Diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma in a child. Clinical picture of diffuse changes in the hepatic system during ultrasound echographic examination. Diffuse changes in the liver during ultrasound diagnostics
If the condition of the liver is normal, its structure is homogeneous, its outlines are clear, the surface is smooth, and the edges are even. At the same time, the vessels of the organ are not enlarged, and the structure of the hepatic ducts does not change. If diffuse changes in the liver occur, its structure is disrupted cellular level. The point is that the parenchyma of the organ, its main tissue, increases. Its main component is hepatocytes.
WHAT DO DIFFUSE CHANGES LOOK LIKE IN THE LIVER
Changes in the parenchyma are detected on ultrasound. During the study, it is revealed that the liver tissue looks lumpy, its surface becomes not smooth, and its outlines are not clear. All these are echo signs of diffuse deformations of the parenchyma. In its normal state, weak echogenicity of the tissues is noted.
Diffuse changes liver disease is not the presence of localized foci of altered parenchyma, but deformation of the liver tissue as a whole. If compaction occurs in only one area, it may be focal-diffuse changes.
Such manifestations may indicate minor pathologies, but we can also talk about serious illnesses. If diffuse changes in the liver are detected, this is not final diagnosis. This phenomenon is a symptom, and upon its detection, further examination is necessary to determine what kind of disease has affected the liver tissue.
If the disease is detected in time, the liver tissue can be restored quite quickly, returning it to its normal structure and ridding the organ of the disease. This cannot be said about advanced cases of the disease, since in the later stages the processes of change in the parenchyma are often irreversible.
Diseases that cause diffuse changes in the parenchyma
The causes of diffuse changes are those diseases that disrupt the functioning of the organ.
 Disorders can be either primary or secondary – resulting from diseases of other organs (for example, diabetes mellitus).
Disorders can be either primary or secondary – resulting from diseases of other organs (for example, diabetes mellitus).
The most common causes of the problem are alcohol abuse and obesity.
The organ can also be damaged by frequent diets, and especially strict. The most dangerous thing is sharp "switching" from a normal diet to a diet with strict restrictions.
Unfortunately, many of them can occur without any symptoms, so they are detected only during examination.
But sometimes they make themselves felt with the following signs:
- Yellowing of the sclera and skin around eyes;
- Dimly expressed painful sensations in the area of the right forearm or right hypochondrium;
- A feeling of heaviness in the area of the right hypochondrium or forearm.
If such signs are observed, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and conduct an examination in order to identify the disease in time.
Changes in the liver parenchyma come in the following forms:
- Hepatic fibrous;
- Hepatic-dystrophic;
- Hepatic-sclerotic;
- Hepatic-hypertrophic;
- Diffuse changes in the liver associated with the accumulation of fluid in the parenchyma.
Types of liver changes
Due to the close relationship of the liver with other organs, diffuse changes can be as follows:

This phenomenon can also occur in children. The reason for this may be congenital pathologies liver. If during pregnancy future mom I had hepatitis, and the baby has such problems. Because of this and the risk of developing other pathologies, termination of pregnancy is usually recommended if a woman is diagnosed with hepatitis during pregnancy.
Changes in a child’s organ may also develop due to antibiotic treatment. Use of toxic drugs children's body is going through a very difficult time.
How to treat diffuse liver changes?
 Given the fact that we're talking about about a symptom, and not about a specific diagnosis, we can talk about its elimination only if the provoking disease is eliminated.
Given the fact that we're talking about about a symptom, and not about a specific diagnosis, we can talk about its elimination only if the provoking disease is eliminated.
Treatment for any of these diseases requires that it be developed by a doctor.
Whatever the disease, it is very important to follow a diet when eliminating it. It has a positive effect on the condition of the liver and is important step, accelerating recovery.
Here are the basic nutritional rules that you need to follow to speed up treatment:
- It is necessary to avoid taking smoked, fried, fatty foods. The list of non-recommended foods also includes heavy, rich broths and decoctions;
- Spicy, sour, salty dishes should also be excluded;
- It is also necessary to give up alcoholic beverages;
- In order for the liver tissue to recover faster, extreme caution should be exercised when taking medications. Treatment should be carried out only with those prescribed by the doctor;
- You should stop smoking or at least significantly reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke;
- Baking, White bread, sweets are products that should also be prohibited;
- You should also avoid products containing a large number of coarse fiber (for example, cabbage), as well as those that enhance fermentation processes (in particular, legumes).
If diffuse changes in the liver are mild, sometimes doctors limit themselves to prescribing hepatoprotectors - drugs that help maintain the liver.
The following drugs have a similar effect:
- "Karsil";
- "Gepabene";
- "Essentiale";
- "Livenziale";
- "Hepalex".
Prevention
To avoid the risk of diffuse hepatic changes, follow these rules:

