control.
Federal Labor Inspectorate (Rostrudinspektsiya) under the Ministry of Labor of Russia - the main body of state supervision and control. She is subordinate to the state labor inspectorates of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and interregional inspectorates. It supervises and controls compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection, regulatory legal acts on compensation for harm caused to the health of an employee, on social insurance and the implementation of collective agreements at enterprises, regardless of ownership.
Federal Mining and Industrial Supervision of Russia (Gosgortekhnadzor) supervises and controls the correct design and safe operation of lifting mechanisms, pressure vessels and safe work in the development of minerals.
State sanitary and epidemiological supervision of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (Gossanepidnadzor) supervises the compliance of enterprises with hygienic and sanitary norms and rules.
State Energy Supervision of Russia (Gosenergonadzor) supervises the correct arrangement and safety of operation of electrical and heat-using installations.
Federal Supervision of Russia for Nuclear and Radiation Safety (Atomnadzor) supervises compliance with the rules for the operation of installations - sources of ionizing radiation.
Fire supervision of Russia (Rospozhnadzor) supervises compliance with fire safety requirements and the implementation of fire prevention measures.
State examination of working conditions of the Russian Federation works in cooperation with the above supervisory authorities and exercises control over dangerous and harmful types of work, determines the list of industries, jobs, professions, positions for which preferential pensions are established, additional holidays, benefits and compensations are provided, provides organizational and methodological guidance for the certification of workplaces working conditions and control over its results, certification of production facilities for compliance with labor protection requirements.
departmental control Occupational safety is maintained by labor protection services of ministries and departments. At enterprises, it is carried out by the labor protection service of the enterprise, and in its absence (with a small number of employees) - labor protection engineers or persons who, by order, are entrusted with the performance of these duties, as well as heads of departments and sections.
public control Trade unions are responsible for the observance of labor legislation and labor protection.
Types of control of working conditions and labor protection can be
complex.
selective,
solid,
attestation,
planned,
unscheduled,
Unscheduled checks carried out by the labor protection service in connection with various failures, accidents, incidents.
Target checks carried out on the scale of the entire production, as a result, production equipment or means of collective protection (ventilation, lighting) are controlled.
Comprehensive checks are carried out on the scale of a separate production site, while all types of equipment, technological processes, means of individual and collective protection and the condition of building structures are controlled for compliance with safety requirements.
Based on the results of the monitoring of working conditions and labor protection, including inspections by the relevant supervisory and control bodies, work is being planned to improve them. Plans may be
promising - associated with the implementation of major plans, the implementation of which is designed for several years,
current - compiled for a year,
operational - aimed at eliminating the consequences different kind accidents
Evaluation of working conditions and labor protection at the enterprise allows you to determine the priority areas of work to improve them. Criteria of the following type are used as integral indicators of this kind of assessment:
labor protection coefficient
K from \u003d (K cn + K b + K vpr) / 3
where K cn is the coefficient of the level of compliance with the rules of labor protection of workers,
K b - equipment safety factor,
К vpr - coefficient of performance of planned work on labor protection
coefficient of the level of compliance with labor protection rules by workers
K cn \u003d (number of employees in compliance with the rules) / total number of employees
equipment safety factor

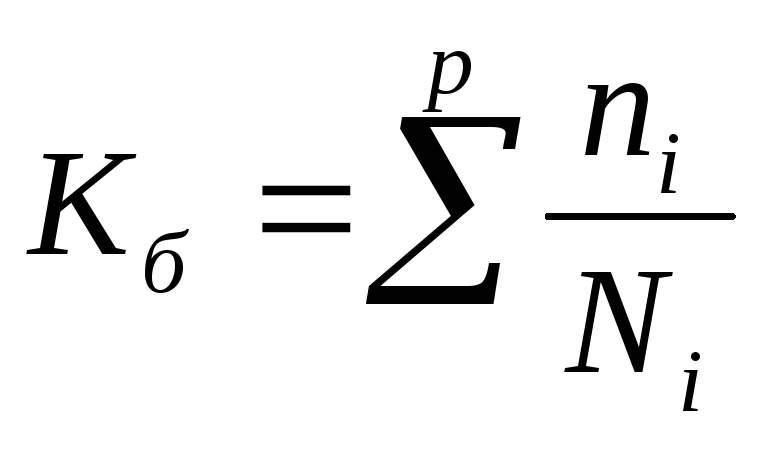
where n i is the number of safety requirements to be fulfilled,
N i is the total number of regulatory requirements,
p is the number of types of equipment in the workshop.
