How and where to do cerebral vessel reg. REG of cerebral vessels: the safest and most accurate study UEG examination transcript
It is important to prevent brain diseases, identify them in time and begin treatment in adults and children in order to avoid serious consequences and save lives. Therefore, modern diagnostic methods are very important. Among them, rheoencephalography (REG) and electroencephalography (EEG) stand out. These medical methods allow you to make an accurate diagnosis and begin effective treatment.
The essence of methods
Rheography is a method of examining the pulse blood supply to parts and organs of the body, during which changes in high-frequency current are recorded as it passes through tissue. Rheography is only a general name for the method. REG is one of its types, which is aimed at studying the blood vessels of the brain. The vessels of the extremities are examined using rheovasography, the lungs - rheopulmonography, etc. Essentially, such a survey can be used for any living site.
When examining the vessels of the head, limbs and any other area, a rheograph device is used. Its basis is an electric current generator and an attachment that converts the obtained measurements into graphical form.
The rheogram is recorded using metal electrodes, which are applied to target areas of the body. Before starting the procedure, a fabric pad is placed between the body surface and the electrodes, which is soaked in a sodium chloride solution. The skin is wiped with an alcohol solution, which allows you to remove the fatty film.
To study the blood flow in a certain area, one electrode is applied at the beginning, the other at the end. For example, if the study involves the limbs, lower leg, the application points are the fossa under the knee and the ankle joint area.
 Using REG, you can determine the cause of headaches
Using REG, you can determine the cause of headaches REG is a simple, safe and harmless option for studying cerebral circulation. This type of rheography makes it possible to determine the elasticity and tone of the brain vessels of the head. The filling of different parts of the brain with blood is also determined, the nature and location of the lesion is diagnosed. The method provides useful data if there are vascular diseases, especially cerebral atherosclerosis. Thanks to REG, the nature of headaches can be determined.
The information value of this diagnostic method increases when performing functional tests. The simplest and most useful is a test with nitroglycerin, the effect of which manifests itself as a typical reaction of decreased vascular tone.
The use of nitroglycerin helps to quickly separate organic and functional disorders. But if the lesion is chronic, the effect of the drug is minimal or completely absent.
To assess the state of patency of the vertebral arteries, tests with changes in head position are used.
Rheoencephalography is better than the ultrasound research method, because it makes it possible to evaluate blood circulation in the tissue volume and determine the condition of even small vessels. If you use REG and ultrasound together, the effectiveness of each method will increase.
Rheoencephalography is useful, but many people, including medical professionals, argue that electroencephalography (EEG) is better. To understand this, it is necessary to understand this research method.
EEG is a study of the functioning of the brain, which is based on recording electrical impulses emanating from individual areas. The brain has many neurons. Each of them is a generator of its own electrical impulse. Impulses must be coordinated within small brain regions. They can weaken or strengthen each other. Registration of such activity also occurs with the help of electrodes that are applied to the scalp (it must be intact). They just pick up these vibrations.
 EEG allows you to identify more problems and make a more accurate diagnosis
EEG allows you to identify more problems and make a more accurate diagnosis This diagnostic method allows you to assess the degree of brain dysfunction, study the changes in wakefulness and sleep, track the effect of medications, clarify other diagnostic methods, and so on.
If we say which is better, EEG or REG, there are more and more reasons to trust electroencephalography. This is explained by the fact that EEG allows us to identify more problems, if any, and make a more accurate diagnosis, which is important when prescribing treatment. However, REG is also used, but can be supplemented by EEG.
How research is carried out
When a doctor prescribes REG of the vessels of the brain, limbs or other area, some patients begin to worry. There is no reason for this. This method does not cause pain. No harm is done to the body, the method is suitable even for children.
From the technical side, the procedure is very simple, but in order to accurately identify the extent of the disease and make a diagnosis, it is important to remember certain measures. The patient needs to lie down or sit down, relax and close his eyes. It is advised to be completely calm during the entire procedure, because stress leads to a sharp narrowing of blood vessels. Therefore, before the procedure you should rest for at least fifteen minutes. For several hours, you should not use drugs with nicotine or those that can affect the level of blood circulation.
During the study, the necessary parts of the head are moistened with alcohol, after which, as already mentioned, electrodes are attached. Sometimes during the procedure the person may be asked to turn their head or perform other minor movements.
To conduct an EEG, the preparation is more serious. There are several important rules.
- 12 hours in advance, you should not consume caffeinated products or energy drinks;
- you need to wash your hair, after which you cannot apply masks, varnishes and other products, otherwise the contact of the electrodes with the skin will not be effective enough;
- It is recommended to eat 2 hours before the procedure;
- You should not be nervous during the procedure;
- It is important for the doctor to tell you what medications are being used, he will decide which ones to stop;
- EEG cannot be performed during ARVI.
If the examination is performed on a child, it is necessary to explain to him how the procedure is carried out so that he is not afraid or nervous. You need to take off your earrings and let your hair down.
The person who will undergo the EEG is brought into a room without noise or light. A cap with electrodes is placed on the head. This is done in a lying or sitting position.
There is no one else in the room; the doctor communicates with the patient through a camera or microphone. To identify hidden epilepsy, different tests are used:
- flash of bright light;
- loud noise;
- falling asleep;
- hyperventilation;
- turning the light on or off.
The duration of the procedure is from 45 minutes to two hours. After it, the patient returns to normal life.
Indications and contraindications
Rheoencephalography is mainly prescribed for the following diseases and conditions:
- regular pain in the head;
- dizziness;
- dystonic manifestations;
- climate sensitivity;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- head and neck injuries;
- memory impairment.
 Rheoencephalography is prescribed for regular pain in the head area
Rheoencephalography is prescribed for regular pain in the head area REG can be prescribed as a prophylaxis depending on the age and condition of the patient. Thanks to a timely procedure, it is possible to prevent the development of diseases associated with decreased vascular elasticity.
REG of cerebral vessels is a harmless and safe procedure. She has practically no contraindications. The most important thing is not to carry out the procedure if there are any wounds on the area of the head that is being examined. REG cannot be performed on newborns.
EEG is indicated for the following conditions and diseases:
- insomnia;
- seizures;
- meningitis;
- pathology of cerebral vessels;
- dizziness;
- panic attacks;
- stuttering;
- autism and so on.
 There are no absolute contraindications to EEG
There are no absolute contraindications to EEG There are no absolute contraindications for performing an EEG. However, for some diseases, an anesthesiologist must be present during the procedure:
- convulsions;
- mental disorders;
results
Without a doubt, when a patient undergoes REG of the vessels of the brain, limbs, EEG and any other study, he wants to understand what the doctor wrote in order to console himself or prepare him for a bad diagnosis.
The most important thing is to understand what the results of such an important type of research as REG of the head vessels show. Decoding is simple, however, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, degree and type of disease.
During the decoding process, the doctor takes into account the person’s age. It is clear that the norms for elasticity and tone are different for elderly and young patients. A brief description of the vibration images that the diagnostics shows can be presented as follows:
- the ascending wave line is sharply directed upward, and the top is slightly rounded;
- the descending line moves smoothly down;
- incisura, which is located in the middle third, followed by a small dicrotic tooth and additional waves.
After rheoencephalography is analyzed, the doctor records a deviation from the norm, if any, which helps him make a conclusion. It is his patient who really wants to interpret, sometimes even reveal the extent of the disease, although he is not able to do this. There are several common types based on REG.
- Dystonic type. It is characterized by a constant change in vascular tone. Hypotonicity often predominates, in which low pulse filling is observed. At the same time, venous outflow may be difficult.
- Angiodystonic type. It differs little from the previous one. The angiodystonic type is characterized by impaired vascular tone due to the fact that the wall has a structural defect. This leads to a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels. This is how a violation occurs in a specific pool.
- Hypertensive type. It is very different from previous types, as it is characterized by a persistent increase in the tone of the afferent vessels in conditions of impaired venous outflow.
It is important to understand that the type of rheoencephalogram cannot be considered as a separate disease or its degree. It accompanies another pathology and is an assistant in identifying it in time. Of course, the interpretation of such a study cannot be compared with the results of blood pressure, although even in this case a specialist diagnosis is necessary.
Interpretation of EEG, REG of the head vessels and extremities, REG ECHO EG, determination of the degree of the disease - these other actions must be performed in a specialized institution in Moscow or another region.
Today there are many private clinics and public hospitals in Moscow and other cities that carry out these types of diagnostics, thanks to which you can make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment. Sometimes this type of research is the only way to determine what is happening to a person. Therefore, if they are prescribed, they should be done as soon as possible.
The brain is one of the most important organs of the human body. The functioning of all other systems depends on it, and ensuring its normal operation is determined by the quality of the blood supply. In assessing the latter, rheoencephalography of cerebral vessels (REG) comes to the rescue.
REG of cerebral vessels - rheoencephalography
Rheoencephalography or REG is a simple, accessible and at the same time highly informative method for diagnosing abnormalities in the condition of blood vessels. It is based on an assessment of their tone, completeness of blood supply, speed of pulse wave propagation, etc. in each part of the brain.
The method is based on the determination of electrical resistance, which is different for venous and arterial blood and tissues. When a current of high frequency but low strength is passed, the change in resistance value is recorded by sensors attached to the head and displayed in the form of curves.
The great advantage and main difference between REG of the brain and MRI is the rapid receipt of study results, since the queue for the latter can be waited for months. Although some diagnosticians are confident that REG is hopelessly outdated and is much inferior in accuracy to MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages
Rheoencephalography has many positive aspects. This:
- absolute safety;
- speed of implementation;
- cheapness;
- obtaining performance indicators of arteries and veins separately;
- complete painlessness.
REG is often performed for preventive purposes due to its complete harmlessness to health.
The procedure as a whole is devoid of any disadvantages, since it can be performed on all categories of patients without exception. The only thing that can be considered one of its shortcomings is the lower accuracy of the data than that of MRI. Nevertheless, its availability and the possibility of combining with other diagnostic methods completely eliminates this negative point.
Indications and contraindications
Rheoencephalography is prescribed for diagnosis:
- atherosclerosis;
- pre-stroke conditions;
- consequences of brain injuries and surgeries;
- hypertension;
- collateral circulation, that is, the flow of blood to tissues through peripheral vessels, bypassing the main ones;
- causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia and vegetative dystonia syndrome.
The study is also indicated for assessing the state of the brain in:
- encephalopathy (migraines and causeless headaches);
- pituitary adenoma;
- recent stroke;
- ischemic disease.
Thus, since the procedure is absolutely safe and provides a lot of information about the functioning of the brain, it may be recommended to undergo it if you have:
- headaches and dizziness;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- injuries in the cervical spine;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- weather dependence;
- tinnitus;
- causeless loss of hearing, memory or vision;
- close relatives with vascular pathologies.
REG is absolutely safe, does not affect the condition of tissues and organs in any way, and therefore has no contraindications or side effects. It can be prescribed for any disease and even for such special categories of patients as pregnant women and newborns. But the doctor will refuse to perform research for infectious diseases of the scalp.
Cerebrovascular accidents - video
Features of the event
The procedure is carried out using a special device - a 2-6 or more channel rheograph, which takes and records data. On average, it takes no more than 10 minutes, although in rare cases it can last for half an hour. A day before the appointed time, you need to stop taking medications that affect blood circulation, in particular Aspirin, and avoid caffeine-containing drinks.
The patient takes a comfortable position, lying or sitting. Electrodes are attached to the scalp (behind the ears, above the eyebrows and on the back of the head), previously degreased with alcohol, and fixed in the correct position with rubber bands. Sometimes, to increase the sensitivity of the sensors, they are coated with a conductive gel.
The more channels the rheograph has, the more accurate the study.
