What is the difference between MRI and MSCT? MSCT - what does such research give to a person?
IN last decades V medical diagnostics a breakthrough occurred - the latest non-invasive methods of examining the body appeared. Invasive diagnostics always imply a violation of the integrity of the organ being examined. However, it is possible to immediately make surgical adjustments, for example, with laparoscopy or arthroscopy. MSCT and MRI methods are methods radiology diagnostics body. What is the difference between them? Let's consider the features of each type of diagnosis.
Features of MSCT
What is MSCT? This is a multislice computed tomography scan. Unlike other hardware diagnostics, it has the shortest time of radiation exposure to the body. How does spiral diagnostics differ from computer diagnostics? Firstly, the time of exposure to x-rays on the body. Secondly, a more detailed layer-by-layer scanning of the body organs.
MSCT provides clearer visualization of the organ or body system being examined. At first, multislice tomography was used to study the brain, and later it was used to scan the whole body.
Note! The difference between MSCT and CT is a lower radiation dose and multilayer visualization of the organ being studied.
The method scans a body area in all planes, just like magnetic tomograph. Only with magnetic resonance tomography the patient must long time be immobilized, and spiral diagnostics take place in a matter of minutes.
The MSCT device takes approximately 300 images per revolution, which significantly increases the information capacity in a short period of time. For example, a CT scanner takes only a few images per revolution. If the examination is carried out using a contrast agent, the device can accurately determine cancerous tumor at the very beginning of development - the CT device does not have this capability.
Features of MRI
Magnetic tomography is the safest diagnostic method, but the most expensive and time-consuming. Sometimes the patient is forced to remain immobilized for more than an hour or even longer. This feature of the device is not suitable for every patient.
Another disadvantage of MRI is the inability to scan patients with metal or electronic implants in the body. Metal distorts the magnetic field and prevents diagnostics, and electronic devices will fail after scanning. This poses an intractable problem, and patients refuse examination.
However, an important advantage of MRI over computer diagnostics is the absence of radiation exposure - scanning can be done several times a day every day. X-ray machines are used once every six months or a year - this is their big drawback.
MRI has the advantage of visualizing only the soft tissues of the body, unlike MSCT. MRI and MSCT are equally good at diagnosing the brain, but for visualization bone structures and dense tissues, it is necessary to choose a computed spiral tomograph. For example, MCT will not be able to detect stones in organs - this is how the devices differ from each other.
Note! Magnetic resonance imaging can be used to examine newborns due to the lack of x-ray radiation.
How else does MRI differ from MSCT? Spiral tomography can be performed in the presence of any implants in the patient’s body - metal or electronic: X-ray radiation does not react to them. Contraindications to the procedure are severe tachycardia, pregnancy/lactation and childhood.

Comparative analysis
Which is better MSCT or MRI, MRI or CT? These types of diagnostics have their advantages, differences and disadvantages. For example, MSCT of the spine will provide more information during scanning than a magnetic tomograph, and magnetic tomography is better used to study the soft tissues of the body. Although in Lately examination of soft tissues can also be carried out using a spiral apparatus.
The issue of diagnostic price also plays a role. The most expensive is diagnostics using a magnetic tomograph, and the cheapest is computed tomography. In terms of price, MSCT is between them. If price does not play a determining role, it is better to choose MRI - this safe method diagnostics If there are obstacles to performing an MRI, then you should prefer spiral tomography to simple computed tomography - the radiation dose is several times lower, and the scanning is more informative.
In terms of information content and clarity of visualization of organs, MRI and MSCT are absolutely equal. Both devices produce multi-layer scanning of the area under study. However, MSCT is significantly superior to magnetic tomography in visualizing dense structures of the body. If you need to examine the bone structure and adjacent organs, you need to choose spiral diagnostics.
Bottom line
Which is better to examine - MRI or MSCT? Both devices are a new word in hardware diagnostics and have a high ability to scan the body in detail. Your doctor will tell you which one to choose. However, the choice will depend on many nuances:
- patient's age;
- health conditions;
- presence/absence of implants in the body;
- the patient's mental state.
For example, magnetic tomography is not prescribed for people with claustrophobia and epilepsy. If a person is unable to control body movements (epilepsy), the pictures will be blurry. The same applies to patients with a fear of closed spaces - they may be in a panic state and cannot control themselves.
Computer spiral diagnostics are carried out after preliminary tests. If the patient's health does not allow it, the scan is not performed. A resonance examination can be performed without prior blood and urine tests.