Changesparenchyma is a reason to start treatment, but not a reason to panic, so consult a doctor in a timely manner.
The liver is a unique organ that performs many functions in the body. It cleanses the blood, produces and inactivates hormones, participates in the digestive process, replenishes energy reserves, and neutralizes foreign aggressive substances and toxic compounds.
Moreover, this organ is created in such a way that its cells do not have nerve endings and with various disorders affecting the liver tissue, it does not hurt. Therefore, most liver diseases occur without severe symptoms and is detected only in advanced stages.
Human long years may not suspect that he is sick until the volume of the liver increases. Then the capsule covering the organ stretches, touching the nerve processes of nearby tissues. Pain occurs in the hypochondrium on the right, the skin turns yellow, and digestive processes. Often, early liver pathologies are detected during examination of other organs. And if the patient is informed about diffuse changes in the liver, he begins to worry. What does this mean, and how to proceed?
Hepatic diffuse transformations include uniform changes in the structure of the liver. This is not a disease, but only a manifestation of the underlying pathology. Changes can be sclerotic, edematous, dystrophic, fibrous in nature. But for the production accurate diagnosis the patient will need to be examined.
This condition can occur at any age, as a result of minor violations liver activity, and because of its severe damage. Diffusion is the relatively uniform interconnection of atoms and molecules. At negative impact Due to damaging factors, these connecting links are disrupted, which affects the balance of the interaction of substances. In the liver, the vascular lumens change, the lobes of the parenchyma are rearranged, and its edges and boundaries change.
Experts identify the following causes of the disorder:

In children, diffuse changes develop with jaundice associated with liver dysfunction, and with diseases of the gallbladder. Negative Impact environment, malnutrition, bad habits, bad heredity - all this can become an impetus for the development of a pathological process.
At the beginning, the restructuring of the liver structure occurs without pronounced symptoms. Sometimes a person may experience nausea and mild pain in the right side. Further, the victims experience:
- constant pain, heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right;
- yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- loss of appetite;
- bloating, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting;
- weight loss;
- bitter taste, dry mouth, thirst;
- nervousness;
- headache;
- chronic fatigue.
Types of pathologies
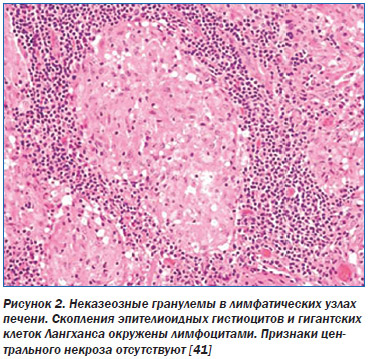
Diffuse changes due to bacterial or viral infection change the intrahepatic ducts, which causes other organs to suffer. They are classified by localization. Lesions may occur:

Diagnostic measures
The main and most informative method Determination of pathology is examination using ultrasound. Such a study of the parenchyma makes it possible to accurately determine the size of the organ, the degree of deviation from the norm, and identify enlarged The lymph nodes, tuberosity, swelling, granularity, helminthic lesions, hemorrhages, neoplasms.
Examination of the hepatic ducts helps determine the size of the lumen, find stones present in the biliary tract, identify blockage of blood vessels, and assess the volume of lymph nodes. When diagnosing the gallbladder, the doctor assesses the condition of the duct and identifies the presence of tumors and stones.

Increased echogenicity indicates the course of pathological processes associated with cholelithiasis and the proliferation of tumor growths. Reduced echogenicity indicates exacerbation of hepatitis and inflammation of the gallbladder.
The patient needs to prepare for the procedure. The day before, avoid eating foods that increase gas formation, take an antispasmodic and do an enema. Based on the results obtained, the specialist will be able to make a diagnosis or refer the patient for additional examination to determine the further course of treatment.
TO additional examinations liver include:
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are non-invasive diagnostic methods that make it possible to see the pathology in the image, assess the severity and location in 3D format;
- radiography;
- biochemical blood test that determines the level of hemoglobin, glucose, lipids, proteins, cholesterol, urea, etc.
Various liver diseases correspond to certain signs that are visible on ultrasound.
- with steatosis, the organ enlarges, its shape changes, and a distinct pattern of the organ’s veins is visible;
- with cirrhosis, the growth of connective tissue increases, the surface of the organ is lumpy, uneven, and the echogenicity is high;
- with abscesses, neoplasms, hemorrhages, specific echo signs are detected;
- with hepatitis, the echo signal increases, the size of the liver increases, and in some places heterogeneity is detected in the tissues.
Therapy methods
Since hepatic diffuse mutations are not a separate diagnosis, but only indicate hidden pathological processes, treatment is based on eliminating the real reason violations.
Traditional methods
Depending on the etiology and nature of the changes, the following traditional treatment regimens are prescribed:

