Corpus luteum 24 mm. Corpus luteum on ultrasound - what does it mean? When to start worrying
Not every woman can explain how the corpus luteum is formed after ovulation and what purpose it serves in the body. Some are horrified by the diagnosis, which indicates this formation, and the doctor cannot always allocate enough time for a detailed explanation. But general information should be accessible to everyone, so this article clearly covers the relationship between the processes occurring during the period of ovulation and the successful maintenance and development of pregnancy.
The number of glands that produce hormonal substances increases when, after ovulation, it forms, which becomes a temporary formation that significantly affects the woman’s reproductive system. The “colored” name comes from lutein, a yellow substance that fills this temporary gland. Its main purpose is to produce the required amount of progesterone, which affects conception and successful pregnancy.
The formation, growth, normal functioning and regression of this gland depend on other endocrine centers - the ovaries and pituitary gland, as well as on the activity of the immune system. In addition to progesterone, the corpus luteum produces androgenic hormone and estradiol.
Formation process
During the secretory phase of the monthly cycle, that is, in its second half, the formation of this yellow formation begins. The process begins with the maturation phase of the follicle ending with its rupture, after which the mature egg begins to move along the fallopian tube. When interacting with a sperm, fertilization occurs and then the cell searches for a suitable place for implantation.
After the follicle bursts and releases the egg, the formation of a new element of the reproductive system begins in the place where it was before.
In this case, two options for further development are possible. One of them is associated with the onset of pregnancy, and the second develops if conception does not occur. The positive thing is that if there is a corpus luteum, it means there was ovulation, so the body functions normally. In the absence of fertilization, a gradual regression of the yellow formation, or its reverse development, begins. At this time, the endometrial layer that has formed for embryo implantation begins to be rejected. In the previous place of the yellow luteal formation, a whitish body appears in the form of a scar area, which also gradually degenerates and disappears.
If successful conception occurs, the duration of how long the corpus luteum lives after ovulation increases. Its functioning is extended up to three months, until the developed layer of the placenta begins to produce progesterone, which is necessary to support the fetus. When pregnancy occurs, it is especially important how long after ovulation the corpus luteum appears and when it begins to produce hormones important for the safety of the fetus.
The development of the temporary endocrine gland consists of several periods. The first stage begins at the moment of rupture of the follicle, after which the active growth of its internal cells immediately occurs. The second stage is known in medicine as the vascularization period, during which a dense network of blood capillaries begins to grow through the new growing tissues in the burst follicle. In some cases, ingrown vessels cause the development of ovarian apoplexy, which causes serious bleeding. Thanks to a good blood supply, progesterone is actively produced in the new formation.

The most active phase is the third, when there is a surge in the functional activity of the gland. It lasts about 10 days until the body understands that there is no pregnancy, at which time the new formation reaches 20 mm. The lutein contained within controls hormonal levels, switching from estrogen to progesterone production. In the absence of pregnancy, reverse development occurs, which ends with menstruation. In the newly formed cells, the processes of their reduction and overgrowth with connective tissue begin. In place of the yellow formation, white appears.
Some pathological manifestations
Despite its temporary existence, the gland formed in the ovary can undergo some pathological processes. The most common cyst is one that arises at the site of the luteal formation. Usually it does not manifest itself with visible symptoms and is a benign element. This can last for several months, and in some cases leads to disruption of the monthly cycle.
In addition, pathology can develop due to impaired blood circulation, which prevents the remnants of the gland from completely dissolving. Fluid accumulates and the size of the formation can exceed 70 mm. If this is discovered during pregnancy, the luteal cyst does not need to be removed, since such deformation does not prevent it from functioning as a progesterone-producing gland. If the corpus luteum hurts, appropriate diagnostics are carried out and the main cause of the pathology is identified.
The presence of a cyst-like formation in the ovarian area is not critically dangerous for a pregnant woman and the developing fetus. The only time serious harm to health can occur is if the shell ruptures. To avoid this phenomenon, you should beware of bruises, sudden movements and injuries, especially in the areas where the active ovary is located. Cysts often resolve spontaneously during the second half of pregnancy or even after childbirth.
Such interconnected processes in a woman’s body, in which the temporary gland is involved, show its important role for:
- successful conception;
- implantation of a fertilized egg;
- normal course of pregnancy;
- preventing miscarriage;
- providing the body with enough hormones.
The concept of “corpus luteum” is very often used in obstetrics and gynecology, which often confuses some women. In reality, this is a non-permanent, liquid formation on the ovary in a certain phase of the cycle, or rather the luteal phase, at the moment after ovulation. Let's consider its physiological norm and size.
What is meant by corpus luteum?
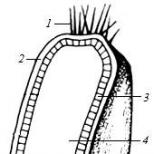
This term is defined as a temporary gland that produces hormones. It is heterogeneous in structure, having irregular shape and edges on ultrasound images. Formation occurs on the left or right ovary during the period of ovulation, 10-16 days of the cycle.
Iron received this name due to the color of its internal structure.
Its size changes during each day of the luteal phase of the cycle. Towards its completion, the temporary gland decreases and disappears completely with the onset of menstruation, since fertilization does not occur.
Let's figure out what it is - the corpus luteum during pregnancy. On ultrasound, it is visible in the gland during the period from fertilization to 10, and sometimes 12 weeks, until the functions of feeding the fetus are transferred to the placenta.
The size of the corpus luteum by day of the cycle during pregnancy on ultrasound sometimes corresponds to 3 centimeters, which is normal for this stage. At the same time, they actively produce much needed progesterone. The extinction of these functions occurs by the 10th week.
Determination of the corpus luteum during pregnancy by ultrasound is also used to determine whether an ectopic pregnancy has occurred. During the examination, a comprehensive assessment of the circumstances and signs is carried out to determine the location of the fertilized egg.