The second half of the last century was marked by the rapid development of science, which allowed doctors to obtain new information using high-quality diagnostic methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and multislice computed tomography (MSCT). However, sometimes it is not possible for a practicing physician to determine which method is most preferable for each individual patient. Today we will try to answer the question of what is the difference between MSCT and MRI, and which research method is suitable for each specific case.
Definition
Multislice computed tomography is based on scanning human body using a fan beam of X-rays. An important aspect in this research is the transmission of X-ray radiation, which converts the received data into electrical signals, transmits them to a computer for further data processing and obtaining image synthesis. Initially computer diagnostics was intended only for the brain, but subsequently a device for scanning the entire body appeared. Today, multislice computed tomography is one of the most highly effective and modern methods research.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the modern and effective methods X-ray diagnostics, which allows you to obtain images of internal bone structures human body. The most important advantage of this research method is the absence of radiation exposure, as well as the fact that it can be carried out taking into account the anatomical and physical characteristics of the patient. Tomography provides an image of an object that is placed in a constant magnetic field.
Comparison
The main advantage of MRI is the ability to obtain images in any plane (including soft tissue structures). This is a non-invasive research method that can be carried out without special preparation of the patient. However, MRI is the most informative when conducting studies of the spine, brain and spinal cord, retroperitoneal space and organs abdominal cavity, pelvic organs, as well as tissues, joints and blood vessels.
The main advantage of MSCT is the ability to obtain thin sections, reformat images in other planes, and display the structure of thin walls tear ducts with assessment of their configuration, construction of three-dimensional structures, assessment of the prevalence of tumors in paranasal sinuses ah of the nose and adjacent structures.
Conclusions website
- MSCT is a method of spirally obtaining image slices of a specific organ. MRI is the acquisition of an image of an object placed in a magnetic field.
- MSCT is more suitable for obtaining images from soft tissue organs, while MRI is ideal for imaging bone tissue.
The latest diagnostic techniques allow practicing doctors to identify pathological processes developing in the human body without grueling manipulations and long waits for their results. The second half of the 20th century was marked by such scientific achievements as multislice computed tomography (MSCT) and.
The use of these qualitative methods made it possible to diagnose the disease on early stages development that has important in carrying out rational treatment without triggering pathology. Qualified specialists choose a specific diagnostic technique for examining a patient depending on each specific case.
Sometimes only the final MSCT data can provide detailed information about the condition of the organ, and in some circumstances, resonance imaging is more informative. In our article we want to provide information about how MSCT and MRI differ, when they are performed and which of these diagnostic methods is preferable.
Applications of nuclear magnetic resonance
The MRI method is based on obtaining medical images of tissues and internal organs human body using devices that vibrate atoms electromagnetic waves. Using this technique helps doctors diagnose:
- foci of inflammatory processes;
- tumor-like formations;
- diseases of bone structures - joints and spinal column;
- violations functional activity circulatory and nervous systems.
The most important advantage of MRI is the absence of radiation exposure and the fact that the examination can be carried out taking into account the physical and anatomical features patient.
When performing an MRI to obtain images of internal tissues, the patient is placed in a device that provides a constant magnetic field
MRI is one of the most modern and safe, non-invasive (does not require intervention in the patient’s body) diagnostic methods. The results of the examination depend on the capabilities of the equipment used; the most informative are the images that were obtained during the procedure performed on a high-field magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
The main advantage of such equipment is high voltage magnetic field(up to 3 T), providing high speed scanning and the quality of the resulting images. The duration of the diagnosis depends on the area being examined, for example, the study of one part of the spinal column lasts about half an hour, the procedure using a contrast agent takes approximately 50–60 minutes.
The main advantage of magnetic resonance imaging is the absence of ionizing radiation that harms the human body! This advantage allows you to examine several areas of the patient’s body at once and repeat the procedures daily.
However, there are a number of restrictions for MRI - undergoing examination is strictly prohibited:
- during pregnancy in the first trimester;
- breastfeeding;
- the presence of electronic or ferromagnetic devices in the patient’s body (prosthetic heart valves, pacemakers, insulin pumps, etc.);
- disorders of the psycho-emotional state (claustrophobia, panic attacks);
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- necessity constant monitoring vital important indicators (blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory movements).

MRI is not performed on patients whose body weight exceeds 120 kg
Use of radiation diagnostics
Multislice tomography is a type of one of the most modern techniques visualization of internal organs and tissues – . The diagnostic method is based on the technique of scanning the patient’s body using X-ray transmission, which converts the received information into electrical signals.