The patient is asked to close his eyes to exclude the influence of external stimuli. Direct readings of tissue resistance are taken by passing weak electrical impulses through the electrodes. This does not cause the patient any pain. The only thing that can cause minor discomfort is the presence of contact paste.
The main difficulty of the study is that the patient may be nervous due to unusual manipulations. This can skew the results, as blood vessels tend to constrict in response to stress.
While taking readings, the doctor may ask the patient to turn around, make some movement, squeeze the carotid artery, hold his breath, or, conversely, take several sharp breaths. This is necessary to assess the reaction of blood vessels to movement, which helps to clarify the diagnosis.
During the procedure, the following is assessed:
- vascular tone;
- blood viscosity;
- pulse wave propagation speed;
- level of blood filling of blood vessels;
- blood flow speed;
- severity of vascular reaction.
If there is a need for an REG for children, parents are advised to mentally prepare their child for the upcoming manipulations in advance so that the child is ready to remain completely still during the procedure.
To increase the accuracy of the study, functional tests can be additionally performed to differentiate organic and functional disorders. They are executed with:
- nicotine resin;
- caffeine;
- nitroglycerin;
- papaverine;
- aminophylline.
This is what the results of a nitroglycerin test look like:
If after taking the drug the amplitude of the waves increases several times, this indicates organic disorders, that is, the presence of changes in the structure of tissues or blood vessels. Often, in addition to rheoencephalography, ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed. This complex of studies provides comprehensive information about the condition of blood vessels, the completeness of which is comparable to MRI.
Decryption must be done by a specialist
Explanation of results - table
| Index | Data |
| A 1, A 1 / A | Late diastolic wave at the middle of the distance between the top of A and the end of the rheowave and its relationship to the amplitude of the rheowave. An indicator of peripheral resistance to outflow from small veins in the middle. An increase in the indicator indicates an increase in this resistance. |
| A, a/T | The duration of the ascending part of the curve is anacrotic. Reflects the ability of large arteries of the brain to stretch during systolic blood flow. The indicator increases with increased elasticity (decreased tone) of blood vessels. |
| Аb, ab/T | The location of the diastolic wave in relation to the main wave. Reflects the tone of small vessels in the area being studied. An increase in the indicator indicates increased elasticity (decreased tone) of small arteries and veins. |
Doctors can decipher it. Using it, I determine how the brain works and whether there are any brain diseases. However, if you really took an “oscillogram” with an oscilloscope, then it’s just 50Hz noise + all sorts of other crap and nothing more))
How did you measure your head with an oscilloscope?
Did someone plug my brain into the socket?
Rheoencephalography of cerebral vessels: the essence of the method, indications, contraindications
Due to its functional characteristics, the brain needs oxygen and nutrients to a much greater extent than many other organs of the human body. Their delivery is ensured by a developed vascular system, “problems” in which - narrowing of the vessel, obstruction (blockage) of it and others - cause disruption of the functioning of one or another part of the brain and lead to the development of various unpleasant and sometimes extremely dangerous symptoms. A diagnostic method called “rheoencephalography”, or REG, will help to assess the state of cerebral blood flow and identify the location of its disturbances. What is the essence of this method, the existing indications and contraindications, as well as the preparation and technique for its implementation will be discussed in our article.
Rheoencephalography: the essence of the method
REG is a non-invasive method of functional diagnostics. It is used to measure the resistance of head tissue to electric current. Everyone knows that blood is an electrolyte. When a brain vessel fills with blood, the electrical resistance values of the tissues decrease, which is what the device records. Then, based on the rate of change in resistance, conclusions are drawn about the speed of blood flow in a particular vessel, and also evaluate other indicators.
Why is REG performed?
Since the results of rheoencephalography describe only the functional state of the cerebral vessels, it is not a definitive diagnostic method - it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the results of this research method alone. However, it makes it possible to identify the fact of cerebral circulation disorders in one or another area of the brain and to concentrate the doctor on further study of this particular area.
REG provides data on the following blood flow parameters:
- vascular tone;
- the degree of blood supply to a particular part of the brain;
- blood flow speed;
- blood viscosity;
- collateral circulation and others.
Indications
This diagnostic method is indicated for all conditions accompanied by symptoms of cerebrovascular accident. Typically this is:
- frequent headaches and dizziness;
- presyncope and fainting;
- noise in ears;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- sleep disorders;
- memory impairment;
- learning disability;
- weather sensitivity (changes in health status associated with changes in weather);
- traumatic brain injuries (concussions, brain contusions);
- history of acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke);
- encephalopathy;
- arterial hypertension;
- arterial hypotension;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- spondylitis;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- migraine;
- diabetes mellitus if its complication, diabetic microangiopathy, is suspected;
- cerebrovascular diseases in close relatives;
- assessment of the effectiveness of previously administered drug or non-drug treatment.
Are there any contraindications?
Rheoencephalography is an absolutely safe diagnostic method, approved for use in almost all categories of patients. The study should not be carried out if:
An REG can be performed only if the patient agrees to the examination, so the patient’s refusal is also a contraindication.
Do you need preparation for the study?
No special preparation is required before performing rheoencephalography.
To obtain the most accurate data, the subject should avoid stress on the eve of the test, and get a good night’s sleep the night before. You should also not smoke, drink strong coffee or black tea, as these actions affect the nervous system, vascular tone and blood pressure, and the results of the study will be distorted.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend that the patient discontinue any medications that affect vascular tone before diagnosis. However, this applies only to course medications - if a person takes such drugs on a regular basis, then the diagnosis should be carried out against the background of his usual therapy.
When you come for an examination, you do not need to immediately go to the diagnostic room. It is worth resting for 15 minutes in a well-ventilated, but not stuffy room, and only then go to the REG.
Those who have (and have) long hair will need to put it in a bun so that it does not interfere with the study.
Method of performing rheoencephalography
The study is carried out using a 2-6-channel rheograph (the more channels provided in the device, the larger area of the brain will be covered by the diagnostic procedure). As a rule, the diagnosis is carried out by nursing staff, and the doctor directly deciphers the data obtained.
During the examination, the patient is in a comfortable position, sitting on a chair or lying on a soft couch, relaxed, with his eyes closed. The specialist places electrodes treated with gel or contact paste on his head, securing them with an elastic band (it runs around the circumference of the head: above the eyebrows, ears and along the back of the head). During the diagnostic process, these electrodes send electrical signals to the brain, and at this time the computer monitor displays the above indicators of the state of the vessels and blood flow in them (in some devices the data is not sent to the computer, but is displayed on paper tape).
The area where electrodes are applied depends on which part of the brain is being diagnosed:
- when examining the external carotid artery, the electrodes should be attached above the eyebrows, outside and in front of the external auditory canal (in other words, in front of the ear);
- when examining the internal carotid artery - on the area of the bridge of the nose and mastoid process (behind the ear);
- when examining the basin of the vertebral arteries - on the mastoid process and occipital protuberances, and in this case it is recommended to take an electrocardiogram simultaneously with the REG.
When the main part of the study is completed, if the doctor considers it necessary, he can conduct one or more functional tests. The most common tests are taking a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue (contraindicated in glaucoma, hypotension and intolerance to this drug), changing the position of the entire body or simply turning and tilting the head (usually used to diagnose vertebral artery syndrome), hyperventilation (deep breathing) for several minutes, holding your breath, any physical activity and others. After the test, the REG recording is repeated and changes in it are assessed.
The duration of the study takes from 10 minutes to half an hour. During it, the patient does not experience any special sensations, he is not in pain (the only thing is that a headache can occur after a functional test with nitroglycerin, as a side effect of this drug).
Decoding REG
In order to correctly interpret the data obtained during REG, the doctor needs to know the exact age of the patient - this is logical, because vascular tone and the nature of blood flow in young, middle-aged and elderly/senile patients are different (what is a pathology for a young person is the norm or a variant of the norm for an elderly person).
The rheoencephalogram has a wave-like appearance, and each segment of this wave has its own name:
- its ascending part is anacrota;
- descending – catacrota;
- between them there is an incisura (actually, the bend itself - the transition of the ascending part to the descending one), immediately behind which a small dicrotic tooth is defined.
When deciphering the REG, the doctor evaluates the following characteristics:
- how regular the waves are;
- what anacrota and catacrota look like;
- the nature of the rounding of the wave top;
- location of the incisura and dicrotic tooth, the depth of the latter;
- presence and type of additional waves.
Concluding the article, I would like to note that although REG is not an independent diagnostic method,
allowing one to verify a particular cardiac or neurological diagnosis, however, if carried out in a timely manner, at the first symptoms, it helps to detect the presence of vascular pathology at an early, initial stage of the disease. A further examination and adequate treatment will lead the patient to a speedy recovery and eliminate complications that could arise if the diagnosis was not made in a timely manner.
And, although today some experts are very skeptical about this diagnostic method, nevertheless, it has a place and is still widely used in many medical institutions.
Why do we need rheoencephalography (REG) of cerebral vessels?
Diseases and their symptoms associated with pathology of cerebral vessels are the first priority for visits to a neurologist. Many people are very frightened by the “scary and incomprehensible” names of the studies that the doctor recommends, because people far from medicine often associate them with suspicion of a fairly serious diagnosis. But this is far from the case, so you should calm down and figure everything out in order.
One of these “incomprehensible” studies is rheoencephalography (REG) of cerebral vessels, upon hearing the name of which some patients are filled with horror due to ignorance. So what is this procedure?
What is rheoencephalography?
Rheoencephalography helps determine the condition of cerebral vessels
The rheoencephalography technique involves passing an alternating electric current through brain tissue and recording the parameters of electrical resistance, which depends on the volume and viscosity of the blood in the vessels of the brain. It is the current resistance indicators that allow us to evaluate the above parameters. When the vessels are full-blooded and dilated, the current resistance increases, and if they are narrowed, then the opposite picture is observed.
Advantages and disadvantages of vascular diagnostics
Currently, rheoencephalography is not used as often as before, because there are more accurate methods for diagnosing conditions of the brain and its vessels, for example, electroencephalography (EEG), computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI is the most accurate diagnostic method ). Due to the fact that not every hospital or clinic (for example, in regional centers) can boast of having modern equipment, REG becomes a wonderful assistant in making a diagnosis.
If a medical and preventive institution has a tomograph, and the doctor still orders to undergo rheoencephalography, then the question arises: “Why REG, and not magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, because the second and third methods are much more informative?”
Many doctors, despite the existence of more modern diagnostic methods, still choose rheoencephalography
Firstly, this is the safest way to diagnose cerebral vascular pathology. Secondly, not everyone can withstand the noise and confined space of a tomograph (this is especially true when examining children, since not all children are able to be in a calm state, especially in the absence of their mother). Thirdly, MRI and CT compared to REG are an expensive examination method. Also, the advantage of rheoencephalography is that with its help the vessels are examined, without affecting “superfluous and unnecessary” areas. On magnetic resonance and computed tomography, both the bones of the skull and soft tissues are visible (most often, these methods become relevant when a serious diagnosis is suspected, for example, a tumor process and others).
A significant disadvantage of REG is that any excitement, worry (and, as a rule, there is no person who would not experience such emotions before undergoing any diagnostic procedure), failure to comply with recommendations for preparing for the procedure can affect the results of the examination.
Indications and contraindications for rheoencephalography
Frequent headaches may be an indication for examination
The doctor may give a referral to undergo rheoencephalography if the patient has the following pathological conditions:
- headaches of varying intensity, localization and duration;
- dizziness;
- cerebral ischemia;
- strokes;
- tinnitus and the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes;
- concussions and bruises of the brain;
- bruises and fractures of the cervical spine and skull bones;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- arterial hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arterial hypotension;
- pathologies of the hypothalamic-pituitary region (in particular, tumor formations);
- encephalopathy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- frequent fainting;
- atherosclerosis;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- memory and sleep disorders;
- visual and auditory disorders;
- weather dependence.