Peculiarities
The formation of the corpus luteum plays an important role in the female body, producing a hormone such as progesterone. For its greater secretion, accordingly, the size of the gland should also not be small. Progesterone prepares the body for pregnancy, while strengthening the endometrium so that the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus in the future. Subsequently, this hormone takes on the function of feeding the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
To understand the full picture of changes in the female body, let’s analyze the phases of the cycle, which are periodically repeated throughout life:
- Menstrual - the initial stage, characterized by the cleansing of the internal cavity of the uterus from what was not needed for fertilization of the egg. A manifestation of this stage is bleeding.
- Proliferative, also called follicular phase. This stage determines the restoration of the endometrium in the uterus and its preparation for the new reception of a fertilized egg after conception. The follicle matures in one of the ovaries. It carries the egg, and mucus is synthesized in the cervical canal, changing its composition.
- Ovulation is the mildest of the stages. Its duration is no more than 1 second. During this time, the egg breaks through the follicle and passes into the abdominal cavity. Its role is very important, since without it pregnancy cannot occur.
- The sector or luteal phase, which is divided into 2 stages. The first includes acceptance, and the second occurs, in turn, in the absence of the introduction of the fertilized egg. Here the disappearance of the corpus luteum occurs and preparation for a new renewal occurs.

There is also information that the corpus luteum, in addition to progesterone, synthesizes important androgens and stradiol.
To summarize the role of this gland, the list of its functions is as follows:
- Production of sufficient quantities of progesterone and other hormones important for the body.
- Fetal nutrition in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Prevention of the development of new follicles.
- Strengthening the endometrium and preparing it for fertilization.
- Decreased contractile function of the uterus.
Formation process
The formation of the corpus luteum is divided into several stages:
- Proliferation is the appearance of a gland after the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. During this process, cell division begins and the formation of lutein, which has a yellowish tint. The corpus luteum acquires uneven edges and a heterogeneous structure.
- Vascularization is the stage of gland growth, during which it wraps around blood vessels and becomes embedded in the epithelial layer. This happens on days 13-17 of the cycle and is a small tumor with normal blood flow.
- Blooming - the corpus luteum reaches its maximum size, acquires brighter outlines and increases blood flow, on days 19-25 of the menstrual cycle.
- Regression - this stage will only occur if fertilization has not occurred and the egg dies. The corpus luteum decreases in size and disappears by the beginning of menstruation. Afterwards, scars or so-called hylian formations remain on the ovary.