Further data processing takes place in a computer and, thanks to specially developed programs, a synthesized layer-by-layer image is displayed on the monitor.
Initially, this diagnostic method was intended only for studying the brain, but medicine does not stand still - today there is equipment for scanning the entire human body. Practicing doctors consider the MSCT method to be the most highly effective way of examining a patient.
It allows you to identify pathological processes such as:
- diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- carcinomas;
- injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- internal bleeding.
The MSCT procedure is absolutely painless for the patient and does not cause him fear of confined spaces. Its duration is from 20 to 30 minutes (if there is a need to use contrast). It is in the time during which the patient must occupy a motionless position that there is one of the main differences between the diagnostic methods of MSCT and MRI.

MSCT allows not only to visualize changes in internal organs, but also to obtain detailed images of cross-sections of tissues throughout the patient’s body
What is the difference between MSCT and MRI?
The main advantage of magnetic resonance imaging is the ability to obtain images in any plane (including soft tissue structures). However, the method is the most informative for examination:
- spinal column;
- pelvic organs;
- spinal cord and brain;
- musculoskeletal system;
- blood vessels.
The main advantage of the method of spiral obtaining thin sections is the possibility of: reformatting the image in a different plane, displaying the walls of organs with assessment of their configuration, constructing three-dimensional structures, and studying the prevalence of tumor-like formations. MSCT and MRI differ in physical phenomena that make it possible to obtain images of human internal organs.
The first method is based on x-rays (although the operating time of the x-ray tube does not exceed 30 seconds), the second works by emitting high-frequency magnetic fields. Both procedures allow high-quality visualization of the object under study and are absolutely safe for humans (after MSCT, no residual amount of X-rays is detected in the patient’s body).
Both diagnostic methods, although completely different, allow you to obtain high-quality information and create a detailed picture of the state of the human body systems. Methods are constantly being improved and sometimes it is difficult to give preference to any of them, but this is an undeniable plus - if there are contraindications for performing one procedure, you can always use the second!
The only area in which the capabilities of MSCT are inferior to magnetic resonance imaging is the central nervous system. Accurate visualization of changes in the spinal cord and brain is only available with MRI! However, many pathological processes can be seen using a multislice tomograph.
Which method should you choose?
MSCT and MRI are used to diagnose various pathological processes– inflammation of tissues, injuries, malignant tumors, developmental defects, degenerative-dystrophic changes. Both methods have special meaning in identifying oncological pathologies, allowing you to study the stage of organ damage, the extent of the tumor in nearby tissues, condition of the lymph nodes.
MSCT is much superior to MRI in the quality of soft tissue visualization, and the resonance method is ideal for obtaining images bone tissue. Due to the speed of obtaining final examination data, multislice tomography is used to diagnose injuries, acute bleeding and other pathological conditions.
A multislice tomograph is less sensitive to human movements than magnetic resonance equipment; thanks to this feature, it is possible to obtain images of organs in real time. In addition, unlike MRI, the presence of metal in the patient’s body, that is, implanted medical devices, vascular walls, cardiac prostheses, is not a contraindication for the procedure.

Using MSCT qualified specialist can perform a minimally invasive procedure - perform a puncture of the lungs and peritoneum, and collect synovial fluid
MRI and MSCT are two types of diagnostics that provide maximum visualization of the state of the patient’s internal organs, tissues and systems. Each examination method has its undeniable advantages:
- MRI provides accurate information in cases of identifying pathological processes in nervous system, soft tissues, joints, vascular bed– without causing any harm to the patient’s health;
- MSCT is less safe, but more informative in diagnosing bleeding, diseases of the digestive, genitourinary and respiratory organs.
The reaction of the human body can be different both to radiation exposure and to magnetic frequencies. A computer spiral examination is prescribed after passing general clinical and biochemical tests blood and urine. If their results indicate a significant change in the patient's health, the scan is not performed. Resonance diagnostics carried out without preliminary laboratory tests.
The question of choosing one or the other diagnostic method For each specific case, the attending physician must decide, taking into account:
- patient's age;
- mental condition;
- the presence or absence of metal objects in the body;
- results of preliminary studies;
- data from anamnesis and clinical symptoms.
Conclusion
Computed tomography and magnetic tomography are performed both in private and public clinical diagnostic centers. Of no small economic importance for the patient is the fact that the cost of MSCT is significantly less price MRI. However, you should know that the success and informativeness of the survey depends on the quality diagnostic equipment and the professionalism of the doctor performing the procedure.