coefficient of performance of planned work on labor protection K vpr
is determined by the ratio of the number of actually completed and planned activities for a given month for all types of plans, instructions, orders
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Hosted at http://www.allbest.ru
Introduction
The study and solution of problems associated with ensuring healthy and safe conditions in which human labor takes place is one of the most important tasks in the development of new technologies and production systems. Exploring and revealing possible causes industrial accidents, occupational diseases, accidents, explosions, fires, and the development of measures and requirements aimed at eliminating these causes make it possible to create safe and favorable conditions for human labor. Comfortable and safe conditions labor is one of the main factors affecting the productivity and safety of work, the health of workers.
Labor protection is a system of legislative acts, socio-economic, organizational, technical and medical - preventive measures and means ensuring safety, preservation of human health and performance in the process of work.
The legal field for management, supervision and control over safety and labor protection is formed by a diverse and developed system of legislative and regulatory legal acts that regulate various issues and aspects of a complex and complex problem ensuring working conditions and safety. To implement the legislative and regulatory requirements, a labor protection management system (OSMS) has been created, each of the elements and bodies of which has its own functions, responsibilities and scope of activity, its order and procedure.
According to the legal level, documents regulating labor safety issues can be divided into legislative acts, regulatory legal acts and other regulations on labor protection of federal legislative and executive authorities Russian Federation, as well as its subjects.
At present, control over the state of labor protection at enterprises is being strengthened. Regulatory legal documents direct management, control and supervision by the state over the state of conditions and organization of labor protection is legally established.
The legal basis for state administration, control and supervision of compliance with the requirements of labor protection and industrial safety are:
1. In the field of labor protection - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
2. In the field of industrial safety - the federal law“On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities” dated July 21, 1997 No. 116, defining public administration industrial safety and state control and supervision over the implementation of industrial safety requirements.
The state management of labor protection consists in the implementation of the main directions of the state policy in the field of labor protection, the development of laws and other regulatory legal acts in this area, as well as requirements for the means of production, technologies and labor organization that guarantee workers health and safe working conditions.
The state management of industrial safety consists in the implementation of the main directions of the state policy in the field of industrial safety, the development of laws and other regulatory legal acts in this area, as well as industrial safety requirements for hazardous production facilities.
State control and supervision is the implementation of actions to control and supervise the execution by state authorities, local governments, their officials, legal entities and citizens of the current legislation.
1. Bodies of state control and supervision of labor protection and industrial safety
1.1 The structure of federal bodies for the management of labor protection, control and supervision of labor protection and industrial safety
In the field of labor protection and industrial safety, the powers between the control and supervisory authorities of the Russian Federation are distributed as follows:
State management of labor protection and industrial safety is carried out by the Government of the Russian Federation directly or on behalf of the federal executive body;
Control and supervision over compliance with labor protection requirements is carried out by the Federal Labor Inspectorate (Rostrudinspektsiya), which is part of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment (Rostrud);
Control and supervision in the healthcare sector is carried out by the Federal Service for Supervision of Healthcare and Social Development (Roszdravnadzor);
Sanitary and epidemiological supervision is carried out by the Federal Service for Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare (Rospotrebnadzor) supervises compliance by enterprises, organizations and institutions with hygienic and sanitary norms and rules. These services (including the Federal Service for Labor and Employment) are part of the Federal Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Health and Social Development);
Management, control and supervision over compliance with industrial safety requirements is carried out by the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision (Rostekhnadzor), which merged the former Gosgortekhnadzor. Supervising and monitoring the correctness of the device and safe operation lifting mechanisms, pressure vessels, as well as the safe conduct of work in the development of minerals, Energonadzor, which oversees the correct design and safety of operation of electrical and heat-using installations. Nuclear Supervision, which supervises compliance with the rules for the operation of installations that are sources of ionizing radiation and environmental control;
Control and supervision of fire safety is carried out by the Fire Service, which is part of the Federal Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergency Situations and Elimination of Consequences of Natural Disasters (MES);
Control and supervision of transport safety is carried out by the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Transport, which is part of the Federal Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation (GIBDD).