Rheoencephalography is considered a completely safe method of functional diagnostics; it can be applied to all categories of the population (from infants to the elderly). The study is not carried out in cases where the patient has defects (wounds and abrasions) and infectious diseases of the scalp.
Preparing for the examination
To obtain accurate results, it is necessary to maintain emotional calm the day before and immediately before the study.
There is no special preparation for the examination. You just need to try to adhere to the following recommendations:
- on the eve of the study, do not take any medications that may affect the condition of blood vessels;
- try to avoid stressful situations the day before and immediately before the study;
- on the day of the study, do not drink coffee or strong tea in the morning;
- do not smoke the day before and before the examination;
- immediately before the study, rest for 15 - 20 minutes;
- Prepare napkins and a towel in advance in order to remove excess gel at the end of the procedure.
Such measures are necessary for calmness of the nervous system and minimal vascular changes (as is known, any excitement or the influence of certain chemicals can change the vascular picture). Following these simple rules will help a specialist assess the condition of the cerebral vessels as accurately as possible and make the correct diagnosis.
Directly in the functional diagnostics room, the specialist prepares the patient for examination by degreasing the skin of the areas that need to be examined and placing rheoencelograph electrodes on them.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Diagnosis is carried out using a special rheograph device (rheoencelograph), connected to a device that records and gives readings (electrocardiograph, computer, electroencephalograph and others). During the examination, the patient should be in a comfortable and relaxed position. Most often he is seated in a special chair. A nurse or doctor places electrodes on the patient's head and secures them with a special elastic band, after lubricating them with paste or gel. For convenience, the tape is positioned so that it runs along the circumference of the head: above the area of the brow ridges, above the ears and along the line of the back of the head.
Rheographic tape is placed along the head circumference line
The areas where electrodes are applied will always be different and depend on which vessels need to be examined:
- if it is necessary to examine the vertebral arteries, electrodes must be applied to the area of the occipital protuberances and mastoid processes;
- if the object of study is the external carotid arteries, the electrodes should be located in the temporal region;
- When examining the internal carotid arteries, electrodes are applied to the area of the mastoid processes and bridge of the nose.
Basically, all vessels are examined at once. The examination takes on average no more than twenty minutes.
One of the main conditions for rheoencephalography is that the patient is calm and relaxed.
The location of the rheoencelograph electrodes depends on the location of the vessels being examined.
In addition to the standard technique for conducting REG, there is a study using so-called functional tests. The most common tests include turning and tilting the head in different directions, taking nitroglycerin (under the tongue), holding your breath, taking deep breaths and full exhalations, changing body position, and physical activity. All readings are also recorded and then compared with those taken at rest.
Possible consequences after REG
As already mentioned, rheoencephalography is a safe diagnostic method used to examine patients of any age group. As a rule, no consequences are observed after this diagnostic procedure at rest.
When performing functional tests, headaches (nitroglycerin has this side effect) and dizziness (after turning the head or physical activity) may occur.
Decoding the results obtained
The obtained parameters are assessed by specialists who decipher the rheoencephalogram
The doctor evaluates the obtained research parameters. Modern technologies have simplified the complex decryption procedure through the use of specialized computer programs. Thanks to this, the patient can receive the results of his examination within ten minutes after the end of the procedure (and not after several days, as was previously the case in many medical institutions). The age of the patient is of great importance, since the rheogram parameters change for each age group.
All data obtained as a result of the examination is converted into a graphic picture (graph), which is very similar in appearance to an electrocardiogram. The device issues them either on paper or on a computer monitor screen.
Parameters assessed by a rheoencephalograph
The wave-like image (each tooth of the rheogram) is divided into special segments that have their own names:
- anacrota (ascending part of the graph);
- top of the graph;
- catacrota (descending part of the graph);
- incisura (teeth on the descending part of the graph);
- dicrotic or dicrotic wave (descending part of the graph located after the incisura).
Based on the parameters of these segments, the following values are estimated:
- roundness or pointedness of the vertices of the graph;
- wave regularity;
- depth of dikrota;
- where is the incisura located?
- appearance of anacrota and catacrota;
- the presence or absence of additional waves in the catacrota.
It should be noted that such parameters of the teeth as amplitude and inclination are no less important. They determine the correspondence of the obtained values with the patient’s age. For example, in young people the teeth are more pronounced and more inclined than in older people.
Important rheoencephalogram indicators in the table
Based on the values of these indicators, a general picture is built about the state of the blood vessels of the brain.
An example of normal rheoencephalographic indicators
Normally, the rheoencephalographic curve is characterized by:
- pointed apexes (with age they become flattened and smoothed), clear incisurae and dicrotes;
- the time of tooth rise is up to 0.1 s, increasing with age to 1.9 s;
- ab/T indicator should not exceed 15%;
- the A1/A indicator should not exceed 70%;
- the C/A indicator should not exceed 75%;
- the asymmetry of blood circulation in the cerebral hemispheres should not exceed 10%.
Patient reviews
Don't be afraid - you won't feel anything. My child, in any case, said that it was even a little ticklish, but there was no pain.
Although many consider diagnosis using REG to be useless, this procedure helped us make the correct diagnosis.
The procedure is very incomprehensible, as is the device itself. I feel like nothing is happening, I don’t feel anything. The only thing the doctor asked during the procedure was “do you feel dizzy?”, I answered that no, I am not dizzy. I was afraid that I should be spinning and would be. But nothing happened. I didn’t feel anything. The whole procedure took about 5 minutes, at the end they gave me a statement and told me to take it to the attending physician. When I asked if everything was okay, the doctor said “yes, it’s fine.” And, in general, this was my conclusion, because the attending physician said the same thing! I still don’t understand what this procedure shows...
What brain examination techniques can a doctor prescribe - video
So, it is now clear that rheoencephalography is a simple procedure that allows you to identify pathologies of blood vessels and blood supply to the brain. Despite the fact that modern medicine offers more advanced diagnostic methods, REG is successfully used to this day, allowing doctors to make an accurate diagnosis of their patients.
Symptoms and treatment
The information is provided for informational and reference purposes; a professional doctor should make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Do not self-medicate. | User Agreement | Contacts | Advertising | © 2018 Medical Consultant - Health On-Line
REG of cerebral vessels: examination procedure, results
A rheoencephalogram is the graphic result of a diagnostic procedure called REG of cerebral vessels. The method has been used for quite a long time. One of the basic sources that describes this method (by Jenker F.L.) was translated from English back in 1966.
As a procedure, rheoencephalography is very simple, but it helps to detect a number of brain diseases even at an early stage, as well as assess the quality of cerebral circulation. Due to its good information content, this diagnosis enjoys authority among doctors, although there are skeptics in the medical community who do not really believe in the objectivity of the method.
We can highlight the obvious advantages of REG diagnostics - its availability and not very high price. The equipment is affordable even for district clinics. Of course, tomography gives a more complete picture, but its availability leaves much to be desired today.
Features of cerebral vessels
- Left and right carotid arteries.
- Left and right vertebral arteries.
In the vascular bed of the brain there are two arterial systems, each of which functions independently:
- Central - with its help, blood supply occurs to the subcortical nodes and the nearby medulla. The central system consists of vessels of the circle of Willis (these are the terminal branches of the carotid and vertebral arteries, interconnected by anastomoses - small vessels connecting one vessel to another), which are located at the base of the brain and basilar arteries.
Blood circulation in the brain is regulated by internal systems that maintain optimal blood flow in all brain structures.
Regulation of cerebral circulation
There are 4 main systems with the help of which the consistency of cerebral circulation is regulated:
- Myogenic - performed due to the response of the smooth muscles of the arterial bed to pressure fluctuations in them. An increase in blood pressure causes an increase in the tone of muscle cells and vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels). A decrease in blood pressure, in turn, causes a decrease in tone and vasodilation (dilation of blood vessels). Myogenic regulation is the leading element of autoregulation of cerebral circulation.
At rest in a healthy person, the intensity of cerebral blood flow is equal to ml/100 g/min. This value is equal to 15% of total cardiac output. The proportion of total body oxygen consumption by the brain is 20% and 17% by glucose. The rate of oxygen consumption by the brain is 3-4 ml/100 g/min.
An approximate value of 15 ml/100 g/min indicates the development of irreversible consequences. If blood circulation stops for up to 7 minutes, a complete breakdown of all regulatory mechanisms occurs, loss of consciousness, coma, and brain death. This occurs due to blockage of the microvasculature due to irreversible changes in the capillary walls and cellular edema.
Important! The main trigger factor for such ischemia is that the brain, unlike other organs, has minimal reserves of its own oxygen.
Even the most minor changes in the blood vessels of the brain of various origins lead to impaired cerebral circulation of varying severity.
Indicators of cerebral circulation
- Intermediate level – characterized by a change in the functional activity of nerve cells. At the same time, their structure does not change; their function is subject to restoration.
Today, one of these methods is rheoencephalography.
Rheoencephalography
This is a method for studying the blood vessels of the brain. The basis of the study is the registration of changes in tissue resistance when exposed to low-magnitude, high-frequency electric current.
Rheoencephalography allows us to draw conclusions about the state of the vascular system of the brain and hemodynamic parameters, in particular:
- Vascular tone.
- Vascular resistance.
- Elasticity of vascular walls.
- Blood flow speed.
- Pulse wave propagation speed.
- The severity of the increase in intracranial pressure.
- The presence, degree, and possibility of developing collateral circulation (this is the formation of networks of blood vessels that bypass the main affected vessel in order to prevent the development of a deficiency of blood supply to a certain organ or tissue area).
Indications for REG
Due to the high information content of the study and the short duration of the study, rheoencephalography is recommended for the following conditions:
- Assessment of the severity of circulatory disorders.
- Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes.
- Head injuries.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment.
- Hearing impairment.
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Migraine.
- Changes in blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Insufficiency of vertebrobasilar origin.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Orthostatic hypotension.
- Encephalopathies of various origins.
- Insomnia.
- Memory impairment.
- Forgetfulness.
- Various diseases of the spine in the cervical region.
- Instability of intracranial pressure.
- Pituitary adenoma.
- Parkinson's disease.
Research technique
The manipulation is carried out using a rheograph having from 2 to 6 channels. The more channels the reograph has, the more informative the results of the procedure will be.
If it is necessary to conduct research in several circulatory pools at once, then the use of polyreographs is necessary.
For the resulting rheoencephalogram to be correct and informative, the following conditions are necessary:
- Take a comfortable position.
- Placement of electrodes on the head in those places where it is necessary to record hemodynamic parameters.
- In the case of examining the internal carotid artery, electrodes are applied to the area of the bridge of the nose and mastoid process (behind the ear from below).
- To obtain data on the external carotid arteries, electrodes are placed above the eyebrow and near the ear canal in front.
- The study of the vertebral arteries involves the application of electrodes to the occipital protuberances and mastoid process. In this case, simultaneous electrocardiography is necessary.
Upon completion of the study, the data obtained are assessed immediately and provided to the patient.
Rheoencephalogram. Decoding
- The ascending part is anacrota.
- The descending part is dikrota.
- Incisura is a dicrotic tooth in the middle third of the descending wave.
Since during rheoencephalography the waves are recorded, with the help of which the blood supply to the brain vessels and their reaction are assessed, there are certain markers that are assessed first.
When receiving REG data of cerebral vessels, the following data are first assessed:
- Waveform.
- The duration of each wave segment.
- Wave amplitude.
- Localization of incisura.
- Regularity of fluctuations.
- Rheographic index is an indicator of the amount of blood flow.
- The dicrotic index is an indicator of vascular tone and peripheral vascular resistance.
- Diastolic index is an indicator of the level of blood outflow and venous tone.