Changes in the gland by day of the cycle
Going through all stages of formation, the corpus luteum changes in size accordingly, remaining in its place until pregnancy and its initial stages or until the end of the luteal phase. This is the norm for this phenomenon.
Normal size of the corpus luteum
It varies depending on the period. The size of the corpus luteum varies by day of the cycle. During examination, the doctor can observe the formed gland only after ovulation; before that there should only be follicles.
In the first few days of the cycle they are no more than 4 millimeters. Before ovulation, they can reach 25 mm.
They differ from the yellow follicle gland in their uniform structure and smooth edges. After it ruptures, and this happens on days 11-16 of the menstrual cycle, a temporary gland begins its formation, the size of which is difficult to determine at this stage. Further, after the onset of vascularization, this becomes possible. The normal size of the corpus luteum by day of the cycle should reach 30 millimeters, but no more. However, if a follicle ruptures, it should not be less than 10 mm, otherwise this situation indicates gland insufficiency, which is the cause of infertility.
The normal size of the corpus luteum by day of the cycle after ovulation is as follows:
- 13-18 days - 15-20 mm.
- 18-21 days - 18-20 mm.
- 21-24 days - 20-27 mm.
- 25-29 days - 10-15 mm.
These figures apply to women whose menstrual cycle is 28-29 days, so the data above is an average.
For example, the normal size of the corpus luteum is 18-19 mm.
Deviations
There are situations in medical practice when the presence of a gland does not correspond to its average values. This is preceded by some conditions and factors. Deviations are possible in the presence of a cyst or insufficiency of the corpus luteum.
If an ultrasound shows an increase in the diameter of the gland, then the doctor will suspect neoplasms. Their nature is a cyst. This pathology occurs due to hormonal imbalance and disappears without any help after several menstrual cycles.
A cyst larger than 40 millimeters requires treatment or surgery such as laparoscopy.
If the formation is more than 60 mm, then there is no way to do without surgical methods, since it can rupture.
If the corpus luteum is small in size by day of the cycle, hormonal therapy and long-term treatment are required due to the fact that most often these indicators are the cause of infertility.

Gynecological symptoms
With some menstrual irregularities and pain, the situation is not always complicated by the manifestations of any serious diseases, but still requires consulting a doctor for advice, as well as undergoing a test such as an ultrasound.
An example of a deviation is the corpus luteum on the 18th day of the cycle, less than 16 millimeters in size, since it will not produce the required amount of progesterone, and when planning pregnancy this leads to disastrous consequences.
Symptoms of enlarged formations are as follows:
- Pain in one of the ovaries, varying in nature.
- Delay of menstruation by more than 6 days.
- Pain in the mammary glands that had not previously bothered you.
- Increase in basal temperature.
- Feeling of painful discomfort in the groin or lower back.
These symptoms indicate the presence of a cyst.

Regular examinations (once a year, and if possible, once every six months) and timely diagnosis are the main recommendations of all specialists.
Avoid all kinds of injuries to the internal organs of the small pelvis, monitor your health and lead a healthy lifestyle as much as possible.

Conclusion
To summarize, it is necessary to determine that the size of the corpus luteum is a diagnostic norm, which is reflected using ultrasound and CT. If there are any deviations from known average sizes, pathology is often detected.
In most cases, an enlargement of the temporary gland indicates neoplasms such as functional cysts that do not require treatment, but there is no need to start such a process; a mandatory examination and supervision of a doctor is required.
Small or even insignificant sizes of the corpus luteum are the cause of hormonal imbalance, that is, an imbalance or some other gynecological disease that must be treated without fail.
To prevent this, an ultrasound examination is also necessary.
In modern medicine, there are a huge number of drugs that normalize imbalances in a woman’s body and help prepare it for the upcoming pregnancy.
The corpus luteum is formed in the second phase of the female cycle, immediately after the ovulation process. The function of the corpus luteum is to produce progesterone. This hormone reduces contractions of the uterine walls, which is necessary for the preservation of the embryo.
When the third week of the menstrual cycle arrives, the main follicle ruptures, releasing the egg. And at the site of its rupture, this yellow gland is formed. By the way, this shade is given to it by the luteinizing hormone of the pituitary gland.
If fertilization has not occurred by this time, the woman begins menstruation, along with which the endometrium is rejected.
The formation of the gland occurs in several stages. The first is called proliferation and begins when an egg is released from the follicle. Follicle cells actively divide, forming the corpus luteum.
The second stage is called vascularization, in which blood vessels grow into epithelial cells. It is believed that it is the temporary gland that is most actively supplied with blood, which determines the high-quality production of progesterone.
The bloom of the temporary gland occurs in the third stage, during which the production of hormones necessary for pregnancy occurs. If the egg has been fertilized, the gland produces hormones until the placenta is formed. This takes about 24 weeks. If there has been no fertilization, the activity of the gland lasts only one to two weeks.
The fourth stage is the final one. This is a regression stage that ends with menstruation if there has been no fertilization. Hormones stop being produced, and luteinizing hormone decreases in quantity. Due to the fact that progesterone is not produced by the corpus luteum, the uterus begins to contract, which gives rise to monthly bleeding in the female body.
If pregnancy occurs, the embryo is implanted into the walls of the uterus. The membranes of the embryo begin to produce hCG, which further stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone. From this time on, the gland begins to play a huge role in the proper development and course of pregnancy until the formation of the placenta. Subsequently, it is she who produces progesterone. During pregnancy, the fourth stage of the corpus luteum occurs after the placenta takes over its functions.
It is worth noting that gland plays a very important role in the development of the female body and in its cyclical processes. The function of the corpus luteum is reduced in adolescents, as well as during menopause. And in a woman 18-35 years old, the iron lasts longer. It is the correct production of progesterone and estrogen that affects how cyclic processes will occur in the female body, and how the embryo is implanted into the walls of the uterus.
Corpus luteum deficiency