Permanent corporate (industrial) monitoring of compliance with the requirements of labor protection and industrial safety in the organization is carried out by:
1. Service (department) of labor protection of the organization;
2. Production control service (PC) of the organization.
The main legislative acts regulating labor protection in the Russian Federation are:
the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
Federal Law "On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities" No. 116-1997;
Federal Law "On Compulsory Social Insurance against Industrial Accidents and Occupational Diseases" No. 125-1998;
Federal Law "On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population" No. 52-1999, etc.;
Labor Code Russian Federation (Code). The Code has found a significant reflection of the issues of labor protection. It states that every employee has the right to working conditions that meet the requirements of safety and hygiene, to mandatory social insurance, for compensation for damage caused to the employee in connection with the performance of labor duties, and a number of others. Special section X “Labor protection” is devoted to labor protection issues, in which the following are legally defined:
* obligations of the employer and employee to ensure safe working conditions;
* medical examinations certain categories of workers (working at transport enterprises, Food Industry, trade, etc. affected by OVPF);
* the need for compliance of production facilities and products with labor protection requirements;
* the rights of workers to labor protection and guarantees of such a right;
* the obligation of employees, including managers, to be trained and tested on labor protection;
* industrial accidents subject to investigation, the employer's obligations in case of an accident, the procedure for investigating accidents, processing investigation materials and considering disagreements on investigation materials.
According to the generality and effect, legislative and regulatory legal acts are divided into five levels.
1. Uniform acts in force throughout Russia for all enterprises, organizations, institutions and establishing the basic principles and rules of the state in the field of labor protection. These include federal laws, decrees of the President, resolutions of the Government and federal ministries and departments. Such acts are approved by the State Duma, the President, the Government, federal ministries and departments (for example, the Ministry of Labor and Social Development).
2. Intersectoral acts in force in all sectors of the economy without exception. These include, for example, labor safety standards, sanitary norms and rules for working with certain hazardous and harmful production factors, hygiene standards, etc. Such regulations are developed and approved only by specially authorized federal bodies.
3. Acts of the subjects of the Federation that are valid only on the territory of the subject and regulate certain issues of labor protection in relation to the subject. They are developed and approved by the legislative and executive bodies of the subjects of the Federation.
4. Sectoral acts that are valid only in a particular industry (metallurgical, chemical, textile) and have no legal force in other industries. They are developed and approved by sectoral ministries and departments or other authorized bodies (for example, Gosgortekhnadzor, Gossanepidnadzor, etc.) in relation to a particular industry.
5. Normative legal acts of the enterprise, which are documents on labor protection that are valid only at a particular enterprise (orders, decisions, instructions).
Legislative and regulatory legal acts more low level should not be contrary to the acts of more high level. Thus, sectoral acts should not contradict intersectoral ones, regional ones - single and intersectoral ones, enterprises - sectoral ones.
1.2 Occupational safety management, supervision and control of labor protection
State management of labor protection is carried out by the Government of the Russian Federation directly or on its behalf by the federal executive body for labor and other federal executive bodies. The distribution of powers in the field of labor protection between federal executive bodies is carried out by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The federal executive authorities, which have been granted the right to exercise certain functions of normative legal regulation, special permitting, supervisory and control functions in the field of labor protection, are obliged to coordinate their decisions in the field of labor protection, as well as coordinate their activities with the federal executive body for labor.
Occupational safety management is carried out by the governing bodies of several levels: federal, regional, municipal, enterprises.
The local administration, in accordance with the Federal Law "On Local Self-Government in the Russian Federation", ensures compliance with sanitary regulations, norms and hygienic standards in the territory of their districts, including at production facilities.