Upon completion of the study, the type of rheoencephalogram is assessed:
- Dystonic is a change in vascular tone of a constant nature, with a predominance of low tone and low pulse filling, associated with difficulty in venous outflow.
When decoding REG data of cerebral vessels, the greatest importance is attached to the following changes:
- A pronounced increase in wave amplitude, steepness, a short ascending wave with a pointed apex, displacement and increase in incisura indicate a decrease in arterial tone.
Difference between REG and EEG
In addition to rheoencephalography, there is such a study as electroencephalography.
The main difference in these two manipulations is that REG is used to analyze the state of cerebral vessels and blood circulation, and EEG is used to study the neural activity of certain areas of the brain.
Cost of rheoencephalography
Such a study can be carried out in a simple clinic, neurological department, as well as in various private medical centers. The price of the study will depend on the location of the study.
Today, the price for performing REG of cerebral vessels is several rubles, depending on the urgency of the procedure, the use of stress tests and the quality of the rheograph itself.
These articles may also be interesting
Is an attack of angina a harbinger of heart disease?
Acute Myocardial Infarction: Symptoms
Unstable angina: symptoms
What is cardiac auscultation? Listening points
Leave your comment X
Search
Categories
Recent Entries
Copyright ©18 Encyclopedia of the Heart
REG of the vessels of the head: when to do the examination and how to decipher it?
Everyone knows that the central nervous system regulates all processes in the body, as well as the fact that all its cells also need respiration and nutrients that come through the blood vessels. The quality of life directly depends on the quality of blood supply, taking into account the functions and tasks assigned to our head. The path of the blood carrying “food” must be smooth and meet only the “green light”. And if in some area there is an obstacle in the form of a narrowing of a vessel, a blockage, or a sharp break in the “road,” then finding out the cause must be immediate and reliable. In this case, REG of cerebral vessels will be the first step in studying the problem.
Vessels leading to the “center”
When the vessels of our body are smooth and elastic, when the heart provides blood circulation evenly and efficiently, which provides nutrition to the tissues and removes unnecessary substances, we are calm and do not even notice these processes. However, under the influence of various factors, the vessels may not withstand and “deteriorate”. They cannot adapt to temperature fluctuations and changes in atmospheric pressure, and lose the ability to easily move from one climate zone to another. The vessels lose the “skills” of quickly responding to the influence of external stimuli, so any excitement or stress can lead to a vascular accident, which rheoencephalography of the brain vessels, taken in a timely manner, will help prevent. The reasons leading to impaired blood flow are as follows:
- The narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels as a result of the deposition of cholesterol plaques disrupts its elasticity, developing the atherosclerotic process. This often leads to myocardial infarction or stroke;
- Increased formation of blood clots can lead to their separation, migration through the bloodstream and closure of the lumen of the vessel (ischemic stroke).
- Previously suffered traumatic brain injuries, which seem to have ended successfully, can lead to an increase in intracranial pressure, which will also be expressed by manifestations of circulatory disorders.
REG of the brain can determine the presence or absence of a subdural hematoma resulting from traumatic brain injury. The hemorrhage formed in the brain tissue will naturally create an obstacle to the normal flow of blood.
If you don’t get too far ahead, but conduct a study when the symptoms are not clearly expressed and create discomfort from time to time, then the REG of the brain will not only determine the condition of the blood vessels, but will also help you choose tactics to prevent serious consequences that put a person’s life at risk.
In addition, REG shows not only the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, but will also evaluate collateral circulation (when the blood flow through the great vessels is obstructed and it is directed “bypassing”).
REG and “non-serious” diseases
There are conditions that, although not fatal, do not allow you to live normally. Now, neurocirculatory dystonia is present in many people, and therefore it is not particularly considered a disease, because “they don’t die from it.” Or, for example, migraine (hemicrania), considered a whim of society ladies, has safely reached our days and does not leave many women alone. Headache medications generally do not help unless the medication contains caffeine.
Considering a woman to be absolutely healthy (after all, there are no signs of any illness), those around her often brush it off. And she herself is slowly beginning to consider herself a malingerer, realizing, however, deep down that a head examination would not hurt. Meanwhile, unbearable headaches come monthly and are associated with the menstrual cycle.
A prescribed and performed REG of the head solves the problem in a matter of minutes, and the use of adequate medications relieves the patient of the fear of monthly physiological conditions. But this is a favorable course of the disease, but there is something else...
Few people know that migraine should not be considered frivolous, because not only women suffer from it, and not only at a young age. Men are also sometimes “lucky” in this regard. And the disease can manifest itself to such an extent that a person completely loses his ability to work and needs to be assigned a disability group.
How is the functioning of the blood vessels in the head analyzed?
When the need arises to do an REG, patients, as a rule, begin to worry. Here you can calm down right away - the method is non-invasive, and therefore painless. The REG procedure does not cause harm to the body and can be performed even in early infancy.
The REG examination of the head is carried out using a 2-6 channel apparatus - a rheograph. Of course, the more channels the device has, the larger the study area will be covered. To solve large problems and record the work of several pools, polyreogreographs are used.
So, the step-by-step REG procedure looks like this:
- The patient is placed comfortably on a soft couch;
- Metal plates (electrodes) are placed on the head, which are previously treated with a special gel to prevent skin irritation;
- The electrodes are attached with a rubber band in the places where it is planned to assess the condition of the vessels.
- Electrodes are applied depending on which part of the brain is subject to REG examination:
- If the doctor is interested in the internal carotid artery basin, then the electrodes will be placed on the bridge of the nose and mastoid process;
- If it concerns the external carotid artery, then the plates will be strengthened in front of the auditory canal and above the eyebrow from the outside (course of the temporal artery);
- Assessment of the functioning of the vessels of the vertebral artery basin involves the application of electrodes to the mastoid (mastoid) process and the occipital protuberances while simultaneously taking an electrocardiogram.
The obtained REG results, the decoding of which requires additional skills, are sent to a doctor who has undergone special training in this area. However, the patient is very eager to find out what is going on in his vessels and what the graph on the tape means, because, as REG is done, he already has a good idea and can even reassure those waiting in the corridor.
In some cases, to obtain more complete information about the function of blood vessels, tests with drugs that act on the vascular wall (nitroglycerin, caffeine, papaverine, aminophylline, etc.) are used.
What do incomprehensible words mean: decoding REG
When a doctor begins to decipher the REG, he is first of all interested in the patient’s age, which must be taken into account to obtain adequate information. Of course, the standards for tone and elasticity will be different for a young and an elderly person. The essence of REG is to record waves that characterize the filling of certain areas of the brain with blood and the reaction of blood vessels to blood filling.
A brief description of the graphical representation of oscillations can be presented as follows:
- The ascending line of the wave (anacrotic) sharply tends upward, its top is slightly rounded;
- Descending (catacrota) goes down smoothly;
- An incisura located in the middle third, followed by a small dicrotic tooth, from where the descending wave descends and a new wave begins.
To decipher the REG, the doctor pays attention to:
- Are the waves regular?
- What is the top and how is it rounded;
- What the components look like (ascending and descending);
- Determines the location of the incisura, dicrotic tooth and the presence of additional waves.
Norms of REG graphs, depending on age
Examination results indicating atherosclerosis
Common types according to REG
After analyzing the rheoencephalography recording, the doctor records the deviation from the norm and makes a conclusion, which the patient strives to quickly read and interpret. The result of the study is to determine the type of vascular behavior:
- The dystonic type is characterized by a constant change in vascular tone, where hypotonicity with reduced pulse filling often predominates, which may be accompanied by difficulty in venous outflow;
- The angiodystonic type differs little from the dystonic type. It is also characterized by disturbances in vascular tone due to a defect in the structure of the vascular wall, leading to a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels and complicating blood circulation in a certain pool;
- The hypertensive type according to REG is somewhat different in this regard; here there is a persistent increase in the tone of the afferent vessels with obstructed venous outflow.
Types of REG cannot be classified as separate diseases, because they only accompany another pathology and serve as a diagnostic guide for determining it.
The difference between REG and other brain studies
Often, when signing up for an REG head examination at medical centers, patients confuse it with other studies that contain the words “electro,” “graphy,” and “encephalo” in their names. This is understandable, all the designations are similar and sometimes it is difficult for people who are far from this terminology to understand. Electroencephalography (EEG) is especially useful in this regard. That’s right, both study the head by applying electrodes and recording data on the work of some area of the head on a paper tape. The differences between REG and EEG are that the first studies the state of blood flow, and the second reveals the activity of neurons in some part of the brain.
Vessels have an indirect effect during EEG, but long-term circulatory disorders will be reflected in the encephalogram. Increased convulsive readiness or other pathological focus on the EEG is clearly detected, which serves for the diagnosis of epilepsy and convulsive syndromes associated with trauma and neuroinfection.
Where, how and how much does it cost?
Undoubtedly, where it is better to undergo an REG of the brain, the price of which ranges from 1000 to 3500 rubles, is decided by the patient. However, it is highly advisable to give preference to well-equipped specialized centers. In addition, the presence of several specialists in this profile will help to sort out difficult situations collectively.
The price of REG, in addition to the level of the clinic and the qualifications of specialists, may depend on the need for functional tests and the impossibility of carrying out the procedure in the institution. Many clinics provide this service and visit your home to conduct the study. Then the cost increases to 00 rubles.
Hello! According to the conclusion, everything is normal in principle, but this study would not show why the headaches, what the reason is. If you want to be examined more thoroughly, it is better to do an MRI of the brain, an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck, an MRI or an X-ray of the cervical spine. With the results you need to go to a neurologist.
Hello! Deciphering such conclusions is almost “fortune telling on coffee grounds,” since it does not show any signs significant for diagnosis and does not allow one to draw conclusions about the presence of pathology. If you have specific complaints, it is better to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck, MR angiography, and consult a neurologist.
Hello! It would be more appropriate to attach not the numbers, but the conclusion of a specialist who learned to correctly decipher the results of an ultrasound examination, although there are no significant deviations in the numbers. As for the neurologist and osteopath, we would advise it is better to listen to the first one. According to MRI, you have disc protrusion and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, with compression of the subarachnoid space through which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. It is difficult to call such a neck “quite decent”, especially since the examination results can also indicate a violation of venous outflow due to structural disorders (protrusion and decreased height of the discs). You need to not only try to eliminate stress, but also pay close attention to your neck - exercise therapy, swimming pool, etc., otherwise you risk getting a hernia, the consequences of which can be very serious.
Hello! REG does not show any specific pathology; in this case, the method is not the most informative at all. The result is an asymmetry of blood supply, a violation of venous outflow, which means absolutely nothing. If you have symptoms of a possible circulatory disorder in the brain (dizziness, fainting, memory loss, headaches, etc.), then MRI, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck, and x-ray of the cervical spine will be much more informative.
Hello! The study showed that there were signs of impaired venous outflow on the left. In the PA pool, the pulse blood filling of the vessels is sharply reduced on both sides. Signs of verberogenic influence on the vertebral arteries. What could it be?
Hello! The result may indicate that there is compression of the vertebral arteries from the spine. Perhaps you suffer from osteochondrosis, hernia or other pathology. To clarify the diagnosis, it is advisable to do an X-ray or MRI of the cervical spine, an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck, and you should also consult a neurologist if there are symptoms of blood flow disorders in the brain.
Hello! The result is a change in the tone of the arteries and difficulty in the outflow of venous blood. REG does not show whether there is a specific pathology and what its causes are, this study does not provide any accurate information regarding vascular disorders, so it is better to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck and/or MR angiography.
Hello! Firstly, you need to calm down and not panic, the study we completed did not show anything bad, but it does not provide the full amount of information, it is better to do an ultrasound scan or MRI, examine the spine, and undergo an ECG. Secondly, interruptions in the heart are most likely associated with stress, and not with diseases of the internal organs, so interruptions can be eliminated by taking sedatives, for the prescription of which it is better to consult a psychotherapist. Avoid stressful situations, normalize your routine, spend more time in the fresh air, provide yourself with adequate sleep, and then interruptions with headaches will almost certainly pass.