ethnoscience
It is known that the liver is a unique organ that can recover. In addition to medications, you can help her folk remedies. There are many recipes that cleanse and restore the liver. As a result, it decreases in size, its structure becomes homogeneous, and pain in the hypochondrium disappears.
Patients should note that cleaning can only be carried out with the permission of a doctor.
You can use it to treat the liver:
- ginger;
- lingonberry leaves;
- Birch buds;
- mint;
- dog-rose fruit.
These phytoingredients help both together and individually. You can use the following recipes to prepare the product:

Prevention nutritional therapy
To prevent diffuse liver degeneration and biliary tract, necessary:
- Healthy food;
- do not overwork;
- use medications as prescribed by your doctor;
- do not refuse annual preventive examinations;
- treat chronic diseases;
- give up bad habits.

Any liver disease requires strict adherence to a diet and a categorical refusal of certain foods. The main food for the patient is boiled, steamed, stewed dishes. All drinks and foods consumed for liver diseases should not be too cold. The diet includes sufficient amounts of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and limits fats. Excluded:
- fatty meats and fish;
- fried dough;
- bakery;
- offal;
- rich broths;
- mushrooms;
- spicy seasonings;
- canned food;
- fatty fermented milk products;
- semi-finished products;
- sausages;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- sparkling sweet water.
Meals should be 5-6 times a day, in small portions. You need to have dinner no later than 2 hours before bedtime. The diet includes:
- crackers;
- hard biscuits;
- Not sour berries and fruits;
- fresh vegetables;
- greenery;
- lean meat and fish;
- rosehip decoction;
- weak tea;
- low-fat cheeses and dairy products;
- omelet, boiled eggs;
- vegetable soups;
- juices, fruit drinks, compotes;
- cereals.
Complications and prognosis
If a patient has diffuse hepatic changes, then the prognosis directly depends on the underlying disease, which caused, although hidden, unpleasant symptoms. Sometimes it's enough to exclude negative factors to return the liver normal sizes and get rid of pathological phenomena.
For steatosis caused by alcohol intoxication, the complete exclusion of provoking factors returns the cells to a healthy state within six months.
It happens that a person has been forced to take medications for decades that have a toxic effect on hepatocytes. IN similar cases the development of diffuse transformations in the liver is inevitable. To prevent complications, doctors prescribe hepatoprotectors (it is better to take them in courses in spring and autumn). These drugs create a protective shell on the surface of the parenchyma that does not allow toxins to pass through.
No less favorable forecasts doctors give when viral diseases. Patients need to take a course antiviral therapy. The main thing is to apply for it in a timely manner medical assistance until the deformation of the tissue has gone too far. In case of cirrhosis and tumor, the normal structure of the liver cannot be restored. But the sooner the patient begins treatment, the greater the chance of stopping pathological changes.
To understand why diffuse modifications are dangerous, it is worth considering patient reviews:
Ivan: “When there was pressure in my right side, nausea after almost every meal, dizziness and yellow skin, I went to the doctor. I am not a fan of hospitals and drugs. I was often sick as a child, so I always wait until the last minute to avoid getting there.
I was admitted to the hospital. An ultrasound revealed diffuse transformations of the organ, and found stones in bile duct. I'm waiting for surgery to remove stones. Probably, if I had rushed earlier, I could have gotten by with pills.”
Victoria: “When, based on the results of the ultrasound, I was diagnosed with “diffuse changes,” I asked my doctor how scary it was. She said it was just a symptom, like a red throat and snot, but it didn't necessarily indicate the flu.
Since special clinical manifestations I didn’t have one, I was recommended Karsil twice a year and diet No. 5. I feel great, thanks healthy eating I even lost a couple of kilos. I’ll go for another ultrasound soon, I think everything will be fine.”
This is not a diagnosis, but disturbances in the structure of the liver, which indicate hidden pathological processes. Medicine does not consider such changes to be a disease, but they must be treated so as not to bring the organ to a state incompatible with life.
What are diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma
This organ is made up of tissue called parenchyma. It is formed mainly from liver cells - hepatocytes, which renew old or dead areas of tissue. The liver is completely regenerated in about a year and a half. If diffuse (that is, affecting the entire organ) changes are detected in it, then more often this means an increase in parenchymal tissue, less often - its decrease. Such violations can be either minor or large-scale.
Even a banal flu does not leave its mark on the liver, but it, as a rule, gets off minimal changes in the parenchyma. Another thing is severe diffuse lesions after hepatitis of any kind, chronic alcohol poisoning or giardiasis. If scar (fibrous) tissue begins to grow in an organ, it will significantly increase in volume and undergo irreversible structural changes.
Signs and symptoms of hepatomegaly
The liver does not complain for a long time about the difficult conditions of its existence. Organ misfortunes are discovered only by chance during an ultrasound due to completely different patient complaints. Often there is an enlargement of the liver - hepatomegaly, as a result of which the structure of the organ begins to degrade. The density of the parenchyma becomes increased, and its echogenicity is many times higher than normal, that is, ultrasound is reflected from the parenchyma at a much higher speed.
With diffuse changes, the enlarged organ is easily detected by palpation, and this diagnostic procedure causes pain to the patient. If such changes do not occur in acute form, a person may not experience it. But as the pathology progresses, the symptoms of hepatomegaly become more obvious. Appears:
- heartburn;
- halitosis;
- nausea;
- yellow tint, itchy skin;
- ascites (fluid in abdominal cavity).