The most important body for managing labor safety is the labor protection service of the enterprise, which monitors compliance with safety requirements determined by legislative and regulatory legal acts, and organizes work to improve conditions and labor protection at the enterprise.
In organizations, at the initiative of the employer and (or) employees, committees (commissions) for labor protection are created. Their composition on a parity basis includes: a labor protection specialist, a representative of the employer, trade unions or other representative body authorized by employees. The model regulation on the committee (commission) for labor protection is approved by the federal executive body for labor. The labor protection committee (commission) organizes joint actions of the employer and employees to ensure labor protection requirements, prevent industrial injuries and occupational diseases, conduct inspections of labor conditions and labor protection at workplaces and inform employees about the results of these inspections, collect proposals for labor protection.
The most important function of the occupational safety management system is supervision and control over compliance with legislative and regulatory legal acts. Supervision and control over labor protection is carried out through state supervision and departmental control.
The Federal Labor Inspectorate (Rostrudinspektsiya) under the Ministry of Health and Social Development is the main body of state supervision and control.
The Fire Supervision of Russia (MES) oversees compliance with fire safety requirements and the implementation of fire prevention measures.
The listed supervisory bodies, as well as the Federal Labor Inspectorate, are built on a territorial basis. Representatives said bodies they have a right:
* unhindered access to subordinate facilities;
* to receive from the executive authorities, local self-government and the management of enterprises, organizations and institutions all the information necessary for their work;
* issue binding orders to employers and officials: impose fines on them in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on administrative offenses;
* suspend the work of individual units and equipment if there is a threat to the life and health of workers until it is eliminated.
Departmental control over labor protection is carried out by labor protection services of ministries and departments. At enterprises, organizations and institutions, this control is carried out by the labor protection services of enterprises, and in their absence (with a small number of employees) - labor protection engineers or persons who, by order, are entrusted with the performance of these duties. In addition, this type of control is carried out by the heads of departments and sections.
Public control over the observance of labor legislation and labor protection is carried out by trade unions, in particular trade union commissions. In addition, authorized (trusted persons) of the labor collective are selected who exercise public control.
Types of control of conditions and labor protection can be selective, continuous, attestation, scheduled, unscheduled, targeted, complex.
Unscheduled inspections are carried out by the labor protection service in connection with various failures, accidents, incidents.
Target inspections are carried out, as a rule, on the scale of the entire production. During their implementation, it is controlled a certain kind production equipment or means of collective protection (for example, ventilation, lighting).
Comprehensive checks are carried out on the scale of a separate production site, while all types of equipment, technological processes, means of collective and individual protection, as well as the condition of the building structures of the premises (workshop) are controlled for compliance with safety requirements.
2. The Federal Labor Inspectorate is a body of state supervision over compliance with labor laws
2.1 Main functions and tasks of the federal labor inspectorate
The Federal Labor Inspectorate is a unified centralized system of state bodies exercising supervision and control over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing norms labor law, on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The Federal Labor Inspectorate in its activities is guided by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal laws, decrees and orders of the President of the Russian Federation, decrees and orders of the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The main task of the federal labor inspectorate is to exercise supervision and control over compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection in order to ensure the protection of the labor rights of citizens, including the right to safe working conditions.
The Federal Labor Inspectorate carries out its activities in cooperation with law enforcement agencies, with federal executive authorities that have been granted the right to exercise, within their powers, the functions of supervision and control, with state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments, associations of employers and associations of trade unions , other state and public organizations.
State supervision and control over compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection is carried out by labor inspectors and other officials of the federal labor inspectorate.
The activities of the federal labor inspectorate are managed by the chief state labor inspector of the Russian Federation, appointed to and dismissed by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Federal labor inspectorates, in accordance with the tasks assigned to them, perform the following main functions:
1) carry out state supervision and control over compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection in the relevant territory;
2) investigate accidents at work in accordance with the established procedure, analyze their causes and develop proposals for the prevention of such cases;
3) consider cases of administrative offenses in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
4) inform the relevant state authorities and local governments about the facts of violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection;
5) participate in work on legal education, dissemination of knowledge on compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection;
6) summarize the experience of applying the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor and labor protection;
7) receive citizens, consider applications, complaints and other appeals of citizens about violations of their labor rights;
8) prepare reports on the results of the activities of the federal labor inspectorate.