Hello! REG is not the most informative study. In your case, it indicates a change in vascular tone, but does not allow any significant conclusions to be drawn. Based on the results, it is impossible to speak about either the pathology of the vessels themselves or the disruption of blood flow, so it is better to resort to other examinations - ultrasound, MRI, based on the results of which and on the basis of an analysis of symptoms, a neurologist will be able to make a diagnosis.
Hello! REG indirectly speaks about the disturbance of blood flow through the vessels of the head, but the cause and nature of the changes cannot be established only from this study, therefore an ultrasound scan should be done not so much out of fear and panic, but to clarify the nature of the blood circulation, especially if there are any complaints. Doppler ultrasound is a much more informative diagnostic method than REG.
Hello! Help me please. They did a REG: pulse blood filling was increased in the VBB, moderate symptoms of dystonia of the hypertensive type, pronounced signs of impaired venous outflow in the VBB. When turning the head to the right, changes in hemodynamics were revealed.
Hello! Based on this study, we can talk about vascular dystonia and difficult outflow of blood through the vertebral and basilar artery system, which are aggravated when turning the head. It is impossible to predict the cause of changes in the REG; it could be congenital vascular pathology, osteochondrosis or herniation of the cervical spine, etc. To clarify the diagnosis, you should visit a neurologist and do additional examinations - ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck, X-ray or MRI of the neck, MRI angiography. Your doctor will tell you what exactly to do.
Hello! According to REG, there is a decrease in blood supply to the brain vessels and their tone. This result must be compared with your complaints and data from other examinations, which is usually done by a neurologist. In addition, REG is not the most informative method of research, so we can recommend supplementing it with MRI of the brain, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck, and X-ray of the neck (depending on symptoms and concomitant diseases). Consult your doctor about what additional tests are best for you to undergo.
Hello! Using REG, one can judge only about altered vascular tone and possible obstruction of venous outflow, but the method does not suggest the cause of these changes due to insufficient information content. Take an additional MRI of the brain, ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck, examine the spine for hernias, osteochondrosis, etc. It is quite possible that some of these studies will show why you are suffering from headaches, and then the treatment will be more targeted.
Hello! According to the REG conclusion, there is a violation of vascular tone (mainly a decrease) and difficulty in venous outflow. These phenomena can cause headaches. It is impossible to judge the reasons based on this study, but you can additionally undergo ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck, MR angiography, radiography or MRI of the cervical spine. Consult a neurologist about what is most appropriate based on your condition and the presence of other diseases (osteochondrosis, for example).
Hello! Please decipher the results of the REG. Headaches are severe.
Hello! Spasm of small vessels in the brain and venous congestion can cause headaches, but the cause of these changes in vascular tone cannot be determined by REG; the method is not sufficiently informative. Perhaps you suffer from arterial hypertension, osteochondrosis, or have congenital anomalies of the vascular bed, etc., therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, it is better to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography.
Hello! Headaches, floaters, noise in the head, before this my back hurt. Please help me decipher REG. In the basin of the internal carotid artery on the left: blood filling is increased by 89%, severe hypervolemia; the tone of large and medium arteries is reduced; the tone of small arteries and arterioles is increased by 8%, mild hypertonicity; The tone of the venules is normal. Venous outflow is impaired. Right: blood supply increased by 68%, severe hypervolemia; the tone of large and medium arteries is normal; the tone of small arteries and arterioles is increased by 21%, mild hypertonicity; The tone of the venules is normal. Venous outflow is impaired. Left-sided asymmetry of blood supply. Right-sided asymmetry of the tone of small arteries and arterioles. Right-sided asymmetry of venular tone. In the basin of the vertebral artery. Left: blood supply increased by 164%, pronounced hypervolemia; the tone of large and medium arteries is normal; the tone of small arteries and arterioles is increased by 14%, mild hypertonicity; The tone of the venules is normal. Right: blood supply increased by 21%, mild hypervolemia; the tone of large and medium arteries is normal; the tone of small arteries and arterioles is increased by 19%, mild hypertonicity; The tone of the venules is normal. Venous outflow is impaired. Left-sided asymmetry of blood supply.
Hello! Based on the results of the REG, we can talk about the unevenness and asymmetry of the blood filling of the vessels and their tone, but this research method does not show the reason for such changes. If you want to get more accurate and detailed information, then undergo an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography. If you have back problems, you can also undergo an X-ray or MRI of the spine.
Hello! This means that there are changes in the tone of the brain vessels, but it is difficult to associate them with your symptoms, and even more so, REG does not indicate the cause of vascular disorders. If you want to be examined in more detail, it is better to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography. If necessary, the doctor may recommend examining the cervical spine (X-ray or MRI).
Hello! Please help me decipher the results of the REG: Volumetric blood flow is increased in all pools on the left and right in the carotid zone with difficulty in venous outflow. When turning the head to the right, there is an improvement in venous outflow on the left in the carotid zone.
Hello! The result indicates an increased volume of blood in the vessels of the brain and difficulty in its outflow through the veins. When turning the head, there is an improvement in venous outflow on the opposite side, and the cause may be changes in the cervical spine. REG does not make it possible to judge the cause of changes in blood circulation, so you are recommended to undergo additional examinations: ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography, radiography or MRI of the cervical spine. You should consult a neurologist with the results of the examinations.
Hello! The result of the REG may indicate functional disorders of cerebral vascular tone, but the study is not informative enough to draw any conclusions. The EEG is deciphered by a neurologist who can correctly interpret the result obtained. We can only say that there are no significant deviations or signs of convulsive readiness, which could be a consequence of the injury. With these results, you should consult in person with a competent pediatric neurologist who will be able to interpret the results correctly and in conjunction with the examination, complaints, etc.
Good afternoon Please decipher the results. A 33-year-old woman has been suffering from migraines and simple headaches in different areas since childhood. Thank you in advance!
Volumetric pulse blood filling is increased in all basins on the right and in the basin of the left internal carotid artery (Fms by 35%, Fmd by 53% Omd 29%).
The tone of the main arteries is reduced in the vertebral artery basin.
The tone of large arteries is reduced in all basins.
The tone of the medium and small arteries is reduced in the basin of the right vertebral artery.
Peripheral vascular resistance is increased in the basin of the vertebral arteries and in the basin of the right internal carotid artery.
In the basin of the vertebral arteries there are signs of obstruction of venous outflow.
Signs of vertebrogenic influence when turning the head to the left.
Hello! The result indicates a change in vascular tone, which may be caused by changes in the spine. If you want to be examined in more detail, it is better to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography, as well as an X-ray or MRI of the cervical spine, since the information obtained from REG is not enough for any conclusions.
Help me understand what this is... Volumetric pulse blood flow in the basin of the left internal carotid artery is moderately reduced. Volumetric pulse blood filling of the posterior parts of the brain is slightly increased. The combined type of cerebral blood flow is spastic in the vessels of the right hemisphere (PVSA, PPA) and normotonic in the vessels of the left hemisphere. The tone of large vessels of the right hemisphere is moderately increased. The tone of medium and small vessels in the basins of both carotid arteries and the right vertebral artery is slightly reduced. Peripheral vascular resistance in the basins of both vertebral arteries is moderately increased. The symmetry of the blood supply to the vessels in the carotid basin of the brain is disrupted due to a decrease in the pulse blood supply in the LVSA. Venous outflow is difficult in both cerebral basins.
Hello! The result of the REG indicates uneven blood circulation in the brain due to vasospasm in the right hemisphere, as well as a violation of the outflow of venous blood. It is impossible to judge the reasons for this phenomenon using REG, therefore, to clarify the nature of changes in the vessels, it is better to do an ultrasound scan or MR angiography. With the result of this study, you should contact a neurologist, who, in accordance with your complaints, will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, if necessary.
Hello! Please decipher:
blood supply is reduced in the carotid and vertebrobasilar areas.
The tone of cerebral vessels is increased. When turning the head, vertebrogenic
no influence noted. Obstruction of venous blood flow. V/cranial
pressure is increased. Heart rate (sitting) = 63.
Hello! The REG can be deciphered correctly by the specialist who conducted the study, or by the doctor who referred for the REG, because you did not even indicate whether there were any symptoms of trouble. We can only say that the tone of cerebral vessels is changed and, possibly, intracranial pressure is increased (REG speaks about this only indirectly). The cause is most likely not related to problems in the spine. To clarify the nature of the pathology, it is better for you to undergo an ultrasound scan or MR angiography; these are more informative methods for diagnosing vascular pathology.
Good afternoon Please help me with decoding! Dystonic changes in cerebral vessels of a mixed (hypertensive-normotonic) type. The tone of the arteries of medium and small caliber is increased to 1-2 degrees in the left hemisphere. Volumetric blood supply to the brain of the hypovolemic type: moderately reduced in the carotid region and in the VBB (with mild MPA D>S). Venous dysfunction grade 1-2 (moderate vasospasm) with difficulty in venous outflow from the basal parts of the brain. Thank you!
Hello! The result may indicate fluctuations in vascular tone, disruption of venous outflow from the cranial cavity, uneven blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, but this study does not show the reasons for such changes. REG is not the most informative diagnostic method; if something worries you, it is better to do an ultrasound scan or MRI.
Please consult us on our conclusion (my son is 3 years and 9 months old):
“Vascular tone according to the normotype.
Volumetric pulse blood filling of the brain in the CB on the left is of an isovolemic type; in the CB on the right and in the VBB of the hypovolemic type, without MPA.
Heart rate during CREG recording was 91 beats/min.
Difficulty of venous outflow from the cranial cavity 0-1 st.
No vertebrogenic dependence was registered during positional tests.”
Hello! Nothing bad can be said about this conclusion, the only thing is that it is worth deciding whether there is still a difficulty in venous outflow or not. In addition, REG is far from the most informative diagnostic method, therefore, if something is bothering your child, it is better to undergo additional examination (ultrasound, MRI). Check these points with a neurologist or pediatrician.
Hello. Help me decipher?! We performed an REG on an 11-year-old child.
Dystonic changes in cerebral vessels of mixed type.
Tone of medium and small caliber arteries with a tendency to hypertonicity.
The tone of the distribution arteries is moderately reduced. Volumetric blood supply to the brain in the carotid system is of the hypervolemic type (moderately increased). in the VBB according to the hypovolemic type (moderately reduced).
During positional tests (turning the head to the left, right, flexion, extension), no vertebrogenic dependence of blood flow to the brain was registered. Thank you!
Hello! REG is not an informative enough method to talk about a specific pathology. Changes in vascular tone often accompany vegetative-vascular dystonia and functional changes in childhood and adolescence. If something is bothering the child, then you should contact a neurologist and, in addition to the REG, undergo other studies.
Good afternoon. Help me please. We went through REG with our child. The child is 10 years old. Volumetric blood filling is increased in all pools on the right (fmd by 7%) (omd by 70%). All pools showed signs of obstructed venous outflow. Functional tests cause blood filling in both pools
Hello! This result may indicate increased blood flow to the brain and difficulty in its outflow from the cranial cavity. There can be many reasons, so with the result you need to go to a neurologist or to the doctor who referred you for an REG.
Hello, I'm 35 years old. I have very bad headaches, help me decipher the REG. Volumetric pulse blood filling of the entire brain is significantly increased. The tone of large vessels in the basins of both carotid arteries is slightly increased. The tone of medium and small vessels in the basin of the left internal carotid artery is slightly increased. Peripheral vascular resistance throughout the brain is slightly increased. The symmetry of the blood supply to the vessels is slightly disturbed.