This factor may be one of the reasons for the impossibility of pregnancy. This may be due to chromosomal pathologies or ovarian pathologies. In the second case, the amount of hormones decreases.
Insufficiency of the corpus luteum can result from pathology of the pituitary gland, which produces lutein.
However, not only diseases of the ovaries and pituitary gland can lead to infertility, but also pathologists of other organs. For example, liver or kidney failure.
Symptoms of improper gland formation can vary. The first and most common is a disrupted menstrual cycle, because the production of progesterone is minimal.
Even if pregnancy occurs, insufficiency of the corpus luteum can affect miscarriage. In this case, the body will not have enough progesterone to eliminate uterine contractions, and the embryo simply will not be able to attach to the walls of the uterus for a long time.
Female egg

The egg is recognized as the largest cell in a woman’s body and one of the most important. It depends on her whether pregnancy occurs. Inside the egg contains a large amount of nutrients for the initial nutrition of the embryo. In this case, we can draw an analogy with a chicken egg, which contains a yolk and a white inside.
A particularly important part of the egg is the nucleus, which contains half of the chromosome set. And the second half must be brought into the egg by the father’s reproductive cell - the sperm. When they fuse, fertilization occurs and a zygote is formed. It contains the complete set of chromosomes necessary for the formation of a person.
It is worth noting that the supply of eggs is formed in utero. At birth, a female child has about one and a half million follicles, which represent future eggs. Until puberty occurs, they do not function and are at rest. Unfortunately, many of these one and a half million die. When puberty occurs, no more than 400 thousand eggs remain in a woman’s body.
How is the main female cell formed?

The maturation of the egg begins with the process of follicle growth in the first menstrual phase.
However, of all those that begin to grow, only one completes it, reaching 2 cm in size.Subsequently, it bursts, the egg comes out, moving along the fallopian tube towards the uterus. The process of ovulation and the movement of the egg causes some discomfort that women feel before menstruation.
If fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube, an embryo enters the walls of the uterus, the journey of which takes about a week. If the egg is not fertilized, it dies immediately after ovulation. It is worth noting that when a follicle ruptures, it is only viable for 48 hours. The sperm has 12-24 hours left for fertilization.
It is worth noting that not every month an egg can mature in a woman’s body. In other words, ovulation may simply not occur during a certain period of time.
Pregnancy and follicle size

Not only ovulation itself is important for pregnancy, but also size, i.e. follicle diameter. The egg can be released from it only if it reaches the required size. The follicle changes in diameter depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. After its completion, for example, its size is on average 2.5-4 mm.
After a week, the dominant follicle can reach 15 mm in size, and at ovulation - 24 mm.It is the large size of the follicle that is reflected in the occurrence of nagging pain in the ovarian area.
Usually 1 egg matures. But sometimes, at the moment of ovulation, 2 eggs are released into the fallopian tubes at once, emerging either from one follicle or from two mature ones.
The process of fertilization and pregnancy

If we consider the process of fertilization in more detail, we can note several stages of the appearance of the embryo and its fixation in the walls of the uterus.
When a spermatozoon, having overcome a gigantic distance, finally reaches the egg, it has to pass through 2 of its shells: the outer one, called the corona radiata, and the inner one, which is called the zona pellucida. The process by which the sperm penetrates the outer membrane is called penetration. At this time, the reservoir with enzymes, which is on the head of the sperm, ruptures. Hyaluronidase comes out of the reservoir, which dissolves the corona radiata. By the way, absolutely all sperm that reach the egg participate in the process of loosening the outer layer of the female cell.
Thus, this is not competition between male reproductive cells, but mutual assistance for the penetration of one single sperm.When it penetrates into the female reproductive cell, a cortical reaction is triggered, namely, granules in the egg are released, changing the composition of its outer and inner shell. Further, no sperm can penetrate her anymore.