Moderate
Signs of minor liver degradation are common. If they appeared in it, then they are also present in the pancreas. An ultrasound diagnostician determines the presence of moderate diffuse lesions in the liver by increased density tissue, heterogeneity of its structure, distortion of the pattern of blood vessels. Parenchyma compaction and other echo signs of pathology can manifest themselves through a feeling of discomfort after a fatty meal, a bitter taste in the mouth, headaches, fatigue, irritability.
According to the type of fatty hepatosis
The liver reacts to metabolic disorders and intoxication of the body in a very unique way: its cells accumulate fat. Over time, steatosis or fatty infiltration develops, simply - obesity of the organ. The disease is insidious in that it is devoid of symptoms and is often detected by chance during ultrasound examination abdominal cavity. Sometimes a person feels nauseous, weak, tired, and drowsy. Then inhibition may appear in his movements, and monotony in his speech. More later than man jaundice, ascites, dizziness, and convulsions occur.

Reactive changes in the liver parenchyma in a child
Functional immaturity of the stomach and intestines in children, the toxic effects of worms often lead to the development reactive hepatitis, that is, caused not by liver pathologies. This disease either has no symptoms or is manifested by mild malaise, digestive disorders, low-grade fever, emotional decline. At adequate treatment diffuse abnormalities can restore liver activity completely.
Pronounced diffuse changes
When the liver is poisoned by various poisons so severely that it is no longer able to neutralize them, its disintegration begins - cirrhosis. If on early stages diffuse-focal degeneration, the organ increases in volume, then at a later stage it decreases and shrinks. Its echostructure is diffusely heterogeneous, and its echogenicity is very high. The patient is persistently haunted by pain in the right hypochondrium and right shoulder; his tongue, sclera and skin under his eyes are jaundiced.

Treatment methods
The main treatment for diffuse lesions in the liver consists primarily of eliminating their causes: obesity, alcohol abuse, taking medications that are toxic to this organ, etc. Amino acids, vitamins E and group B improve the condition of the organ. To ensure that liver cells are restored, hepatologists (or therapists) prescribe medications:
- Essentiale forte N;
- Phosphogliv;
- FanDetox;
- Heptral;
- Result Pro;
- Gepabene.