Hello! The result indicates a possible disruption of blood flow in the head due to increased blood pressure, vasospasm, etc. It is impossible to draw conclusions about the cause of the headache based on REG alone, so it is recommended to also do an MRI of the brain, an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck, and consult a neurologist or endocrinologist , check kidney function.
Hello. If you know, write what drugs can be used to improve this interpretation of REG: 1) volumetric pulse blood filling is increased in the ICA basin 2) the tone of medium-caliber arteries is increased in the ICA-SBA basin 3) the tone of small-caliber arteries is increased in the SMA basin 4) venous outflow is not difficult 5) functional tests: bending forward - reduces the volume of cerebral perfusion and worsens venous outflow; tilting - reduces venous outflow.
Hello! We do not prescribe medications over the Internet, and based on the results of the REG, even a neurologist at the clinic will not do this. To choose the right treatment, you need to know the symptoms, complaints, and data from other examinations, so it is better for you to consult the doctor who prescribed the REG.
Good afternoon Help me decipher the results of the REG. Decreased tone of the distribution arteries in lead FM (by 13%). On the FP “Fn after the test” the following are observed: NO SIGNIFICANT CHANGES DETECTED. CONCLUSION: HYPERTENSIVE VARIANT REG. VENOUS OUTFLOW IS NORMAL. NO VERTEBROGENIC INFLUENCE ON RHEOVAVE IS FIXED.
Hello! Explanation - in conclusion: there are no changes, venous outflow is normal, there is no cause for concern either.
Hello! Please decipher the results of REG and MRI for a 13-year-old child, he has a constant headache, during childbirth there was tight entanglement, cerebral ischemia and cardiopathy, he was constantly sick with a temperature of 40 for 5 days. MRI - diffuse Virchow-Robin dilatation, moderate swelling of the mucous membranes of the main sinus, cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth, maxillary sinuses, expansion of the diameter of the bulbous jugular vein on the right to 1.5 cm with its close adherence to the bottom of the tympanic cavity. Pulse blood pressure is reduced in the basin of the left internal carotid artery and in the basin of the right vertebral artery. The tone of the medium and small arteries is increased in the basin of the internal carotid arteries, peripheral vascular resistance is increased in all basins. Thank you.
Hello! The described changes may be a consequence of intrauterine hypoxia, hence the disturbance of vascular tone and headaches. A neurologist can help by prescribing appropriate treatment, but you must be prepared for the fact that the headaches will not completely go away. Perhaps with age, when the child grows up, there will be an improvement.
Good afternoon. I'm going through honey. commission for contract service. The attitude was issued to the ship. The neurologist told me to undergo an REG. Examination result:
Dystonic type of REG. Manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type with symptoms of venous insufficiency. A decrease in blood supply in the vertebrobasilar region is possible due to the peripheral resistance of medium-sized and small-caliber venules.
Could you decipher the diagnosis and say how serious it is, because to serve on a ship you need category A? Thank you.
Hello! The diagnosis is not made solely on the basis of REG, moreover, this is not the most informative research method. To clarify the condition of the vessels of the head, it is better to do an ultrasound scan or MR angiography. According to REG, we can only talk about vegetative-vascular dystonia, but the presence of symptoms, complaints, and the results of other examinations are also important.
Volumetric pulse blood filling of the entire brain is moderately increased; the tone of large vessels in the basins of both carotid arteries and the right vertebral artery is moderately increased; the tone of medium and small vessels in the basins of the right internal carotid and left vertebral arteries is slightly increased; peripheral vascular resistance of the head is within the age norm; the symmetry of the blood supply to the vessels is slightly disturbed; decipher it, please. Thank you in advance. Natalia.
Hello! The result indicates increased blood flow and increased tone of cerebral vessels, which may be the result of nervous strain, arterial hypertension, etc. You can find out more detailed information from the doctor who referred you for this study.
Good afternoon I underwent an REG, wrote a conclusion, help me decipher: The volumetric pulse blood supply in the carotid system and in the VBB is increased. Dystonic changes in blood vessels of the hypotonic type. Venous outflow is not obstructed. During positional tests, no vertebrogenic dependence of cerebral blood flow was registered. Thank you in advance.
Hello! There is a change in vascular tone, but probably not related to the condition of the spine. The causes of vascular dystonia are not clear, but you can additionally undergo ultrasound or MR angiography.
Hello, please tell me, is it possible to pass a medical examination at the Ministry of Internal Affairs with such an REG result?! Signs of moderate vasospasm of medium and small vessels, decreased venous tone, difficulty in venous outflow in all vascular areas. When turning the head to the sides, there are no special changes. CONCLUSION: angiodystonic type of REG with symptoms of venous dysfunction.
Hello! REG is not a sufficiently informative study to talk about the nature of the disorders and their cause, so it is better to additionally undergo an ultrasound scan or MR angiography. More detailed information can be obtained from a neurologist, and you will receive permission to work based on the specific diagnosis established (if the disease is present).
Hello, please tell me what the following REG conclusion means? Often there are headaches in the back of the head and
in the left hemisphere. Sometimes tinnitus and dizziness.
FM lead (carotid basin)
Pulse blood flow is normal on the left, sharply increased on the right
PC asymmetry is pronounced
Hypotension of the arterial network is significant on the right
The tone of arterioles and pericapillaries is insignificant. elevated
Before function REO samples - signs of vasospasm: yes
Venous outflow is insignificant. burdened
Peripheral vascular resistance increased
OM lead (vertebral artery basin)
Pulse blood flow is sharply increased
Asymmetry of PC in physiol. permissible within
Arterial hypotension. network is insignificant
The tone of arterioles and pericappillars means. elevated
Venous outflow is moderately obstructed
Peripheral vessel. resistance increased
The elasticity of the vascular wall is not changed
Responsiveness to vasodilation test is satisfactory
Hello! The conclusion means that there are fluctuations in vascular tone, and the outflow of venous blood is also impaired, but since REG is not a sufficiently informative study, you can undergo an ultrasound scan or MR angiography to clarify the condition of the vessels.
Hello, please tell me what does it mean: significant hypotonicity of large-caliber arteries? For what reason could this be and what could it affect in the future?
Hello! Using REG, one can only roughly judge the presence of pathology. Hypotonicity of the arteries most often accompanies vegetative-vascular dystonia. To clarify the nature of the changes, you can undergo an ultrasound scan or MR angiography, as well as visit a neurologist.
Hello, help me decipher the conclusion. Diffuse decrease in venous tone, diffuse obstruction of venous outflow. In the basin of the internal carotid arteries: asymmetry of blood flow, hypertonicity of the arteriole on the left. In the vertebrobasilar region: an increase in the amplitude of blood filling of the vessels, hypertonicity of the arterioles, hypertonicity of the arterioles on the left. Help please, I'm very afraid.
Hello! Based on this conclusion, nothing definite can be said. Yes, vascular tone is changed with asymmetry of blood flow, venous outflow is complicated, but the REG does not indicate the reason for the changes, this is not an informative enough method. You may have arterial hypertension, cervical osteochondrosis, or developmental features of cerebral vessels. To clarify the nature of the changes and their causes, we recommend performing an ultrasound scan or MR angiography. In any case, don’t be afraid, you don’t have a terrible diagnosis yet.
Hello! Please tell me, I am very worried about the results of the REG. Thank you in advance!
Hello! Spasm of small and medium-sized vessels may be associated with arterial hypertension, impaired blood flow through the vertebral arteries due to their pathology or changes in the cervical spine. The vertebrogenic effect on the vertebral arteries means that the cause may be cervical osteochondrosis and other changes. It is quite difficult to give an exact answer based on the REG, especially since you did not indicate your age or the presence of any other diseases. If you want to examine the vessels and blood flow in more detail, it is better to do an ultrasound scan or MR angiography, and with this result it is better to consult a neurologist.
Hello. Please explain the conclusion. Does nothing pose a threat to life? My therapist diagnosed me with vegetative-vascular dystonia, so I’m very afraid. Thank you very much in advance.
Hello! Based on the results of the REG, one can only judge the change in vascular tone. There are no threats to life, the result is quite consistent with VSD. If you want to find out more precisely about your vessels, then do an ultrasound scan or MR angiography, these are much more informative methods than REG.
Good afternoon. Please explain the conclusion, especially this point: in the basin of the internal carotid artery. Left: pulse blood filling increased by 31%, mild hypervolemia; Venous outflow is impaired. Right: pulse blood filling increased by 120% (this figure is scary), pronounced hypervolemia; Venous outflow is impaired. Right-sided asymmetry of blood supply.
Tell me what the threat is and what to do? It's the weekend already, the clinic is closed.
Hello! This conclusion does not indicate a threat to life, so you can safely survive the weekend. The result of the REG indicates uneven filling of the vessels with blood: in some parts there is more of it than necessary (hypervolemia), in others there may be a deficiency. Don’t let the figure of 120% scare you, since REG does not always reflect the true state of the vessels and often gives not entirely correct indicators. Since it is impossible to talk about the causes and draw specific conclusions using REG, it is better to undergo an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck or MR angiography, which are much more informative. An examination of the cervical spine will not hurt either. Visit a neurologist who will tell you what to do next, but don’t panic, there is no emergency.
Good afternoon, I did an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck in conclusion: Sleepy
the artery lumen is free. The intima-media complex is normal. C-bend right
ICA in the precranial region with a 60% FSC gradient. Vertebral arteries
C-shaped curved in the bony canal of the spine. When turning your head
a decrease in LSV in the VBB of up to 30% is recorded from the level of the 5th cervical vertebra.
Asymmetry of the diameters of the vertebral arteries d
there is no base of the brain. Poorly functioning ACA on both sides. Blood flow in
The MCA and ACA are symmetrical, laminar without LSC deficiency. Please tell me what’s wrong with me, I’m worried about constant dizziness, nausea, and headaches.
Hello! Since you have identified changes in the course of blood vessels (bends), asymmetry of the lumens of the vertebral arteries, it is most likely that your complaints are associated with blood flow disorders. In such cases, vascular drugs do not always have the expected effect, so you still need to consult a vascular surgeon about the possibility of surgical treatment.
Hello, this is the conclusion of REG (I’m 14)
Conclusion on the left: a mixed type of cerebral hemodynamic disorder, with a pronounced difficulty in venous outflow, and a sharply reduced blood supply to the vessels of the brain. Conclusion on the right: the tone of cerebral vessels is within normal limits, venous outflow is obstructed, and the blood supply to potential cerebral vessels is sharply reduced.
Please tell me what's wrong with me?
Hello! According to the conclusion of the REG, it is impossible to make a diagnosis; this can be done by a neurologist based on complaints and other examinations. Your blood circulation through the vessels of the brain is impaired, nothing more can be said.
The activity of the brain is based on a regular supply of oxygen, carried out through complex vascular formations. The vascular network is represented by all types of blood vessels - from the smallest capillaries to large arteries. Their coordinated work is the key to the normal functioning of the brain.
In some cases, if the circulatory process is disrupted, even in a small area, many pathologies of both a reversible and irreversible nature can develop. To track the first minor changes, REG of cerebral vessels is often used, which allows us to understand the causes and identify the location of the lesion.
The essence and principle of the study
What is REG? If we decipher the abbreviation and translate it into Greek, it turns out that rheoencephalography is “reo” - “flow”, “encephalo” - “brain”, “graphia” - “I write, I depict”. All together forms a record of the blood supply to the brain. For such an examination of the head, a weak electric high-frequency current is used, the passage of which changes the value of tissue resistance.
Blood, like almost all liquids, is an electrolyte, and when blood vessels are filled with it, electrical resistance values decrease. The obtained values are recorded on a tape by a specially designed device (rheograph), which results in a curve called an encephalogram. Afterwards, based on the data, the rate of change in resistance is assessed, which indicates the rate of blood flow, vessel filling and other indicators.