After the fusion of male and female germ cells, a zygote is formed, which then divides and forms blastomeres. After a week, the embryo attaches to the walls of the uterus.
Fertilization and pregnancy problems
If the egg does not enter the fallopian tubes, it cannot be fertilized. There can be many reasons for this. One of the main ones is the maturation of an empty follicle or stopping its development at the final stage. Infertility in most cases is associated with these reasons.
Among the causes of infertility include disorders in the endocrine system, drug or alcohol abuse, smoking, diseases of the female genital organs, in particular the ovaries.
By the way, bad habits that the mother was unable to give up during pregnancy can affect the number of follicles of the female embryo in the womb.In other words, at birth there will be not 1,500,000, but much less.

Also, the death of eggs may not be natural, but provoked. Experts say that exposure to ethyl alcohol is very dangerous for these cells. It causes their premature death. Banal stress leading to hormonal imbalances, lack of sleep, and an active lifestyle can have a negative impact.
If a woman does not become pregnant for many weeks, an examination is required to determine the reasons for this situation. They are both temporary and permanent.
If we talk about the causes of infertility from the female body, then it often occurs due to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. In this case, the sperm cannot end up in the amular section of the tubes, where the egg awaits their arrival.

Infertility may be associated with the presence of a large number of adhesions that occur due to an infectious lesion. Due to adhesions, the eggs cannot move to the amulatory compartment. Sometimes in a woman the process of conceiving an embryo is influenced by two of these factors at once. In this case, the doctor determines tuboperitoneal infertility.
It could also just be an ovarian cyst, although it usually does not cause such serious problems. In fact, a cyst is a fluid-filled formation that occurs at the site of a ruptured follicle.
Very often, the inability to get pregnant is influenced by hormonal disorders. They are associated with the occurrence of many diseases that do not allow ovulation to occur. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome. In this case, not one cyst, but many, forms on the ovary.
There is also a cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary. Usually the cyst resolves after 2 menstrual cycles, or 12 weeks. However, if the cyst does not go away after this, surgery is required.
When the female genital organs are underdeveloped, infertility is also often observed.
There is also immunological infertility, which gives rise to the formation of antisperm bodies. In this case, the glands produce substances that are toxic to sperm.
If a woman has abnormalities in the cervical canal, this leads to a change in the composition of the mucus of the uterine cervix. Thick consistency will prevent sperm from penetrating the egg.
Even cervical erosion, which also affects the consistency of mucus, can lead to infertility.
Endometriosis is also noted as a common cause. In this case, the endometrium grows, which prevents the egg from maturing or the embryo from attaching to the walls of the uterus.
On the part of the male body, infertility can be caused by ejaculation disorder or erectile dysfunction.
If a man’s body produces a lot of prolactin and other female hormones, then seminal fluid levels deteriorate and cannot lead to pregnancy.
As medical practice shows, a common cause of male infertility is damage to the testicles, which stops spermatogenesis.
But abnormalities of the male genital organs can also be a cause of infertility. An interesting case from a medical point of view is hypospadias. In this case, the man's urethra is formed in the wrong place, which prevents sperm from entering the vagina.
The natural functioning of a woman’s reproductive system involves follicle growth, ovulation and the formation of the luteal sac - the so-called. Sometimes, during an ultrasound scan, patients are found to have an old corpus luteum in the ovary. This diagnosis raises a lot of questions, doubts and concerns. An important nuance that interests the fairer sex is whether this tumor needs to be treated.