Unlike the previously existing Rostrudinspektsiya, federal labor inspectorates have vertical (in the system of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation), rather than horizontal subordination and do not depend in their activities on state authorities, local governments.
The main tasks of the federal labor inspectorate:
a) ensuring observance and protection of labor rights and freedoms of citizens, including their right to safe working conditions;
b) Ensuring that employers comply with labor laws;
c) providing the parties to labor relations with information about the most effective means and methods of compliance with labor laws;
d) bringing to the attention of the relevant state authorities the facts of violations, actions (inaction) or abuses that do not fall under the laws and other regulatory legal acts.
Representatives of employees in the social partnership are trade unions and (or) other representatives elected by employees.
Coordination of the activities of state supervision and control bodies and public control bodies carried out by trade unions (their associations), on issues of compliance with laws and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, is carried out by the federal labor inspectorate.
2.2 Basic powers and powers of the federal labor inspectorate
State labor inspectors (legal, labor protection) in the exercise of supervisory and control activities have the right to:
a) freely visit organizations of all organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership at any time of the day in the presence of certificates of the established form for the purpose of conducting an inspection;
b) request from employers and their representatives, executive authorities and local governments and receive free of charge from them documents, explanations, information necessary to perform supervisory and control functions;
c) seize for analysis samples of used or processed materials and substances with notification of the employer or his representative and draw up an appropriate act;
d) investigate accidents at work in the prescribed manner;
e) present employers and their representatives with binding instructions to eliminate violations of labor legislation and other normative legal acts containing labor law norms, to restore the violated rights of employees, to bring those responsible for these violations to disciplinary liability or to remove them from office;
f) suspend the work of organizations, individual production units and equipment in case of detection of violations of labor protection requirements that pose a threat to the life and health of workers, until these violations are eliminated;
g) submit to the courts, in the presence of the conclusions of the state examination of working conditions, demands for the liquidation of organizations or the termination of the activities of their structural divisions due to violation of labor protection requirements;
h) suspend from work persons who have not completed training in the prescribed manner safe methods and methods of performing work, briefing on labor protection, internships at workplaces and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements;
i) prohibit the use and production of personal and collective protective equipment for employees that do not have certificates of conformity or do not meet the requirements of labor protection;
j) issue permits for construction, reconstruction, technical re-equipment of production facilities, production and introduction of new equipment, introduction of new technologies and conclusions on the possibility of commissioning new or reconstructed production facilities;
k) attract to administrative responsibility in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation, persons guilty of violating laws and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms. If necessary, invite them to the labor inspectorate in connection with cases and materials in progress, as well as send them to law enforcement recruitment materials specified persons criminal liability, sue in court;
l) act as experts in court on claims for violation of laws and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, for compensation for harm caused to the health of workers at work.
State labor inspectors, who, in exercising their rights and performing their duties, are authorized representatives of the state and are under its protection. They are independent of state bodies, officials and are guided only by the Constitution of the Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts.
The main authority of the federal labor inspectorate is to exercise state supervision and control over compliance with labor legislation in all organizations through inspections, examinations, issuing binding orders to eliminate identified labor offenses, and bringing the perpetrators to justice in accordance with federal law. All other powers are subordinate to this master.
Control measures, including those carried out by federal labor inspectorates, may be scheduled or unscheduled.
In relation to one legal entity, each state control (supervision) body may carry out a planned control measure no more than once every two years.
An unscheduled inspection, the subject of which is control over the execution of instructions to eliminate the identified violations, is subject to the activities of a legal entity if, as a result of a planned measure to control violations of mandatory requirements, it is revealed.