According to indications, courses of treatment with antibiotics, antivirals, anthelmintics and choleretic drugs. Operative methods Treatments are used when it is necessary to remove stones and tumors in the liver. Patients are prescribed diet table No. 5 with a ban on fatty, spicy and smoked foods. Salty, sweet, sour food, alcohol and soda are also prohibited. Priority is given to lean varieties of meat and boiled fish, dairy dishes and soups, cereals and vegetables.
Liver parenchyma is the tissue of which it is composed. In the process of performing its functions (maintaining normal composition blood, removal of toxins from the body, transportation of bile and others) it faces the influence of various harmful factors. Homogeneous parenchyma can undergo various changes. The cells of this organ (hepatocytes) can degenerate and even die.
Features and types of changes in the liver parenchyma
Liver tissue can change in its composition, shape, and density. Depending on the nature and extent of these changes, they can be divided into:
- Focal;
- Local;
- Diffuse.
Using ultrasound, an echoscopy of the liver is performed, which produces a picture from which a diagnosis of the disease can be made.
Focal changes indicate the presence of a single damaged or compacted lesion.
With local changes, the pathology affects individual areas of the parenchyma.
Diffuse changes affect the entire organ. They can be caused not only by disease of the liver itself, but also by cardiac pathology or disruption of the pancreas. Of the two lobes of the liver, the right one, which is larger in size, experiences a greater load. Therefore, diffuse changes in the right lobe are detected more often.
Pronounced signs of diffuse changes do not always indicate serious illnesses. Moderate changes may appear when consuming certain products. Slightly enlarged liver small child may also be explained by the characteristics of children's physiology. And only if it progresses with age, then such a pathology should cause concern.
Even if the detected diffuse changes do not affect the person’s well-being, it is necessary to undergo an examination, blood tests, and a test for markers, since this anomaly may be a symptom of latent viral hepatitis or malignant tumors.
The nature of diffuse changes in the parenchyma
In case of disease of the liver, as well as other organs directly related to it (gall, bladder, intestines, pancreas), degeneration processes of various types can occur in the parenchymal tissue:
The ultrasound method is based on the ability of body tissues to reflect ultrasound. At different painful conditions Liver examination helps detect the following abnormalities:
- Parenchyma compaction;
- Heterogeneity of structure;
- Increase in size.
When examined using ultrasound, echo signs and characteristic indicators are studied:
- The size of the right and left lobes;
- Clarity of outlines;
- Structure of parenchymal tissue;
- Correctness of the pattern of liver vessels;
- Echogenicity is the ability to reflect ultrasound.
There is a norm of parenchyma echogenicity for healthy liver. If the echo pattern is increased or decreased, suspicions of a specific diagnosis should be confirmed by laboratory tests.
The device displays data on the intensity of the sound reflection process. The echogenicity of healthy tissue is taken as normal. Sound reflection damaged tissue differs depending on the changes that have occurred. Thus, excess fat in parenchymal tissue reduces this characteristic, and compaction of the parenchyma means that it is increased.
Healthy liver tissue contains a lot of water. With fatty degeneration, diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma occur, which is expressed in a decrease in water content due to the accumulation of fat. At the same time, the speed of sound reflection increases, and the echogenicity index decreases. This picture is observed in liver hepatosis.
At infectious diseases liver ( viral hepatitis), inflammatory processes parenchyma density increases due to tissue swelling. The speed of sound reflection becomes lower than normal, and increased echogenicity is observed. The human condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Jaundice;
- Digestive disorder;
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver);
- Pain in right side;
- Vomit.
Similar signs can be observed with liver injuries, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis. In addition, an increase in echo characteristics can occur with obesity, as well as with drug intoxication.
Changes in the liver parenchyma, treatment and prevention
If the examination reveals a disease that has caused changes in the liver tissue, then it is necessary to undergo treatment as soon as possible aimed at removing toxic substances from the liver and restoring liver cells. It is necessary to take drugs that improve performance digestive system(enzymes for restoring intestinal flora), anti-inflammatory drugs. Reception plays an important role choleretic drugs and antispasmodics that can facilitate the passage of bile and pancreatic stones.
It is necessary to cleanse the liver of toxins, including using folk remedies - using decoctions of medicinal herbal infusions or infusions medicinal plants. In some cases, it is necessary to take painkillers and vitamins (especially group B).
Before you start taking medicines, you need to quit smoking, completely forget about alcoholic drinks, and also be sure to follow a diet. Food should be low in calories, without pepper, spices and salt. You can only eat boiled or steamed dishes and low-fat dairy products. Sweet and sour foods should also be excluded from the diet. Fruits are very healthy, but only when they are ripe and not sour. We need to fight obesity. Diet and control bad habits plays a therapeutic role as well as preventive role in the improvement of liver parenchyma.
Who said that it is impossible to cure severe liver diseases?
- Many methods have been tried, but nothing helps...
- And now you are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that will give you the long-awaited well-being!
An effective treatment for the liver does exist. Follow the link and find out what doctors recommend!