As a rule, commercial clinics have installed the latest devices that increase diagnostic information and reduce X-ray radiation (in the case of MSCT), and highly qualified specialists have accumulated great experience in carrying out tomographic studies.
There are a number diagnostic procedures, which are used to clarify the diagnosis, detect the source of the disease, additional factors. Such diagnostic methods include MRI and MSCT. Despite the similar principle of operation, the results of studies using these methods may be different, as well as the scope of their application.
Many people wonder which is better: MRI or MSCT. These procedures differ in the principle of influence and in the results obtained. They are used for various types diagnostics: MRI is most informative when studying soft tissues, and MSCT better visualizes dense tissues (bones, joints).
MRI can be performed on children of any age (if necessary, under general anesthesia); MSCT is contraindicated for children.
MRI
MRI is a procedure performed using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. This is done to obtain high definition images. It is carried out wherever it is necessary to view the condition of the tissues, showing the examined area in a section. A series of photographs is taken step by step with an interval of 5 mm or less.
This manipulation is most often used to clarify a diagnosis previously made with the help of other diagnostic studies. The procedure is safe and can be performed on both an open and closed tomograph. This does not change the quality of the pictures. Using MRI, data is obtained about:
- functional state of the internal organ;
- the presence or absence of its pathology;
- the presence of a focus of infection or inflammation;
- reasons that caused inflammatory processes.
MRI allows you to detect the presence of tumors in the early stages of development, when symptoms have not yet appeared and the disease is just beginning to progress. But it is not used for preventive research due to the high cost of the procedure - up to 6-7 thousand rubles per session.
The diagnostic method has its contraindications:
- Mental disorders, phobias.
- The presence of metal objects in the patient’s body (braces, metal dentures, hemostatic clips, etc.).
- Availability of electronic devices.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- The patient's serious condition.
- Tattoos with dyes that include metallic compounds.
When performing MRI with contrast, there are contraindications such as hypersensitivity to the drug, hemolytic anemia, chronic renal failure, pregnancy.
MSCT
MSCT, or multislice computed tomography, is a diagnostic method that allows you to obtain high-definition images. This X-ray examination, which is superior to radiography in terms of information content. It allows you to quickly obtain information about the condition of human organs. With its help, not only the presence of pathology, but also treatment tactics are determined in a timely manner.
The advantages of this procedure are improved image quality, increased scanning speed, improved contrast resolution, noise/signal ratio, larger anatomical coverage, and reduced radiation exposure to the patient. Essentially, it is an X-ray in 3D. The radiation exposure for this procedure is slightly higher than with radiography, but lower than with CT.
Sometimes the study requires the use of a contrast agent, as is the case with MRI. The method allows you to obtain information that is not available through classical diagnostics using conventional methods.
Important! To conduct MSCT, you must have a previous X-ray or. Only in this case can you accurately determine the area of interest and make the research targeted. The result will be a reduction in radiation exposure.
After the MSCT procedure, as after MRI, the patient receives a written opinion from a diagnostician. If necessary, the results are written to disk or pictures are printed. But the provided service, as a rule, is already paid for additionally.
Modern devices MSCT helps to obtain images High Quality with the lowest possible radiation exposure for humans. Data collection speed is faster. Information is displayed in real time. The images show bone and other dense tissues in detail at a resolution of 0.32 mm.
In general, the procedure is noted as quite comfortable and safe for the patient, and therefore suitable for both teenagers and adults. However, the impact is carried out with some restrictions. Despite the reduced radiation dose, examinations can be done no more than twice a year. In other cases, the indications and the degree of need for manipulation are considered.
MSCT, unlike MRI, absolute contraindications No. But in cases with pregnant, lactating women, children, the doctor compares potential harm and the benefit of the research method.
Relative contraindications are:
- barium suspension in the gastrointestinal tract during examination of the abdominal organs;
- claustrophobia;
- mental disorders;
- patient weight more than 150 kg;
- a condition in which the patient cannot hold his breath during the scan;
- plaster cast or metal elements.
In general, the procedure is freely performed on almost all patients, except for children, who cannot hold their breath during the examination. It is worth mentioning that MSCT has a high cost, and therefore, before undergoing it, you should check with your doctor what the price for the examination and additional services will be.