The gynecologist will tell the patient whether the corpus luteum from the last cycle can remain, how to deal with it (and whether it needs to be done at all). To understand the doctor as correctly as possible, it is necessary to have an idea of the formation of this gland. The corpus luteum is a vesicle that forms at the site of a ruptured follicle. It supplies the important progesterone needed to maintain pregnancy. If fertilization does not take place, the gland regresses, leaving a small scar in its place.
Women who are found to have it are recommended to have an ultrasound after the completion of their next menstruation. The optimal period for examination is 5-7 days of the cycle. During this period of time, the ovaries take on their smallest size, and the uterine cavity is cleared of the endometrial layer. It is easier for a sonologist to see pathological processes if they exist in a woman’s pelvis.
The fact that the corpus luteum in the ovary did not regress after menstruation frightens patients. Women worry completely in vain. A large luteal sac (more than 30 mm in diameter), called a cyst, will resolve within 2-4 cycles.
During this time, menstruation may be more or less abundant and shift somewhat. After each bleeding, the volume of the corpus luteum will be smaller until a scar forms in its place.
There is no urgent need to monitor this process constantly. But if the doctor has doubts about the type of cyst and the possibility of its functioning, then at the beginning of the cycle of each month the woman is prescribed an examination.
VT from last cycle
It happens less often that a corpus luteum of natural size remains in the ovary, which is not a cyst. This happens with hormonal imbalance. Corpus luteum from the last cycle is diagnosed in young girls with irregular menstruation, and nursing women and women who have recently given birth are also affected by these problems.
A luteal sac detected at the beginning of the cycle leads the specialist to think about a possible pregnancy. If menstruation was light, short-lived and different from usual, then it is worth conducting a more thorough examination. In the short term, the ultrasound diagnostic device may not show the fertilized egg. The scan should be repeated after 7-14 days.
Does anything need to be done about this?
If the corpus luteum does not resolve after menstruation, then it can indirectly affect the menstrual cycle. It all depends on what level of progesterone in the body it maintains. It is believed that if menstruation has already occurred, then the hormone is not enough to disrupt the systematic bleeding. Consequently, there will be no malfunctions in the reproductive system.
The old corpus luteum cannot disrupt the process of natural conception in subsequent months either. Therefore, patients planning pregnancy should not worry. It is recommended to undergo another diagnosis after 1-2 months to make sure that this growth has disappeared.
During repeated ultrasounds, the sonologist may detect two corpora lutea. This happens when examined in the second phase of the cycle. In this case, one luteal sac performs its natural function, while the other continues to shrink, without having any effect on the patient’s body.
Treatment is necessary for a woman, provided that at the beginning of the cycle the corpus luteum is visible for several months. Therapy is also prescribed to patients who have complaints of poor health: pain, discomfort, irregular menstruation. The luteal sac is expected to disappear on its own, as it does in most cases. However, for every rule there is an exception.
Treatment
Hormonal correction is the most common, safe and effective way to treat the old corpus luteum. Oral contraceptives are individually selected for the patient, the effect of which is aimed at “putting to sleep” the ovaries. The mechanism of action of the drugs is associated with the suppression of natural processes such as ovulation and menstruation.
The release of hormones is blocked, as a result of which the corpus luteum cyst, located in the ovary for a long time, disappears in 1-2 months. Taking oral contraceptives is recommended for patients for 3-6 months. If pregnancy is not planned in the near future, then you can use this method as the main one to prevent it.
 Physiotherapy is prescribed to women with a corpus luteum cyst, in parallel with hormonal drugs. Manipulations involve laser or magnetic therapy, electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis, as well as irrigation and mud baths. A course of 3-10 sessions will allow you to achieve noticeable reductions in the luteal sac, relieve inflammation and prevent possible complications.