What does REG determine?
Considering that the data from rheoencephalography of the brain allow us to assess only the functional state of the blood vessels, it cannot be considered a final examination. Based on the materials received, it is not possible to make a diagnosis. But this technique allows you to determine the presence of pathologies of cerebral circulation and their specific localization, which will help the doctor concentrate on it during further examination.
REG of the head provides information about the following characteristics of blood flow:
- about vascular tone;
- degree of filling;
- blood flow speed;
- blood viscosity;
- collateral circulation.
The REG procedure makes it possible to recognize the differences between true disturbances in the movement of blood through the vessels of the head and those caused as a result of diseases of the cervical spine.
When is an examination necessary?
Rheoencephalography of cerebral vessels is performed for all signs of cerebral circulatory disorders. These can be either individual manifestations or pathological conditions – diseases characterized by a whole complex of symptoms. Symptoms leading to diagnosis are considered to be:
- dizziness and periodic headaches, migraines;
- fainting and pre-syncope;
- decreased vision and hearing, whistling, tinnitus;
- disturbance of sleep, memory, learning ability;
- weather sensitivity (the effect of weather on health).
Degree of atherosclerosis on REG
Pathologies requiring the appointment of REG of the head include:
- traumatic brain injuries (bruises, concussions);
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- history of acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- vertebral artery syndrome, encephalopathy, spondylitis;
- vegetative-vascular and neurocirculatory dystonia;
- arterial hypo- and hypertension;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
An REG study is recommended in cases of heredity aggravated by vascular diseases of the brain, and diabetes mellitus when signs of its complications - microangiopathy (damage to small vessels) appear. It is also prescribed to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment - medication, phyto-, physiotherapeutic or other methods.
Are there any contraindications?
It will be difficult to diagnose people with mental illness if they cannot remain calm, or with certain types of pathologies accompanied by uncontrolled head movements. Also, to carry out diagnostics, it is necessary to obtain the patient’s permission for examination. Otherwise, his refusal is considered a contraindication, and the procedure cannot be prescribed.
Is preliminary preparation required for REG?
There is no clear set of rules for carrying out this procedure - there are only a few recommendations that help obtain the most accurate results. The first thing a patient should take care of is minimizing anxiety and stress. Be sure to get a good night's sleep and rest the day before the examination. Before diagnosis, it is prohibited to drink black tea, strong coffee, drinks containing alcohol, and you must refrain from smoking. Since this can have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, increase the tone of the blood vessels of the head and neck, as well as blood pressure, which will lead to distortion of examination materials.
The last meal should be no later than 1.5–2 hours before the procedure; ideally, the examination is carried out on an empty stomach. In some cases, the doctor may stop taking medications that affect vascular tone before the study. But this applies only to course medications - if the patient takes these drugs on a regular basis, then the diagnosis is carried out against their background.
Having arrived for the procedure, the patient does not have to immediately go to the diagnostic room. First, he needs to rest and relax for at least 15–20 minutes, sit in a well-ventilated room or corridor, and then go for rheoencephalography. People with long hair should bring an elastic band with them to the examination to tie it into a ponytail. Since when applying electrodes, the hair will interfere with the diagnosis, and will also become more dirty with the contact paste or gel used.
Diagnostic process
The procedure is performed using a 2–6-channel rheograph, the capabilities of which are directly related to the number of channels, that is, the more channels there are in the device, the more areas of the brain can be examined. As a rule, the diagnostic procedure itself is carried out by a medical employee with mid-level qualifications, while the recorded materials are deciphered directly by the doctor.
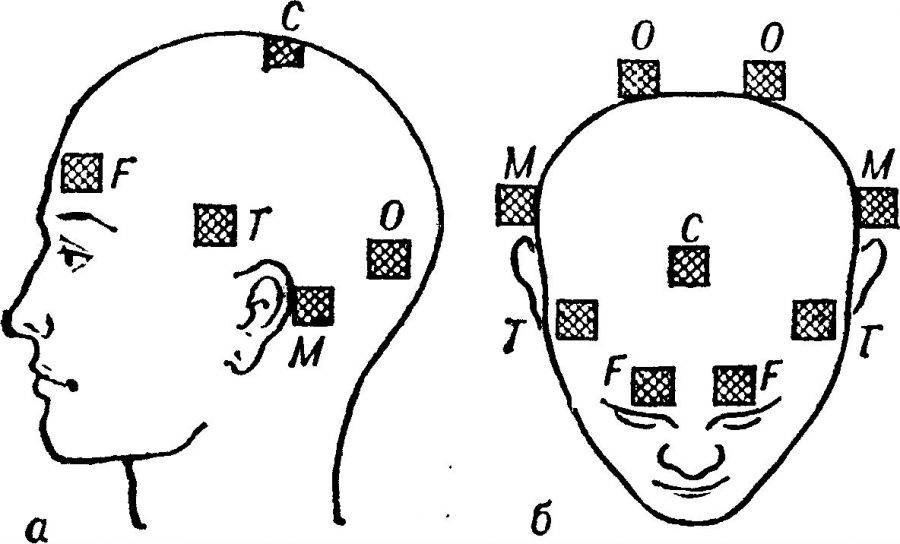
The principle of fixing electrodes for REG
To undergo an REG of the brain, the patient is asked to lie down comfortably on a couch or sit down, try to relax and close his eyes. A medical worker attaches electrodes to his head, having previously applied gel or contact paste to them, and secures them with an elastic band. It is fixed along the circumference of the skull - above the eyebrows, ears and covers the back of the head. When diagnosing, electrical signals are sent through electrodes to the brain, and at this time information is displayed on the computer screen characterizing the condition of the vessels and blood circulation in them.
In less modern rheographs, the research results are not transferred to a computer, but are recorded on paper tape. The location of the electrodes is determined by the need to examine a specific area of the brain. So, if necessary, study:
- the external carotid artery, electrical conductors are placed above the eyebrows outside and in front of the external ear opening;
- internal carotid artery - fixed on the surface of the bridge of the nose and behind the auricle, in the area of the mastoid process;
- basin of the vertebral arteries - fixed to the surface of the occipital protuberances and mastoid process, and it is recommended to take an ECG simultaneously with the REG.
After completing the main part of the examination, if the doctor deems it necessary, functional tests are carried out. They can be assigned one or several at once. The most common tests include:
- taking nitroglycerin – 1 tablet under the tongue (contraindicated for persons with glaucoma, hypotension and allergies to the drug);
- changing the position of the body - all or only tilting and turning the head;
- hyperventilation (deep breathing) for 3–5 minutes;
- holding your breath and additional physical activity.
After completing the functional tests, a repeat REG is performed and the differences between the two rheograms are assessed. The examination lasts about 10 minutes. During its passage, a person does not experience any unpleasant sensations; the only thing that can bother you is a headache due to taking nitroglycerin. This medication sometimes gives a similar negative effect. Then the specialist proceeds to deciphering the results.
Deciphering the rheoencephalogram
To correctly interpret the data obtained from taking REG of the vessels of the head, the diagnostician must know information about the exact age of the person who underwent the procedure. This is due to the difference in the nature of blood circulation and vascular tone in subjects of different age categories. That is, what is considered the norm for the elderly and senile will be a clear deviation from the norm for young people or children.
The rheoencephalogram looks like a wave-like curve, and each of its fragments has a corresponding name. The ascending part is called anacrota, the descending part is called catacrota, the bend between them is called incisura and the small tooth after it is called dicrota. When decoding, the specialist evaluates the following characteristics:
- regularity of wave oscillations;
- appearance of anacrota and catacrota;
- wave peak features;
- the location of the initizura and dikrota, the depth of the latter;
- the presence and nature of additional bends.
Based on evaluative judgments of the rheogram data, the doctor makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of blood flow disturbances in the area of the brain being studied. And, if necessary, makes recommendations for the patient’s subsequent actions.

Normal REG indicators for certain age categories
Features of REG diagnostics
It should be noted that rheoencephalography is not an independent diagnosis - it does not allow confirming one or another diagnosis - cardiac, neurological, or angiopathic. However, if prescribed in time, it shows the presence of vascular pathologies in the early stages of the disease. As a rule, REG is prescribed in parallel with other diagnostic techniques that help to comprehensively assess the activity of the brain and cardiovascular system.
Doctors often recommend an ECG (electrocardiogram) of the heart and an EEG (electroencephalogram) of the brain. The results of these procedures will make it possible to more accurately study the functioning of the heart muscle and evaluate the biocurrents of brain activity. This will significantly narrow the range of search and identification of pathological processes, make it possible to prescribe adequate treatment and provide the patient with relief from symptoms that reduce the quality of life.
Recently, REG has begun to be used less in diagnostics, as vascular Dopplerography has replaced it. But in practice, it is noted that the indicators recorded during rheoencephalography cannot be recorded with ultrasonic waves. Therefore, these methods are not mutually exclusive, but, on the contrary, complement each other.
Dopplerography makes it possible to assess the structural anatomy of the vascular beds, while REG helps to study their functional state, that is, to determine the quality of their work and compliance with standards. Even though some experts are quite skeptical about this diagnostic method, it is not abandoned in many medical institutions. And the patient, having received an appointment for the procedure, will be able to undergo it both in public hospitals and in private clinics.
It is much easier to find people who will voluntarily die than those who will patiently suffer from constant pain.
Almost every inhabitant of our planet experiences a headache sooner or later. For some, this acquaintance occurs in childhood, for others - already in adulthood. As a rule, such a symptom does not alarm its owner (well, who hasn’t suffered from a headache?). And in 80% of cases, pain really is not a threat to health or life, but the rest of such cases are associated with serious and dangerous diseases. Therefore, it is very important to understand which headaches are episodic and are associated, for example, with overwork of the body, and in which cases it is worth sounding the alarm.
We believe that in the CIS there are too many barriers to effective care for the population with headaches, which include clinical, social and political-economic ones. The information collected on the site will help overcome some of the barriers - we tried to include the maximum amount of useful information about everything related to headaches, its causes, possible complications and consequences, diagnosis and treatment of various types of cephalgia, useful tips and lifestyle recommendations, so that you never I no longer had headaches.
We must remember! Any type and location of pain, including headaches, is a signal from the body that something has gone wrong inside, and it is necessary to quickly fix everything so that your health does not suffer. Therefore, you should not take a headache as a given, live and put up with it, but as a call to active action.

Did you know that...

- Headache is one of the most common complaints, along with dizziness, that patients present to the doctor. Seeking medical help for this issue accounts for almost 70% of all visits to the doctor.
- Previously, it was believed that children did not develop primary headaches, but today it has been proven that children suffer from migraines no less than adults. By the age of 7, up to 40% of children complain of cephalgia, and by 15 – all 75%.
- In the world, approximately 10% of the population suffers from migraines, but no more than 25% of them seek specialized medical care. The rest continue to endure such torment.
- Headache is not a separate disease (with the exception of primary types, when the true cause of the pain cannot be established), but one of many symptoms of the underlying disease. There are practically no pathologies that could not cause cephalalgia.

- The brain itself never hurts because there are no pain receptors in its tissue. Brain vessels, membranes, muscles and fascia of the head hurt when they are compressed, stretched, spasms, damaged, or intoxicated.

- Headache is often a side effect of many medications. Therefore, first you need to analyze all the medications that you take, for example, oral contraceptives, nitroglycerin, etc. cause cephalgia. There is also the concept of overuse headache, when cephalgia is provoked by uncontrolled use of headache medications, no matter how strange it sounds.
- Hypertension causes headaches much less frequently than is commonly believed.
- Very often, headaches are associated with diseases that do not affect the brain at all - cervical osteochondrosis, ear diseases, dental problems, eye pathology.
- Headache is one of the most common health problems for office workers.
- According to statistics, 40 million Russians have problems with blood pressure.