The difference between MRI and MSCT of the brain
MRI and MSCT of this area are carried out generally in the same areas, with the same goals. If we consider the procedures in more detail, we can see the features of the impact, namely: various indications to the appointment.
Indications for this procedure in the brain area are:
- Inflammatory, tumor pathologies of this area (the study is often combined with MRI).
- Malformation ( congenital pathology) cerebral vessels, intracranial vessels.
- Brain circulatory disorders in the acute phase.
- Damage, diseases of the skull bones.
- Traumatic brain injuries (one of the most common injuries in adolescents).
- Consequences of inflammatory, traumatic conditions (cortical atrophy, cysts, etc.).
Multislice CT of the brain is usually performed without the use of contrast medications. But sometimes the use of contrast may still be necessary, for example, with large tumors.
The procedure is carried out when there is acute disorders blood circulation in this area; to clarify the condition of the skull bones, as well as early stages traumatic brain injury.
Important! Most often, MSCT is prescribed as a replacement study for MRI if there are absolute contraindications to the latter.
Studies of cerebral vessels are carried out with monophasic contrast enhancement, which is injected with an electronic syringe. This type of diagnosis is non-invasive, unlike selective angiography.
The procedure takes from 5 to 10 minutes. Prescribed for:
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- dynamic control upon completion of vascular surgery;
- vascular malformation;
- suspected vessel damage;
- pathological tortuosity of blood vessels identified in another way.
MSCT of the brain in the area of the temporal bone is performed to determine the causes of hearing loss, as well as for dizziness and pathologies of the balance organ. This is a non-alternative type of radiation examination.
Photographs of the orbital bones are helpful in the study of tumors and pseudotumors in the affected area. Often used instead for injuries to the orbit or eye. For this zone, spiral CT remains the most preferable, as it is the most informative.
The nose and paranasal sinuses are examined using MSCT to assess the condition of the nasal septum, as well as to identify inflammatory, tumor lesions paranasal sinuses.
MRI of the brain
This procedure shows high accuracy and information content in the study of the brain. MRI is prescribed for:
- injuries and bruises that are accompanied by internal bleeding;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system;
- brain tumors, including pituitary adenoma;
- pathologies of cerebral vessels;
- damage to the organs of vision and hearing;
- paroxysmal states;
- speech disorders;
- abnormal development of blood vessels;
- epilepsy;
- constant headaches of unknown origin;
- multiple sclerosis;
- neurodegenerative diseases.
MRI allows you to obtain informative data. Sometimes the use of contrast is required, which is a contraindication for persons with allergic diseases.
Can MRI and MSCT be done on the same day?
Despite the similarity of the data obtained, a combination of these procedures is often required. Such manipulations are especially often required when diagnosing vascular pathologies, since the information obtained from each study will be different and provide new clues for making a diagnosis. The result of the examination will be a more accurate assessment of the patient’s condition and correctly prescribed treatment.
If you suspect pathological changes in brain tissue or cerebral vessels, the doctor will prescribe an examination for the patient, which will include the use of one of the scanning techniques - MSCT or MRI. What is multislice CT? In what cases and how is such research carried out? How is it different from MRI? Let's find out in this article.
What is MSCT for brain research?
Multislice CT for brain research is a scanning technique that allows for volumetric reconstruction of structures located inside cranium patient. This becomes possible due to the fact that the tomograph is a short time conducts great amount very thin sections.
The essence of the study
MSCT technology is based on physical properties X-rays, which are used to visualize structures inside the human skull. Modern devices are equipped with parallel detectors that have high sensitivity. They register X-rays, which pass through the patient’s skull and transmit the received data to a computer. Specialized software processes the information, on the basis of which it forms an anatomical section of the area being scanned.
How long does the procedure take?
How long does a tomography examination take? Multislice CT examination does not require a long stay in uncomfortable position, such as MRI. The entire procedure, taking into account preparatory manipulations, takes 10–20 minutes. In this case, the brain scanning process itself will take from a few seconds to a couple of minutes.
Using Contrast
In MSCT diagnostics of the brain, contrast is rarely used. A procedure with contrast is prescribed in cases where there is a suspicion of volumetric formations in the brain. A contrast agent is always used in multi-slice CT of the vessels of the head and the circle of Willis to visualize bone tissue damage and disorders cerebral circulation V acute form, as well as if it is impossible to perform an MRI for any reason. In such situations, an iodine-based composition is used, which is administered to the patient intravenously.