Physiotherapy is prescribed to women with a corpus luteum cyst, in parallel with hormonal drugs. Manipulations involve laser or magnetic therapy, electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis, as well as irrigation and mud baths. A course of 3-10 sessions will allow you to achieve noticeable reductions in the luteal sac, relieve inflammation and prevent possible complications.
Surgical treatment is rarely practiced. It is necessary for patients with old cysts that do not shrink within six months. If the tumor suddenly begins to grow, then its removal is also indicated. Emergency surgery may be required if there is a complication: twisting of the pedicle of the large corpus luteum or its rupture.
Preference is given to the laparoscopic method: it is the least traumatic. In some cases, when it is impossible to do laparoscopy, laparotomy is performed. Resection of the ovary followed by suturing allows you to remove the corpus luteum completely in one procedure. In difficult cases, an oophorectomy on one side is required - complete removal of the ovary.
Treatment of the old corpus luteum is carried out infrequently. Usually, women are not at all aware that after menstruation a luteal formation from the previous cycle remains in the ovary, because it does not cause trouble and does not have pronounced symptoms. To find out about the condition of the reproductive organs and evaluate the functioning of the ovaries, you need to contact a gynecologist.
What do gynecologists and uzologists mean when they say that there is a corpus luteum in the ovary? What is it, what should it be (and should it be at all), what function does it perform in the female body?
The body of a healthy woman is a kind of well-oiled mechanism that every month cyclically performs its work: an attempt to give birth to a new life. If fertilization does not occur, the mature egg, remaining unfertilized, will leave the body, exiting with menstrual flow. And in a month the situation will repeat, and this repetition is a pattern confirming that the woman is healthy and quite capable of bearing children.
But it’s not just the egg that matures every cycle. For a potential pregnancy to occur, the corpus luteum is also necessary.
The corpus luteum (or otherwise, the luteal) is the temporary endocrine gland of the ovary, which received this name because of the yellowish tint of the substance it contains - a special pregnancy hormone. Sometimes called VT for short.
The corpus luteum forms after ovulation. When a mature egg leaves the ovary, the follicle containing it ruptures, and in the luteal phase of the cycle, granulosa follicular cells begin to form the corpus luteum; on ultrasound, this process is noticeable almost immediately after ovulation.
The corpus luteum goes through several stages of development:
- The first stage is the proliferation of cells of the burst follicle (follicolocytes), it starts immediately after ovulation;
- The second stage is characterized by the process of proliferation of blood vessels in the tissues of the body;
- In the third stage, the corpus luteum on the ovary begins to produce hormones. This process starts approximately seven days after the egg leaves the follicle, when the gland reaches its maximum size: the production of progesterone and estrogen begins. These hormones of the corpus luteum take on the role of preparing the body for pregnancy: they activate the growth of the endometrium in the uterus so that the possible implantation of the embryo is successful.
- The fourth stage depends on whether conception has occurred or not. This determines the life expectancy of a VT.
How long does it live
How long does the corpus luteum live? If the egg is not fertilized, after a few days it begins to shrink, degenerating into scar tissue, the production of progesterone slows down, which serves as a signal for the beginning of menstruation: both the unused egg and rejected endometrial cells are released with the blood. In gynecology, degenerated VT is called a whitish body; it gradually disappears, and another scar appears on the ovary. Due to this, the structure of the ovaries is characteristically scarred.
VT sizes
Observation of this process is carried out using such a simple method as ultrasound. This is usually necessary at the planning stage and in the first weeks of pregnancy, as well as in the treatment of infertility or other ovarian pathologies.