Unscheduled control measures are carried out by state control (supervision) bodies also in the following cases:
Receiving information from legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, public authorities on the occurrence of emergencies, changes or violations of technological processes, as well as on the failure of structures, equipment that can directly harm the life, health of people, the environment and property of citizens, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs;
Threats to the health and life of citizens, pollution environment, damage to property, including in relation to homogeneous goods (works, services) of other legal entities and (or) individual entrepreneurs;
Appeals of citizens, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs with complaints about violations of their rights and legitimate interests by actions (inaction) of other legal entities related to their failure to comply with mandatory requirements, as well as obtaining other information supported by documents and other evidence indicating the presence of signs of such violations .
Unscheduled control measures may be carried out by a reasoned decision of the state control (supervision) body. Based on the frequency of planned control measures established by law, it seems that the period of time for which the organization is subject to verification should also be two years.
The state labor inspector may carry out control (supervision) measures only if he has the appropriate order (order). The form of this document is not officially approved, therefore, each inspection develops it independently. When entering the organization, the inspecting official is obliged to present the order, as well as his official certificate, to the head of the organization being inspected.
The order must include:
Number and date of the document;
The name of the body of the federal labor inspectorate conducting the inspection;
Surname, name, patronymic of the state labor inspector authorized to carry out control measures;
Name of the organization to be verified;
Goals, objectives, subject of the event;
Legal grounds for conducting control, including regulatory legal acts, the requirements of which are subject to verification;
Date of start and end of control activities.
State legal inspectors during the inspection request the following documents: collective agreement; employment contract. Internal labor regulations; staffing; vacation schedule; a document establishing the procedure for processing personal data of employees; work books; full liability contracts. Other documents; orders (personnel, production) and the grounds for them; book of registration of orders; book of accounting for the movement of labor books. Personal cards of employees (form No. T-2); payroll records; timesheets for the use of working time (form No. T-13); overtime log book; journal of registration of travel certificates; list of employees under the age of 18. List of pregnant workers and working women with children under the age of three, single mothers; persons caring for children with disabilities and disabled since childhood. List of disabled workers; list of workers employed in work with harmful and (or) hazardous conditions labor; information on overdue wage arrears (form No. 3-F); information about the presence / absence of debts for other payments. The list of documents is directly established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Registration of the results of the audit begins with the issuance of the act. Usually it is called like this: The act of checking compliance with labor legislation and labor protection.
The document is drawn up by an official in any case: both when it is necessary to record the identified violations, and when no flaws are noted in the company. The inspection report is drawn up in two copies - one remains with the inspector, the other is handed over to the employer (his representative) against receipt.
The act specifies:
Date, time and place of its compilation;
Name of the body carrying out the inspection;
Date and number of the order;
Surname, name, patronymic and position of the inspector;
Name of the organization, last name, first name, patronymic, position of the representative of the organization present during the inspection;
Date, time and place of the inspection;
List of documents requested during the inspection;
Information about the results of the audit, including the identified violations;
Information about familiarization or refusal to familiarize with the content of the act of the representative of the organization;
Signature of the official who carried out the verification.
By signing the act, the head confirms that he is familiar with the document. This does not mean that he agrees with the results of the test. Opinion of the first person of the company in this case may not coincide with the opinion of the inspector.
In contrast to the act of verification, an order is issued only in the event of violations in the work of the organization.
This is the final verdict of the legal inspector, allowing you to judge the observance of the law in your organization. The purpose of the document is to give the employer binding instructions to eliminate existing violations and to bring those responsible to disciplinary responsibility.
The document indicates the period during which the employer needs to correct certain violations, and the period during which the legal inspector should be informed about this.
One copy of the prescription with copies of the annexes (protocols of research and examinations, explanations of employees) is handed over to the employer or his representative against receipt. The order may also be sent to the organization by mail with acknowledgment of receipt. Later, the notification is attached to the copy of the prescription, which remains in the case of the checking inspector.
When familiarizing with the protocol, his rights and obligations should be explained. In particular, the right to get acquainted with the contents of the protocol, the right to refuse to sign it. All comments, objections, explanations regarding the content of the document must be taken into account by the inspector and drawn up as an addition to the protocol.
Decisions of state labor inspectors may be appealed against to the relevant head of subordination, the chief state labor inspector of the Russian Federation and (or) to judicial order. Decisions of the chief state labor inspector of the Russian Federation may be appealed in court.