Nursing women during lactation should take into account that the contrast is removed from the body within 24 hours and until complete removal can negatively affect the composition of milk. For this reason, after a contrast-enhanced scan, it is recommended to refrain from breastfeeding for 24 – 36 hours.
Indications for prescribing MSCT of the head
Brain diagnostics are carried out only when indicated. The procedure involves exposure to X-ray radiation on the human body, so it is not prescribed unless necessary or “for preventive purposes.” Indications for MSCT examination of the head are:
- diagnosis of pathologies of the temporal bones that can cause hearing impairment;
- detection of tumor formations in the brain;
- if a patient has signs of a stroke, MSCT helps to identify blood clots or bleeding;
- when performing a biopsy, tomography provides the ability to control the procedure;
- testing the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory therapy malignant neoplasms in the brain (as operational methods, and conservative);
- establishing the reasons for changes in the degree of consciousness or its loss;
- in case of strokes, this is necessary to visualize the sites of brain lesions when selecting the optimal strategy for further treatment;
- surgical planning;
- to identify pathological processes in the middle ear;
- if you suspect intracranial hypertension or hydrocephalus - to study changes in the cavities of the brain;
- diagnosis of vascular abnormalities;
- diagnostics pathological reasons, provoking the occurrence of symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, paralysis, vision pathologies, numbness, confusion.
How is multislice computed tomography performed?

Multislice computed tomography is carried out in specialized rooms equipped with modern equipment. The patient changes into loose clothes that do not restrict movement, removes all metal elements from the body (jewelry, piercings, watches, dentures). Before starting the procedure, you need to take as much as possible comfortable position. The scanning is painless and causes virtually no discomfort to the person. If we're talking about about an examination using a radiopaque contrast agent, the patient may feel hot or bad taste metal in the oral cavity.
Differences between MRI and MSCT
When diagnosing pathological conditions of the brain, it vascular system and bone tissue of the skull may be examined using MRI or MSCT. In some cases (for example, if it is necessary to clarify or confirm preliminary diagnosis), the patient has to undergo both types of scans. For this reason, many are concerned about the question of whether there is a difference between magnetic resonance and multi-slice computed tomography, and which technique is better.
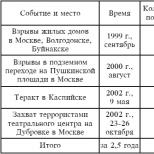
| Characteristic | Magnetic resonance imaging | Multislice computed tomography |
| Physical phenomena underlying the technique | Exposure to magnetic field, high frequency radiation | X-rays |
| Diagnosis during pregnancy | Contraindicated in the first 12 weeks | Contraindicated |
| Examination of children | Can be performed from birth (up to 7 years - under general anesthesia) | Contraindicated |
| Presence of electronic implants | Contraindicated | This scan is done with caution |
| Average diagnostic time | 30 – 40 minutes | 10 – 20 minutes |
| Examination of overweight patients | Up to 130 kg | Up to 170 kg |
| Tattoos | Contraindicated if the design is made with a dye containing metal particles | No limits |
| For claustrophobia | Carried out in open type devices | No limits |
| How often can diagnostics be carried out? | No limits | Safe – once a year. If necessary, the number of examinations can be increased to 3 |
| Contrast agent | Gadolinium | Iodine-based solutions |
| Differentiation by indications | Ideal for scanning hollow organs and soft tissues | An ideal way to study bone tissue |
Only the attending physician can make a choice in favor of using one or another technique, or recommend undergoing both types of examination. It should be based on individual characteristics the patient’s body, take into account his medical history and the presence or absence of contraindications in each specific case.
Contraindications and risks of multislice CT
Multislice technique computed tomography is based on the same physical phenomena that underlie ordinary CT. The list of contraindications to the use of this method of scanning the human body is similar. Conditions for which multislice CT is not recommended include:
- multiple myelomas;
- allergy to radiopaque contrast agent;
- asthma;
- renal failure;
- decompensated heart failure;
- pregnancy;
- reception medications in the form of metformin in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus– if MSCT is necessary, the medication is temporarily discontinued (one day before the procedure), after completion of the examination, therapy is resumed.
Examination using MSCT is associated with certain risks. The patient must be warned about them by the doctor prescribing the examination procedure. It should be borne in mind that modern tomographs emit a small amount of radiation, so the likelihood of risks occurring is minimized, but not completely eliminated.
The main consequences include:
- allergic reaction to the components of the radiopaque solution (iodine, dye);
- malfunctions of insulin pumps, neurostimulators and other implanted electronic devices;
- oncogenic risk (the risk group includes patients young subject to repeated procedures).