The most favorable time according to the days of the cycle for research is the second week (7-10 days from the moment of the last menstruation). If it is necessary to more accurately monitor the functioning of the ovaries and the development of follicles, ultrasound is performed three times, approximately according to the following scheme:
- immediately after the end of menstruation;
- on the days of ovulation (days 14-17);
- on the 22-23rd day of the beginning of the cycle.
The size of the corpus luteum immediately after ovulation is about 12 - 20 millimeters. With each day of the cycle, VT increases in size, which reaches its peak towards the end of the cycle, on days 19-28. At this time, the normal size of the VT is 23-29 mm.
VT on ultrasound
On ultrasound, the corpus luteum is defined as a round, heterogeneous formation. It can also be seen with the research method through the abdominal wall (transabdominal ultrasound technique), but more reliable diagnostic results are obtained with the transvaginal method using an intravaginal sensor. This procedure is painless and may only cause psychological discomfort. What is the result of these gynecological examinations?
If VT is visualized in the ovary on ultrasound, this confirms that ovulation has occurred, but does not mean that pregnancy has occurred. The gland only provides favorable conditions for conception and makes its occurrence possible: progesterone triggers the preparation of the uterine epithelium for the attachment of the embryo. It occurs even in virgins.
You can find a corpus luteum in the right ovary, and this indicates that it was on the right side that the ovary was active in this cycle, and if a corpus luteum formed in the left ovary, this means that the dominant follicle has matured on the left side. The order of ovarian activity is not always sequential; normally, both ovulate, each through a cycle. But it may also be that for several cycles in a row, or even constantly, only one of these paired organs is responsible for ovulation, and then the corpus luteum is formed either on the right or on the left. The location of the active ovary does not affect conception.
If no VT was detected, then most likely there was no ovulation this month. Such an “empty” cycle is called anovulatory. This can be considered the norm during transitional stages of development for the female body: during the period of establishing a cycle in adolescence, after childbirth during lactation, during menopause. In reproductive age, anovulation indicates hormonal disorders and pathologies of the reproductive system.
It also happens that it was not possible to track when the corpus luteum appears, but pregnancy has occurred. This is only possible if the specialist who carried out the diagnostics was inattentive or the device was outdated. Without VT, pregnancy cannot progress: in the absence of hormonal supply, the fetus will die.
Pathologies
Pathologies of VT are few in number, but occur quite often, being a common cause of infertility. Pathologies include, first of all:
- absence of a gland;
- insufficiency (hypofunction);
- cyst.
Absence of VT
The absence of VT is also a sign of the absence of ovulation, which means the impossibility of conception. Even with IVF, the corpus luteum is necessary, and doctors can induce it artificially - hormonal stimulation.
VT failure
Body deficiency does not mean its absence, but this diagnosis is made when progesterone production is low. In this case, a normally functioning ovary with a corpus luteum releases a full-fledged egg capable of fertilization. But due to a lack of progesterone, there is a risk of miscarriage.
This pathology can be diagnosed by ultrasound if the size of the gland does not correspond to the prescribed size (less than 10 millimeters). To clarify the diagnosis, the patient undergoes a laboratory blood test to determine the concentration of progesterone.
VT cyst
If the size of the corpus luteum exceeds the norm (30 mm or more), the doctor can diagnose a cyst. In this case, the gland does not fade away, continuing to produce progesterone. This means that pregnancy against the background of a cyst is quite possible, and its development can proceed normally. 
A corpus luteum cyst usually does not cause harm to the female body, as it disappears along with the gradually fading corpus luteum. But in rare cases, complications are still possible, so with such a diagnosis, observation by a specialist is necessary.
Pathologies do not include:
- the presence of an “old” yellow body that has not had time to degenerate into a whitish one, which does not affect the work of a timely formed new body, since it simply does not function;
- two corpus luteum: they can form simultaneously in different ovaries or in one, and this confirms the simultaneous maturation of two follicles, which increases the chance of developing a multiple pregnancy if both eggs are successfully fertilized at once.
If you suspect a pathology during pregnancy planning, you should definitely undergo an ultrasound and laboratory blood tests.
Despite the fact that the VT is a very small, and even temporary, endocrine gland, it plays an important role in the female body. Month after month, thanks to this auxiliary gland, it becomes possible to conceive and bear a baby.
Question answer
 Obstetrician-gynecologist Elena Artemyeva answers patients’ questions.
Obstetrician-gynecologist Elena Artemyeva answers patients’ questions.
— I’m 28, diagnosed with infertility, endometriosis. She underwent treatment: first laparoscopy, then medications. I had an ultrasound scan and here is the result. The contours of the uterus are clear. The endometrium is secretory type, M-echo 15 mm, left ovary 60x41x53 mm, V-70 cm3, with a round hypoechoic formation with a mesh internal structure. The right ovary is 27x14x20 mm, V-40 cm3, with follicles up to 12 mm. Conclusion: signs of cystic formation of the left ovary (corpus luteum cyst). It is very dangerous?
- Normally, the ovary grows every month, during ovulation it bursts, and an egg is released from there. A VT cyst is a formation that remains from a burst follicle after ovulation. Do another ultrasound on day 8-9 of the cycle. If it is a cyst, then it will “resolve” and there will be no harm from it.
— On the 12th day of the cycle, I was diagnosed with a dominant follicle of 23 mm. And on the 23rd day - a corpus luteum of 12 mm with blood flow. I am pregnant?
— An ultrasound shows that there was ovulation. It’s too early to say whether there is a pregnancy. But in this cycle it is possible, because ovulation occurred. Donate blood for hCG.
— I don’t ovulate, I’ve been seeing a doctor for a long time, I’m undergoing treatment (I drink Chimes, Actovegin, etc.). During the last cycle I went for an ultrasound three times. They didn’t see a dominant follicle in me, they said that there could be no pregnancy in this cycle. But on day 23, an ultrasound showed a corpus luteum of 22 mm. How could this happen?
- This means that the ultrasound specialists “looked” at your dominant follicle, this sometimes happens. VT is formed on the ovary at the site of follicle maturation. This means that you ovulated, and there was a chance of getting pregnant this cycle. But even if you don't get pregnant this time, you may ovulate in your next cycle, so hope for the best.