An alternative jurisdiction of labor disputes on issues of state supervision and control has been established, i.e. this question left to the discretion of the administrative officer of the organization. You can appeal against the decision of the state labor inspector to the relevant head of subordination, i.e. to the head of the Rostrudinspektsiya body in which this state labor inspector works, or to the chief state labor inspector and (or) to the court. Thus, the complainant has the right to file two complaints at the same time: one - to the chief labor inspector, the other - to the court.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I would like to conclude that the issue of labor protection is one of the most important at the present stage of the life of our society. At a time when employers set themselves the main task as quickly as possible and with a minimum investment of funds to extract the largest number profits, and taking advantage of the Lately in our country there is a shortage of jobs, when our citizens are ready to do the dirtiest work for meager wages, they pay little attention, and sometimes even ignore the requirements of labor safety.
The increase in the number of occupational diseases, industrial accidents leading to injuries and sometimes deaths, all this makes us think about the perfection of our legislation in the field of labor protection, and it seems that our legislative, executive and judicial bodies of state power still have a lot to do work in this direction.
legal industrial federal healthcare
List of sources used
1. Andreev S.V. Occupational safety from "A" to "Z": pract. allowance / S.V. Andreev, O.S. Efremov. - Issue. 3. - M.: Alfa-Press, 2006. - 392p.
2. Devisilov V.A. Occupational safety: textbook. / V.A. Devisilov. - 3rd ed., Rev. and additional - M.: Forum: Infa-M, 2007. - 448s.
3. On the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of March 30, 1999 No. 52-FZ.
4. Labor Code of the Russian Federation: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of 30.12. 2001 No. 197-FZ: as amended. and additional acc. with the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of July 24, 2009 No. 206-FZ.
5. On the approval of the Standard Regulations on the committee (commission) for labor protection: Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2006 No. 413.
7. About federal service on environmental, technological and nuclear supervision: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 30, 2004 No. 401.
8. On improving the system for investigating and recording occupational diseases in the Russian Federation: Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated May 28, 2001 No. 176.
9. On the approval of the Regulations on the investigation and registration of occupational diseases: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2000 No. 967.
Hosted on Allbest.ru
...Similar Documents
course work, added 03/17/2011
Legal basis life safety. Principles of state policy in the field of labor protection. Legislative bases of labor protection, Federal law. Instructions for labor protection at the enterprise. State supervision and public control.
abstract, added 02/23/2009
Contribution of M.V. Lomonosov in the development of labor protection in Russia. Directions of state policy in the field of labor protection and safety. State supervision and control. Prospects for the development of science. Synergistic model of "expenditure and recovery".
test, added 01/14/2014
Basic concepts, requirements and organization of labor protection. Rights and obligations of the employee and the employer in the field of labor protection. Legal status state labor inspector. State supervision over compliance with the requirements for the safe conduct of work.
term paper, added 06/02/2015
State supervision and control over compliance with the requirements of legislative and other normative acts on labor protection is carried out by the federal labor inspectorate. Requirements for environmental protection for trade and public catering enterprises.
test, added 04/17/2008
Legislative and regulatory framework for labor protection, principles of state policy. Guarantees of the rights to labor protection, state supervision and public control. Training and testing of knowledge, types of briefings, investigation and accounting of accidents.
tutorial, added 05/01/2010
State supervision and public control over labor protection. The main factors of industrial safety. Organization of labor and nature protection service at the enterprise. Occupational safety training and types of instruction. Traumatism and methods of its study.
term paper, added 08/10/2011
The procedure and regulatory framework, as well as the bodies exercising state supervision and control, their rights, obligations, competencies. Ventilation of industrial relations. Emergencies natural character, rules of conduct in them.
test, added 06/09/2013
State supervision and control over compliance with labor protection legislation. Ionizing radiation and methods of protection. State examination of working conditions. Sources and scope of ionizing radiation. Radioactivity, radiation doses.
control work, added 11/20/2008
Safety regulations in the mining industry. Legislative acts and normative documents on labor protection. State and public control. Guidelines on the organization and implementation of the State Mining Supervision.