- According to numerous studies, women are more susceptible to headaches due to migraine than men.
- Headaches spare no one. According to historical data, Julius Caesar, Alexander the Great, Peter I, Ludwig Beethoven, Charles Darwin, Pyotr Tchaikovsky, Sigmund Freud, Napoleon, Anton Chekhov, Alfred Nobel and others suffered from migraines.
Types and mechanisms of headache development

The first mention of headaches, the clinical picture of which resembles migraine, dates back to 5000 BC. Throughout its history, humanity has repeatedly tried to understand what is the matter and how to get rid of cephalgia. There were both failures and successful attempts. They first tried to classify headaches in 1962, because as many patients as there are, so many types of pain can be found (this is a subjective feeling and until today there are no objective methods for measuring the magnitude of headache). This classification existed until 1988, when the International Headache Committee issued new guidelines on the types and definitions of the main types of cephalalgias. We still use this classification (ICGB-2), with a small edition in 2004.
Despite the fact that this classification most fully describes and explains the nature of headaches, in some cases the existing variant of cephalalgia is difficult to attribute to a specific category.
According to the NIH (National Institute of Health) classification, there are 5 categories of headaches that explain the mechanism of pain (pathogenetic classification). According to the NIH, primary headaches are those that are not associated with organic changes in the brain, blood vessels, membranes and other anatomical structures. That is, when examining such a patient, the doctor does not find a single pathological change that could explain the cause of the headache. Secondary headaches are always associated with some kind of structural or functional changes, for example, increased blood pressure, brain tumors, cerebral atherosclerosis, intoxication, cervical osteochondrosis, etc.
Mechanisms of headache development
Vascular headache– narrowing, compression or pathological expansion of the arteries or veins of the head, slowing of blood flow with the development of cerebral hypoxia, blocking of the lumen of blood vessels with blood clots, emboli, atherosclerotic plaques.
Muscle tension cephalalgia– activation of pain receptors in the muscles or aponeurosis of the head during prolonged tension for some reason.
CSF headache– develops with increased or decreased intracranial pressure, with displacement of brain structures, their compression, for example, by an aneurysm, cyst or tumor.
Neuralgic type of pain– occurs when the fibers of the cranial nerves are irritated or compressed, as well as when the nerve sheath is damaged by any pathological process (trigeminal neuralgia, occipital neuralgia, pathology of the vestibular nerve, etc.). As a rule, such pain is perceived by patients as shooting, electric shock.
Psychalgia– headache of central origin, when all the above-described components are absent, and the pain is caused by disturbances in the system of endogenous opiates and monoamines of the brain, for example, Parkinson's disease.
Need to know! Very rarely a headache can be attributed to one type; much more often it is mixed, when several, or even all, mechanisms of cephalgia are involved.
Video about the main types of headaches:
Main causes of headaches

There are approximately 200 causes that are considered common, and even more rare. We will briefly look at the most common ones, since more than 95% of cases belong here. So, if you have a headache, then the first thing you need to do is determine which category of cephalgia your sensations fall into - primary or secondary headaches.
Common causes of primary cephalgia

Must remember! A doctor can make a diagnosis of primary cephalgia only after a thorough examination of the patient, the results of which did not reveal any organic changes that could lead to such symptoms.
It is very important to know and follow this rule. Because dangerous diseases, for example, brain tumors, also initially manifest themselves as a mild headache, over time it intensifies, other pathological symptoms are added and a true diagnosis is established. But often this happens too late and nothing can be done. Therefore, early diagnosis is the key to successful treatment.
Migraine This is one of the most common causes of headaches. Migraine pain is very typical, sometimes just a description of the attack is enough to make a diagnosis. But we must not forget that severe brain damage must be excluded.

The exact cause of migraine has not been established today, but there are theories that try to explain this symptom; you can find them in the corresponding section of our website.
An attack can be provoked by:
- stress factors and emotional experiences;
- some types of food, for example, chocolate products, nuts, hard cheeses, smoked and spicy foods;
- drinking alcohol, especially red wine;
- physical and mental overload;
- lack of sleep or, conversely, prolonged sleep;
- smoking;
- change of weather.

Migraine pain can be recognized by the following symptoms. The pain is one-sided, develops as a pulsation, is very intense in its strength, is accompanied by dizziness, the urge to vomit and increased sensitivity to public stimuli (light, sounds), and is intensified by any physical effort. The attack lasts without treatment from 4 hours to 3 days.
In some cases, a regular migraine attack can drag on and develop into migraine status, which is an emergency condition and requires intensive treatment, as it can trigger a cerebral stroke.
Tension headache– it is this disorder that predominates among all primary cephalgia. It appears at the end of the working day, has low or medium intensity, diffuse localization, compressive or constricting in nature. Sometimes patients characterize it as a helmet placed on the head.
The pain lasts from 30 minutes to 4 hours. It disappears on its own after resting, sleeping, or taking a regular pain reliever. Not accompanied by nausea, dizziness or other alarming signs.

Cluster headache– it is also called cluster or histamine. This is a very severe (on a visual analog pain scale it is rated at a maximum of 10 points), paroxysmal, unilateral headache. Localized in the eye area, temporal lobe, lasts a few seconds or minutes, but in series of attacks. A characteristic symptom of cluster pain is redness of the mucous membrane of the eye on the affected side, discharge of tears, nasal congestion and rhinorrhea, increased sweating of the face, constriction of the pupil on the side of the pain.
Sometimes cluster pain can be so severe that it leads to a person’s suicidal attempts. It is also considered a characteristic feature that the pain is eliminated by taking indomethacin and never changes its side.
Common causes of secondary cephalgia
Blood pressure fluctuation– not only hypertension, but also arterial hypotension can lead to headaches. Pain due to changes in blood pressure refers to vascular causes, when the cerebral arteries narrow or dilate and the brain tissue does not receive enough oxygen or its hyperperfusion is observed.
 Risk factors and development of hypertension - high blood pressure
Risk factors and development of hypertension - high blood pressure 
A headache can occur in 3 cases:
- a sharp increase in pressure - a hypertensive crisis due to the lack of control therapy or psycho-emotional stress;
- a decrease in pressure below normal (90/60) in case of hypotension, anemia, orthostatic hypotension, blood loss, shock, overdose of medications for hypertension;
- with the development of complications on the side of blood vessels against the background of prolonged hypertension and cerebral atherosclerosis - chronic ischemic disease of the brain.
On the pages of our website you will find all the necessary information on how to treat arterial hypertension, how to protect yourself from its consequences, the right lifestyle and nutritional habits so that you do not have a stroke or heart attack. Also learn how to provide first aid in case of hypertensive crisis and suspected stroke.

Headaches associated with head trauma are very common among young people (road accidents, sports and household injuries). Cephalgia accompanies an acute period of traumatic brain injury, and can remain for life after such an episode. It so happens that after a mild TBI, for example, a concussion, the patient does not adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations or does not seek medical help at all, and after 2-3 months he develops post-traumatic migraine pain. In the corresponding section of our website you will find all the necessary algorithm on how to behave, what you can do, and what is strictly prohibited in case of head injuries.
Acute cerebrovascular accidents(stroke and micro-stroke) always occur with severe headache, regardless of the type of lesion, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. But with such a vascular catastrophe, cephalgia fades into the background and is not the main diagnostic criterion. In case of alarming symptoms described below, you should definitely call an ambulance, as the likelihood of a stroke is very high.
 How to recognize a stroke and first aid - infographics
How to recognize a stroke and first aid - infographics Alarming headache symptoms:
- pain occurred suddenly or for the first time, especially in older people and in children (a sign of a brain tumor);
- it is very intense, estimated on a pain scale of 8-10 points;
- accompanied by impaired consciousness, speech, muscle weakness, vision (stroke symptom);
- if a person cannot move any limb;
- at the same time you can see persistent fever, a hemorrhagic rash on the body (a sign of meningitis);
- if a pregnant woman has developed cephalalgia, epileptic seizures and hypertension (a symptom of eclampsia).

Brain tumors always accompanied by pain. It is primarily associated with an increase in pressure inside the skull and compression of the brain structures by the growing neoplasm. Characteristic signs of pain syndrome can be considered:
- appears or intensifies in the morning after sleep and in a horizontal position;
- the pain is progressive in nature - each subsequent attack is stronger than the previous one;
- accompanied by nausea and vomiting, which do not bring relief;
- patients always complain of dizziness;
- As the disease progresses, focal neurological symptoms appear (paresis, paralysis, visual impairment, speech, hearing, mental impairment, seizures, etc.).
CNS infections. Infectious damage to the meninges, meningitis, or brain tissue, encephalitis, always occurs with a headache. These are very serious diseases that mainly affect young children and lead to severe complications that can lead to death within a few hours if medical attention is not provided.
Parents should be alerted to such signs as a sharp deterioration in the child’s condition, the appearance of a severe headache and high fever, which cannot be reduced in any way (conventional medications do not help), the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash on the body, and impaired consciousness.
Dizziness is a faithful companion to headaches
As already mentioned, dizziness is also a common complaint of people when visiting a doctor, and even more often it is observed together with a headache. On our website you can find answers to questions about why dizziness develops with normal, high and low blood pressure, with cervical osteochondrosis, with vegetative-vascular dystonia, with menstrual bleeding, after eating and many other specific situations.
 Weather sensitivity is a cause of blood pressure problems
Weather sensitivity is a cause of blood pressure problems  Normal blood pressure - infographics
Normal blood pressure - infographics In general, it is customary to distinguish between true dizziness, which is associated with damage to the central or peripheral part of the vestibular analyzer, and false, associated with all other causes. You will learn to distinguish the symptoms of real dizziness from other pathological signs, for example, lightheadedness, and you will also be able to professionally provide first aid for vertigo for yourself and others. Headache in pregnant women requires special attention and special treatment that is safe for the fetus
Often a headache finds a person in unusual conditions, for example, a headache can occur during pregnancy, in nursing mothers, after sexual intercourse, a hearty lunch, etc. Often in such situations, people do not know what this is connected with, what can be done to get rid of for headaches and their prevention.
This is especially important for pregnant and nursing mothers to know. After all, in this case, cephalgia cannot be stopped with the usual painkiller pills, because most of them are harmful to the fetus or baby. On the pages of this site you will find clear recommendations on what to do in such cases and what it involves. You will find out which medications can be used without fear of harming the baby, and which ones should be strictly forgotten. You will also find advice on alternative methods of eliminating headaches, which sometimes turn out to be no less effective than standard ones, for example, acupressure for headaches.
Diagnostic program
Diagnosing a headache is very easy, but finding its true cause is a more difficult task. For accurate diagnosis, doctors use several familiar and modern techniques:
- general laboratory tests of blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid;
- radiography of the spinal column and skull;
- MRI, CT, PET-CT of the brain and spine;
- angiography of cerebral vessels to identify vascular diseases, for example, aneurysms of the cerebral arteries;
- electroencephalography, myography, rheoencephalography and other electrophysiological methods for diagnosing the functional state of the brain.
You can try to diagnose the cause of your headache yourself, using self-diagnosis tables and information from our website, and then contact a neurologist.
 Table for initial diagnosis of headaches How to make an appointment with a doctor
Table for initial diagnosis of headaches How to make an appointment with a doctor Video about what a headache hides:
As you can see, there are a lot of reasons for a seemingly ordinary headache. All of them require different medical tactics and diagnostic methods, some are not dangerous, while others pose a direct threat to health and life.
We tried to collect in one place all the information that a person might need when looking for answers to questions about the causes and treatment of their headaches. It must be remembered that self-medication can be dangerous to health, but this does not mean that the patient should not understand the essence of his disease and the principles of combating it. It is for this purpose that we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the materials on the site, because our main goal is to bring benefit and do good!





